![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
109 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What disease is often associated with tattoos?
|
Hep C
|
|
|
What material can be used up to 18 years following the development of a scar to help minimize it?
|
Silicone patching
|
|
|
Why is lanolin terrible for dry skin?
|
it is made with wool
|
|
|
What are the 9 functions of the skin?
|
1. Protection
2. prevents penetration 3. Perception 4. Temp regulation 5. Identification 6. communication 7. wound repair 8. absorption and excretion 9. Production of vitamin D |
|
|
Which layer of the skin is characterized by a horny layer of dead cells, melanin and keratin are formed?
|
Epidermis
|
|
|
Describe the dermis.
|
Supportive layer, connective tissue, appendages embedded vasculature and peripheral nervous system
|
|
|
THe subcutaneous layer is composed of___.
|
Fat
|
|
|
What common skin disorders often affect the epidermal layer?
|
-Vitiligo
-atopic dermatitis -cafe au lait spots -impetigo |
|
|
if a lesion effects both the dermis and the epidermis, how would it be described?
|
Altered surface markings plus distinct borders, edema, scales, vesicles, crust, color changes including red
|
|
|
Which disorders effect both the epidermis and the dermis?
|
-Psoriasis
-Atopic dermatitis -cutaneous lupus erythematosus -contact dermatitis |
|
|
What is the name of the thickening of the skin?
|
lichenification
|
|
|
If a lesion occurs at the dermal layer, how would it be generally described?
|
Normal surface markings with color changes and dermal firmess
|
|
|
what skin lesions often occur in the dermis?
|
-Urticaria
-granuloma annulare -hemangioma -blue nevus |
|
|
What skin lesions can occur in the subcutaneous tissue?
|
-hematoma
-erythema nodosum |
|
|
what is a common example of hypopigmentation often seen in children?
|
TInea alba: sign that the child has tendencies to be atopic
|
|
|
If a child has tinea alba, what is he or she predisposed to?
|
allergies
|
|
|
Where are aprocrine sweat glands found?
|
-ear canal
-armpit -nipples -ano/genital region |
|
|
Sweat glands on the forehead, armpits, palms and feet are often ___?
|
eccrine
|
|
|
Give examples of what can cause temporary pallor?
|
fear, exam room too cool
|
|
|
If a pigment change lies in the epidermis, how long does it take to go away?
|
6 months
|
|
|
In darkly pigmented children the ___ ____ causes a prominent papular and follicular pattern.
|
pilar apparatus
|
|
|
____ response: hypertrophic scars?
|
mesenchymal
|
|
|
how many times would a child with hyperkeratosis pilaris have to scratch to cause lichenification?
|
140,000
|
|
|
What is the name of the autoimmune disease which causes destruction and loss of the melanocytes?
|
Vitiligo
|
|
|
What disorder is vitiligo often associated with>?
|
hypothyroidism
|
|
|
Describe oculocutaneous albinism and what it is associated with.
|
-Body is unable to produce melanin
-red/orange hair -must protect skin since will develop freckles, actinic keratoses and carcinoma -associated with NYSTAGMUS and photophobia |
|
|
What is Koebner Phenomenon?
|
Linear papules that occur after being scratched in an area.
Think poison ivy!! |
|
|
What are the prime areas to assess when determining abnormal variations in skin COLOR?
|
Mucus membranes, conjunctiva, and the hands
|
|
|
what are 5 examples of abnormal variations in skin color?
|
1. pallor
2. erythema 3. cyanosis 4. jaundice 5. increased pigmentation |
|
|
What are the 2 phases of Raynauds?
|
Pallor and erythema
Rubor is often associated with an autoimmune disorder such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis |
|
|
True or False: mongolian spots blanch?
|
False
|
|
|
True or false: palmar erythema during pregnancy is an abnormal finding?
|
False
|
|
|
What is the clinical term for a port wine stain?
|
Nevus Flammeus
|
|
|
Where on the body do port wine stains often fade?
|
around the eyelids or face
|
|
|
If a port wine stain covers an area of the trigeminal nerve, what should the patient be worked up for?
|
Sturge-weber
|
|
|
What is the medical term for an abnormal mole? what can occur if the pt has 2 or more?
|
Dysplastic nevi
2 or more may be dysplastic nevi syndrome |
|
|
what is acanthosis nigricans? what is it a sign of?
|
Dirty neck
occurs in obesity and is a sign of increased insulin levels |
|
|
True or False: Steven Johnson's is life threatening?
|
True
|
|
|
List the primary skin lesions.
|
-macule
-patch -papule -plaque -nodule -tumor -wheal -urticaria -vesicle -bulla -pustule -cyst |
|
|
What is the name of a macular rash that is common for a drug erruptions?
|
confluent/morbilliform
|
|
|
Exposure to bleach on the hand can cause which lesions?
|
Contact dermatitis which are flat lesions patches
|
|
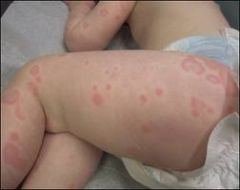
What is this an example of?
|
Wheal: urticaria.
|
|
|
What are the lesions called after urticaria has been scratched extensively?
|
White dermagraphism
|
|
|
name a disease often associated with nodules?
|
neurofibromatosis
|
|
|
If a lipoma occurs on the ___ it must be removed?
|
joint
|
|
|
How does varicella spread?
|
Starts trunkal and spreads out up and down
|
|
|
what type of lesions are associated with varicella?
|
vesicles
|
|
|
If an individual reacts to an iodine sensitivity, what kind of lesions will occur?
|
vesicles in the area of the drip
|
|
|
If an individual presents to the clinical with bullae and vesicles that run along a dermatone and stop at the midline, what is their likely diagnosis?
|
Herpes zoster
|
|
|
What skin disorder is only seen in infancy and involves pustules located on the ankle most commonly in black babies?
|
Acral Pustulosis of childhood
|
|
|
Describe psoriasis.
|
Scaly plaques located most commonly on the forearm and often follows a line.
|
|
|
How can one determine herpes from varicella?
|
Herpres are vesicles in a group/clustered
|
|
|
List the secondary lesions
|
-crust
-scale -fissure -erosion -ulcer -excoriation -scar -atrophic scar -lichenification -keloid |
|
|
Other than the forearm, where is another common location for psoriasis?
|
Sclap
|
|
|
Give and example of a disorder associated with scaling?
|
tinea pedis
|
|
|
What is the likely diagnosis of a child who comes into the office with mild scaling and erythema around the mouth?
|
Lip lickers dermatitis
|
|
|
Which form of secondary lesions is often seen on the lips of herpes simplex?
|
crust
|
|
|
If a honey comb crusting is seen on the skin, what is the likely diagnosis?
|
secondary infection possible impetigo
|
|
|
What is the name of a singluar, locular lesion that drains from one area?
|
Furuncle
|
|
|
If a lesions has many openings that drains through multiple areas, it is referred to as a ___.
|
carbuncle
|
|
|
If a person presents with multiple atrophies (striae) that are purple in color, what should they be worked up for?
|
Cushings
|
|
|
What is the only product that has been found to flatten keratosis pilaris?
|
lac hydrin
|
|
|
Which population is often prone to striae gravidarum?
|
Pregnant women
|
|
|
If petechiae are located on the abdomen, what should the person be worked up for?
|
Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura
|
|
|
If petechiae is located on the face, what is the likely cause?
|
Severe vomiting or pressure from coughing.
|
|
|
What type of lesions are petechiae?
|
vascular
|
|
|
What are the vascular lesions?
|
-petechiae
-purpura -ecchymosis -spider angioma -telangiectasia -hemangioma |
|
|
What are the lesions that are neither primary or secondary?
|
Excematous and Hyperkratosis
|
|
|
Define eczematous.
|
inflammatory skin lesions that are poorly marginated, erythematous and sometimes with vesiculations
|
|
|
What is hyperkeratosis?
|
thickening of the corneum stratum
|
|
|
What age group commonly gets seborrhea
? |
6-10 weeks old
|
|
|
What is the preferred treatment for hemangiomas?
|
Beta blockers
|
|
|
If a lesion is described as discoid, what is its shape?
|
disk like
|
|
|
What is the name of lesions that are droplike in shape?
|
Guttate
|
|
|
Coin shaped lesions are charted as ____.
|
Nummular
|
|
|
What is a common name of seborrhea?
|
Cradle cap
|
|
|
What are the 5 ways to describe how lesions are configured?
|
1. Linear lesion
2. Herpetiform lesions 3. Dermatomal 4. Annular 5. Arciform |
|
|
What are some common lesions that have herpetiform configuration?
|
gingivitis, any groups lesions
|
|
|
What type of allergy is poison ivy?
|
Type 4 allergy: Tcell allergy
|
|
|
Describe granuloma annulare.
|
Ringlike erythematic lesion that is flat in the middle and raised on the borders with no scaling. Often found on the ankle in children. Associated with DM in adults.
|
|
|
Give 3 examples of annular: ringlike lesions.
|
1. nummular excema
2. granuloma annulare 3. Tinea corporus |
|
|
What disorder often has a butterfly distribution?
|
Lupus
|
|
|
What is the 6 pronged approach to documenting the location and distribution of a rash?
|
1- sun exposed area
2. flexural rashes 3. acneform 4. acrodermatitis 5. clothing covered sites 6. pityriasis |
|
|
What are the common disorders found in flexural region?
|
-atopic dermatitis
-fungal infections like tinea cruris -inverse psoriasis -intertrigo -candidiasis -toilet seat dermatitis |
|
|
other than acne, what other lesion has an acneform distribution?
|
pityriasis versicolor
|
|
|
Which skin disorders have an acrodermatitis distribution?
|
-Viral exanthema caused by coxsakie
-dyshidrotic exzcema -post streptococcal peeling -tinea pedis |
|
|
What should HCP look for on the acrodermatitis region during may-october?
|
exanthem of coxsackie
|
|
|
What are the common skin disorders associated in the sun exposed areas?
|
-Viral exanthem photo enhancements
-Lupus erythematous |
|
|
The common skin lesions with pityriasis distribution are ___?
|
1. Pityriasis rosea
2. Drug reaction 3. secondary syphilis 4. Guttate psoriasis |
|
|
Contact dermatitis, miliaria and psoriasis in summer are located and distributed on which area of the body?
|
Clothing covered sites
|
|
|
Where are the common sites on the body for atopic dermatitis lesions in adults?
|
Neck, antecubal region, wrists and ankles
|
|
|
What are the 9 ways to classify the shape/configuration of a lesion?
|
1. annular: circular
2. confluent 3. discrete 4. grouped 5. gyrate 6. target 7. linear 8. polycyclic 9. zosteriform |
|
|
What is the spreading pattern of measles?
|
Starts behind the ears
|
|
|
What type of lesion is known to be painful?
|
herpes zoster
|
|
|
What is a common itchy lesion?
|
tinea corpus
|
|
|
True or false: granuloma annulare is itchy and painful?
|
False: it is nothing
|
|
|
True or false: koebner's phenomenom have pustular lesions?
|
FALSE!! Papular!
|
|
|
What is monilial intertrigo? and where is it located?
|
Form of candidiasis and is found in the folds of the body. Often under the breasts or armpits.
|
|
|
Where is Monilial Balanitis found?
|
candidiasis on the penis
|
|
|
What is monilial balanitis?
|
red candidia on the shaft
|
|
|
What is the medical term for warts?
|
Verruca
|
|
|
What is Verruca plantaris?
|
Plantar warts
|
|
|
Describe condyloma accuminatum.
|
cauliflower like warts on the genitals caused by HPV
|
|
|
Describe Scabies
|
The most common symptoms of scabies are intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash. The scabies mite usually is spread by direct, prolonged, skin-to-skin contact with a person who has scabies.
|
|
|
What is alopecia areata?
|
A total loss of hair in one area or over a large portion of the head or body.
|
|
|
What is the name of the disorder where there is a large area of the hair that is white?
|
alopecia areata: loss of melanocytes
|
|
|
What is disorder commonly associated with hursitism?
|
polycystic ovarian syndrome
|
|
|
What are Beau lines?
|
LInear lines on the nails that can occur after a very high fever
|
|
|
What is onychomycosis and where is it most common?
|
Fungal infection, most commonly in the nails also known at tinea unguium
|

