![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Social Psychology |
The scientific field that seeks to understand the nature and causes of individual behavior and thought through social situations |
|
|
|
Hindsight Bias |
"I knew it all all along" The tendency of people to overestimate their ability to have predicted an outcome that could not possibly have been predicted |
|
|
|
Why is relying on common sense dangerous? |
It often suggests a confusing and inconsistent picture of human behavior. Scientific method used for more conclusive evidence. |
|
|
|
How is social psych connected to other fields |
Because it is a science and uses several methods that can be used to study a wide range of topics in other fields |
|
|
|
Hypothesis |
A tentative statement about the relationship between 2 or more variables |
|
|
|
Theory |
A concept/idea that is testable fact-based model for understanding thoughts/emotions/behaviors |
|
|
|
Spurious Relationship |
Correlation Does Not Equal Causation Two events/variables that have no direct connection |
|
|
|
Example of Spurious Relationship |
Amount of ice creams sold and deaths by drownings |
|
|
|
Operationalization |
Being able to measure something that is not directly measurable |
|
|
|
Sampling Issues |
Sampling Bias 3rd Variable Manipulation of Variables
|
|
|
|
Ethical Issues |
Competence Confidentiality Informed Consent Relationships with vulnerable people |
|
|
|
Schemas |
Mental frameworks centering around a specific theme that helps us to organize social info |
|
|
|
What do schemas have to do with processing and retrieving info? |
Attention: what info we notice Encode: when info stored in memory Retrieve: recover info from memory to use it |
|
|
|
Priming |
Process where recent experience increases the use of a concept, trait, or schema |
|
|
|
How are stereotypes formed? |
Through social categorization which helps make the world more predictable. Once formed, they act as cognitive schemas |
|
|
|
How do schemas aid our memory? |
Help remember previous experiences Help make predictions about the world Provide clarity in ambiguous situations. ***Depends on level of specificity*** |
|
|
|
How do schemas aid our memory? |
Help remember previous experiences Help make predictions about the world Provide clarity in ambiguous situations. ***Depends on level of specificity*** |
|
|
|
Problems with schemas |
Influence the way we process and gather info and can become reality |
|
|
|
Self-fulfilling prophecy |
Prediction that, in a sense, makes itself come true. |
|
|
|
Different types of schemas |
Objects Ourselves Other people Groups of people About events |
|
|
|
Schemas do with memory reconstruction and eyewitness testimony |
Won't be able to remember all the facts. Could possibly be untruthful because you don't remember. Can over-exaggerate. |
|
|
|
Heuristics |
Simple rules for making complex decisions or drawing inferences in a rapid and seemingly effortless manner |
|
|
|
Representativeness Heuristic |
A strategy for making judgements based on the extent to which current stimuli or events resemble other stimuli or categories |
|
|
|
Representativeness Heuristic |
A strategy for making judgements based on the extent to which current stimuli or events resemble other stimuli or categories |
|
|
|
Availability Heuristic |
A strategy for making judgements on the basis of how easily specific kinds of info can be brought to mind |
|
|
|
Counterfactual thinking |
Tendency to imagine other outcomes in a situation than the ones that actually occurred |
Example: 89 & 83 on exam (upward and downward) |
|
|
Magical Thinking & 3 types |
"Rational Thought" Law of Contagion Law of Similarity Thoughts/Actions influence physical world |
|
|
|
Law of Contagion |
Something seems contagious although not |
|
|
|
Law of Contagion |
Something seems contagious although not |
|
|
|
Law of Similarity |
Things that loom alike are alike |
|
|
|
Law of Contagion |
Something seems contagious although not |
|
|
|
Law of Similarity |
Things that loom alike are alike |
|
|
|
Thoughts/Actions influence physical world |
Wear same socks whether you lose the sofball game or not |
|
|
|
6 universal emotional expressioms |
Anger Fear Happiness Sadness Disgust Surprise |
|
|
|
Examples of nonverbal communication |
Emblems, Illustrators, Regulators, Adaptors
Eye contact, personal space, touching, scent, |
|
|
|
Research in Deception |
Everyone engages in it at least once Strong nonverbal cues: Microexpressions Eye contact Exaggerated facial expressions |
|
|
|
Attribution |
Understanding the causes of others behavior (Want to know how AND why) |
|
|
|
Internal Attribution |
An event or a persons behavior is due to personal factors (traits, abilities, or feelings) |
|
|
|
Internal Attribution |
An event or a persons behavior is due to personal factors (traits, abilities, or feelings) |
|
|
|
External Attribution |
Infer that a persons behavior is due to situational factors |
|
|
|
Kelley's Corvariation Model |
People use 3 pieces of info to determine whether a cause on behavior is internal or external |
|
|
|
Kelley's Corvariation Model |
People use 3 pieces of info to determine whether a cause on behavior is internal or external |
|
|
|
Consistency |
Constant - Same Time |
|
|
|
Consensus |
Agreement - Everyone agrees |
|
|
|
Distinctiveness |
Stands out - Unique |
|
|
|
Fundamental Attribution Error (FAE) |
Correspondence Bias The tendency to overestimate the impact of dispositional cues on others behavior |
|
|
|
Fundamental Attribution Error (FAE) |
Correspondence Bias The tendency to overestimate the impact of dispositional cues on others behavior |
|
|
|
How is Actor-Observer an extension to FAE |
Actor observer effect overestimates others behaviors like FAE, but also other peoples and the environment |
|
|
|
Example of Actor-Observer Bias |
One person is smoking, other is drinking. The person who is smoking says drinking is gross BUT smoking is also gross |
|
|
|
Self-Serving Bias |
Any cognitive or perceptual process that is distorted by the need to maintain and enhance self esteem |
|
|
|
What affects our impressions of others |
Physical Appearance Body Language Traits Values Principles |
|
|
|
Implicit Personality Theory |
The general expectations that we build about a person after we know something of their central traits |
|
|
|
Confirmation Bias |
The tendency to interpret new evidence as confirmation of one's existing beliefs or theories |
|
|
|
Confirmation Bias |
The tendency to interpret new evidence as confirmation of one's existing beliefs or theories |
|
|
|
Attitudes |
Evaluations of various aspects of the social world |
|
|
|
Measuring Attitudes |
Likert Scale (Scale of 1-10...strongly agree/disagree) |
|
|
|
Social Learning |
The process through which we acquire new information, forms of behavior, or attitudes from other persons |
|
|
|
Theory of Planned Behavior |

|
|
|
|
Elaboration Liklihood Model |
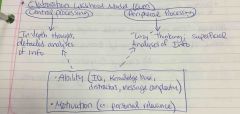
|
|
|
|
Elaboration Liklihood Model |
|
|
|
|
4 Factors that Influence Persuasion |
Ads Billboards Speeches Commercials |
|
|
|
Cognitive Dissonance Theory |
An internal state that results when individuals notice inconsistency among 2 or more attitudes or between their attitudes and their behavior |
|
|
|
How can you reduce cognitive dissonance |
Change Behavior Change Cognitions Add supporting cognitions |
|
|
|
Leon Festinger Study |
Originally proposed the social comparison theory which cognitive dissonance is one form of social comparison
|
|
|
|
When does cognitive dissonance occur? |
When there is a discrepancy between beliefs and behaviors and something must change in order to eliminate/reduce the dissonance |
|
|
|
3 Different Types of Researches |
Descriptive Correlational Experimental |
|
|
|
Descriptive Research |
Assess the amount of average level of a given variable in a population |
|
|
|
Correlational Research |
Studies whether changes in one variable are related to changes in another variable (positive and negative) |
|

