![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Macule |
Primary lesion. Less than 1cm. Flat.
** Common lesion |
|
|
Patch |
Primary lesion. Greater than 1cm. Flat.
Larger macule. |
|
|
Papule |
Primary lesion. Less than 1cm. Raised.
Ex : wart, insect bite, mole, milia.
** Common lesion |
|
|
Plaque |
Primary lesion. Greater than 1 cm. Raised.
Large papule. |
|
|
Nodule |
Primary lesion. Greater than 1cm. Raised.
Extends into dermis. Deep plaque. HCP can palpate and feel the inside of the dermis |
|
|
Tumor |
Primary lesion. Greater than 2cm. Raised.
"Mass" |
|
|
Wheal |
Primary lesion. All sizes. Both raised and flat. |
|
|
Urticaria |
Primary lesion. All sizes. Both raised and flat.
Grouping of wheals. Ex : hives. |
|
|
Vesicle |
Primary lesions Less than 1cm. Raised. Fluid filled.
Ex. blisters, zoster (herpes), chicken pox
** Common lesion |
|
|
Bulla |
Primary lesions Greater than 1cm. Raised. Fluid filled.
Larger vesicles. Common in second degree burns. |
|
|
Cyst |
Primary lesion. All sizes. Raised. Fluid filled.
Cavity that extends deep into dermis. May be hard to differentiate from nodule unless opened. |
|
|
Pustule |
Primary lesion. All sizes. Raised. Fluid-filled.
Filled with pus. Ex : acne (whiteheads)
** Common lesion. |
|
|
Primary lesions |
Lesions that have first appeared on the skin |
|
|
Secondary lesions |
Primary lesions that have since changed form/ characteristics to a new kind of lesion. |
|
|
Crust |
Secondary lesion.
Scab or dried exudate |
|
|
Scale |
Secondary lesion.
Plaque with scales and/or flaky skin. Ex : Psoriasis |
|
|
Fissue |
Secondary lession.
Linear crack that is pink or red in appearance. |
|
|
Erosion |
Secondary lesion.
Shallow depression. Superficial only. |
|
|
Ulcer |
Secondary lesion.
Depression that goes deep to the dermis layer (and beyond). |
|
|
Excoriation |
Secondary lesion.
Reddened area from scratches. Self-inflicted. May have crusting. |
|
|
Scar |
Secondary lesion.
Healed lesion with mark (most permanent) |
|
|
Atrophic Scar |
Secondary lesion.
Purple/red or clear in color. Also called "Stretch marks" or "Striate"
|
|
|
Lichenification |
Secondary lesion.
Thickened area that often builds up from damage Also called a "callus". |
|
|
Keloid |
Secondary lesion.
Elevated scar that is often colored. Certain areas of the body and ethnic backgrounds are more prone to it. |
|
|
Vascular lesions |
Lesions involving the vessels underneath the skin.
Often red or purple in appearance. |
|
|
Petechiae |
Vascular lesion. Less than 1cm. Flat.
Pinpoint dots (macular lesions). Often red in color.
** Can be a sign of clotting issues or toxicity |
|
|
Ecchymosis |
Vascular lesion. Any size. Flat.
Also known as a "bruise" |
|
|
Purpura |
Vascular lesion. Greater than 1cm. Flat
Can look like bruising (purple, red, etc.)
** Can be a sign of toxicity |
|
|
Hemangioma |
Bening vessel mass. |
|
|
Areas Prone to Bruising . . . |
- Upper chest - Back - Face - Neck |
|
|
Functions of the Skin |
- Protection - Barrier - Temperature regulation - Wound repair - Absorption/ excretion - Production of Vitamin D - Perception / sensation (touch, pain, temperature, pressure) - Identification - Communication (nonverbal) |
|
|
Epidermis |
Outermost layer of skin. Tough but thin.
Replaced every 4 weeks.
|
|
|
Keratin |
Tough, fibrous protein |
|
|
Melanin |
Brown tones to the skin and hair.
All individuals have the same amount of melanocytes. The amount of melanin secreted is what varies -- this is genetically, hormonally or environmentally determined. |
|
|
Carotene |
Influences orange tones |
|
|
Dermis |
Inner, supportive layer of skin
Consists of connective tissue (collagen), nerves, sensory receptors, blood vessels, lymphatics, hair follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat glands |
|
|
Subcutaneous Layer |
Layer beneath the dermis/epidermis.
Contains the adipose (fat) tissue to protect and insulate the body |
|
|
Sebaceous Glands |
Produces sebum (lubricating) |
|
|
Eccrine Sweat Glands |
All-over glands that produce sweat. No smell. |
|
|
Apocrine Sweat Glands. |
Produces thick, milk secretions. Located in the armpit and groin regions. Activated at puberty. |
|
|
Nails |
Hard plates of keratin. |
|
|
Pallor |
Pale or white |
|
|
Erythema / erythemic |
Redness or pink-colouring |
|
|
Cyanosis / cyanotic |
Bluish or mottled color |
|
|
Jaundice |
Yellow color.
"Icteric" |
|
|
Subjective Data / History for Skin Assessment |
- Previous history - Changes (pigment, lesions, texture) - Pruritis - Excessive bruising - Rash / lesions - Medications - Hair loss - Nail changes - Environmental/ occupational exposure - Self-care behaviors |
|
|
"Previous History of Skin Disease" |
- treatment - skin allergies - birthmark - tattoos - piercings |
|
|
Change in Skin Color |
What's the change?
General or localized? |
|
|
Change in Lesions |
Include moles, freckles, sores, etc. |
|
|
Change in Skin Textue |
Dryness? Moisture? |
|
|
Pruritis |
Itching |
|
|
Excessive Bruising |
More than 20-30 bruises.
Also include bruises in unusual places (behind the ear?) or bruises in the same area but different stages of healing |
|
|
Rash / Lesion |
Any? |
|
|
Medications |
Include ANY medications, supplements, etc. |
|
|
Hair Loss |
Include pattern, location, change in texture and color |
|
|
Nail Change |
Include texture, color or shape |
|
|
Environmental / Occupational Hazards |
Excessive sun exposure? Chemical exposure? Excessive hand-washing? |
|
|
Self-Care Behaviors |
Skin self examinations? What skincare products are used? How is everything cared for? Sunscreen use? |
|
|
ABCDE Assessment for Moles |
Use the ABCDE for HCP/self-exam of moles. . .
Asymmetry → asymmetrical is cause for concern Border → jagged borders are cause for concern Color → multiple/ non-brown colors are cause for concern Diameter → >6 mm/1cm is cause for concern Evolution → any change is cause for concern |
|
|
Skin Examination / Objective Data |
Inspect and palpate . . . 1. Color/ general pigmentation 2. Hair 3. Nails 4. Lesions 5. Temperature 6. Moisture/ dryness 7. Texture 8. Edema 9. Mobility + turgor 10. Vascular lesions or bruising |
|
|
Color / General Pigmentation (exam) |
Ex : "Skintone is dark brown. Consistent with ethnic background." |
|
|
Hair (exam) |
Inspect and palpate. Take note of . . . 1. color 2. texture 3. distribution 4. lesions (or presence of parasites) |
|
|
Nails (exam) |
Inspect and palpate. Take note of . . . 1. texture 2. contour 3. color |
|
|
Lesions (exam) |
Take note of . . . 1. location 2. color 3. size 4. symmetry 5. pattern 6. elevation 7. odor 8. drainage or discharge 9 . pain 10. edges |
|
|
Temperature (exam) |
Ex : "Temperature is warm to touch", "Temperature is cool to touch"
|
|
|
Moisture / dryness (exam) |
Is skin in tact?
Ex : "Skin feels moist" |
|
|
Edema (exam) |
To check for edema, push with thumb and take note of swelling.
+1 (mild pitting) → slight indent, no swelling +2 (moderate) → indentation subsides rapidly +3 (deep) → indentation remains for short time, swollen appearance +4 (very deep) → indentation lasts for a long time, very swollen |
|
|
Skin Mobility / Skin Turgor (exam) |
Test on back of hand.
Ex : "Turgor returns to baseline in 3 seconds." |
|
|
Vascular Lesions / Bruising (exam) |
Take note where, color, size, etc. |
|
|
Generalized (pattern) |
Spread throughout the body |
|
|
Zosterform (pattern) |
Unilateral. Does NOT cross the midline. |
|
|
Localized (pattern) |
On one area of the body |
|
|
Decubitus Ulcer |
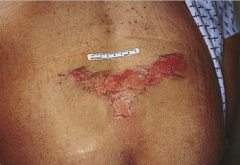
"Pressure ulcer" Undergoes 4 stages leading through each layer (epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous and into muscle) |
|
|
Diaper Dermatitis / Contact Dermatitis |
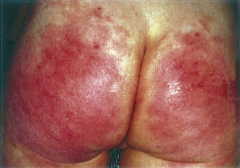
Macular patch with poorly defined borders. Inflammatory disease caused by skin irritation from ammonia, heat, moisture, diapers, etc. |
|
|
Impetigo |
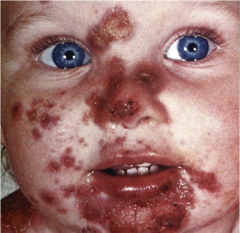
Moist, thin-roofed vesicles with erythematous base. Ruptures to form a honey-colored crust. Contagious bacterial infection of the skin. |
|
|
Eczema |
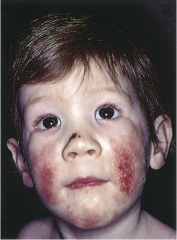
Erythematous papules and vesicles with weeping, oozing and crusts. Pruritus. Often associated with family history of allergies. |
|
|
Varicella (Chicken Pox) |
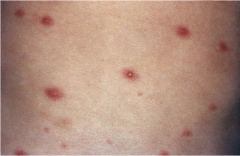
Shiny vesicles on a erythematous base. Often erupts, becomes pustules and then crusts. Intensely pruritic. |
|
|
Allergic Drug Reaction |
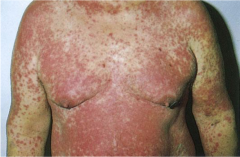
Erythematous and symmetrical rash, usually generalized. |
|
|
Tinea Corporis ("ringworm") |
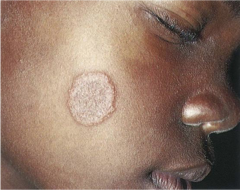
White scales forming multiple circular lesions with clear centers.
Light up in blacklight. |
|
|
Tinea Pedis ("Athlete's Foot") |
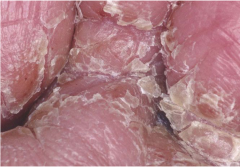
Fungal infection.
First appears as vesicles and then grows scaly and hard. |
|
|
Psoriasis |
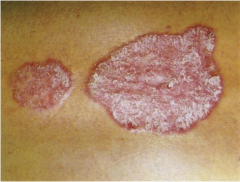
Scaly, erythematous patch with silvery scales on top. |
|
|
Tinea Versicolor |
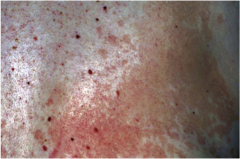
Fine, scaling patches of pink, tan or white that is caused by a superficial fungal infection. |
|
|
Candidiasis |
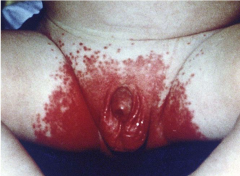
Scalding red moist patches with sharply demarcated borders and some loose scales.
Usually in genital areas. |
|
|
Herpes Zoster / Shingles |
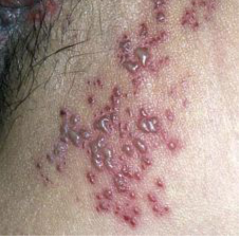
Small, grouped vesicles emerging in a zosterform pattern.
Reactivation of the dormant virus of chickenpox. |
|
|
Melanoma |
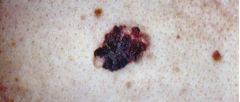
Malignant skin tumors.
Identify via the "ABCDE method" |
|
|
Kaposi's Sarcoma |
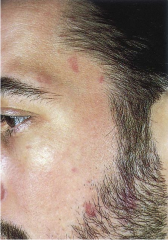
Vascular tumors presenting as pink papular (patch) lesions scattered.
Common tumor in HIV-infected persons. |
|
|
Seborrheic Dermatitis |
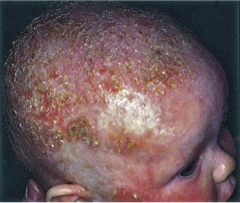
"Cradle Cap" Thick yellow (to white), greasy adherent scaling w/ mild erythema on scalp and forehead. Common in early infancy. |
|
|
Alopecia Areata |
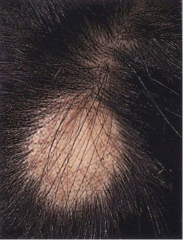
Sudden appearance of sharply circumscribed, round or oval balding patch- usually with smooth, soft skin underneath |
|
|
Pediculosis Capitis |
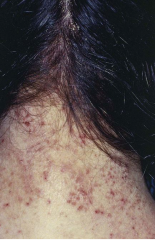
Infestation manifested by intense itching of the scalp. The nits (eggs) are easier to see- appearing as translucent bodies adherent to shaft. |
|
|
Folliculitis |
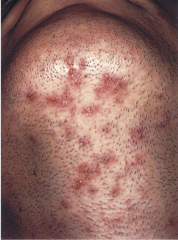
Superficial infection of hair follicles. Consists of multiple pustules with visible white heads and an erythemateous base. |
|
|
Nail Clubbing |
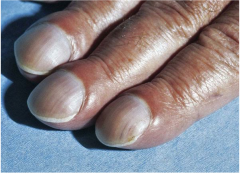
Inner nail elevates. Nail bed is greater than 180 degrees. |
|
|
Hirsutism |
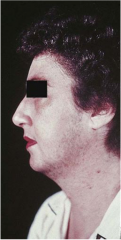
Excess body hair in females forming a male sexual pattern; caused by endocrine or metabolic dysfunction. Sometimes idiopathic. |
|
|
"Approximated" |
Close. Use to describe legion edges for an open wound.
Ex : well-approximated |
|
|
Stitches |
Stitches must be noted.
What kind? In tact? How many? |
|
|
"Tender to Palpation" |
Objective data!!
** Do not put in the wrong category. If patient has to report it, it is objective, irregardless if it comes up during the physical exam |
|
|
Heplock / IV |
Any breaks must be noted.
When there is a heplock/IV break in skin, be sure to note the following . . . - Is it hard? - Is it red? - Any pain? - Any drainage? |
|
|
Dressings |
- How big is the dressing? (4x4, 2x2) - Location of dressing? - Odor of drainage? - Type/ color of drainage? - Any other relevant information . . .
Do NOT lift up the dressing to see underneath. Describe only what you see on the dressing. |

