![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
124 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Are bones vascular |
Yes |
|
|
Are ligaments vascular |
No, they are avascular |
|
|
Are cartilages vascular |
No, they are avascular |
|
|
What are the three types of cartilages |
Fibro, hyaline, and elastic |
|

Describe hyaline cartilage |
Provides flexibility, support, and resilience Most abundant type |
|
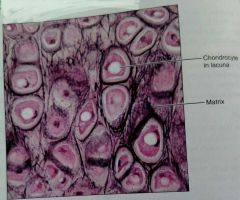
Describe elastic cartilage |
Similar structures to hyaline cartilage but contains elastic fibers which increase elasticity |
|
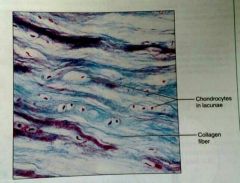
Describe fibrocartilage |
Has many collagen fibers to strengthen |
|
|
How many classifications of bones by shape are there |
4 |
|
|
What are the 4 types of bones classified by shape |
Long bones, Short bones, Flat bones, Irregular bones |
|
|
What are long bones |
Longer than they are wide |
|
|
What are short bones |
Cube shaped bones in the carpals and tarsals, include sesamoid bones |
|
|
What are sesamoid bones |
Bones shaped like sesame seeds ex: patella |
|
|
What are flat bones |
Thin, flat and slightly curved |
|
|
What are irregular bones |
Bones in complicated shapes |
|
|
What is a tuberosity |
Rounded projection |
|
|
What is a crest |
A narrow prominent ridge |
|
|
What is a trochanter |
Large, blunt, irregular surface |
|
|
What is a line |
A now ridge of bone |
|
|
What is a tubercle |
A small rounded projection, small tuberosity |
|
|
What is an epicondyle |
A raised area above a condyle |
|
|
What is a projection |
Structure that helps for joints |
|
|
What are the 4 kinds of projections |
Head, Facet, Condyle, Ramus |
|
|
What is a facet |
A smooth, nearly flat articular projection |
|
|
What is a ramus |
An arm like bar |
|
|
What is a meatus |
Canal-like passageway |
|
|
Sinus |
Cavity within a bone |
|
|
Fossa |
Shallow depression |
|
|
Groove |
Furrow |
|
|
Fissure |
Narrow slit In a bone |
|
|
Foramen |
Round or oval opening through a bone |
|
|
What are two parts of a long bone |
Diaphysis and epiphyses |
|
|
What is a diaphysis part of a long bone |
The shaft |
|
|
What is the epiphyses of the long bone |
The expanded ends |
|
|
What are two parts of bone coverings |
Periosteum (outer) Endosteum (inner) |
|
|
What is the outer layer of a bone covering |
Periosteum |
|
|
What is periosteum |
The outer, fibrous layer of the bone, contains cells, nerve fibers, and is vascular (blood and lymph) |
|
|
What are the types of cells in the osteogenic layer of periosteum |
Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts, and osteogenic cells |
|
|
What are osteoblasts |
Bone forming cells |
|
|
What are osteoclasts |
Bone destroying cells |
|
|
What are osteogenic cells |
Stem cells |
|
|
What is the inner layer of bone covering |
Endosteum |
|
|
What is the endosteum |
A delicate membrane that contains Osteoblasts and oateoclasts |
|
|
What is hematopoietic tissue |
Red bone marrow |
|
|
What is the location of of red bone marrow in adults |
Head of femur and humerous, and in flat bones |
|
|
Where is red bone marrow in infants |
Medullary cavities and all spaces in spongy bone |
|
|
What are osteocytes |
Mature bone cells |
|

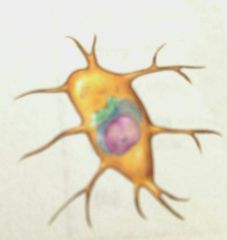
What is this kind of cell |
An osteogenic (stem) cell |
|

What is this kind of cell |
An Osteoblasts cell that forms bones |
|
What is this kind of cell |
Osteocytes, a mature cell that maintains the bone matrix |
|
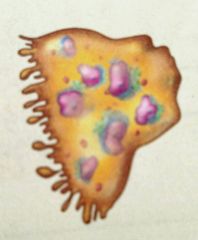
What is this kind of cell |
An osteoclast, a cell that breaks down the bone |
|
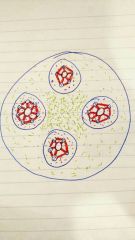
What are the red canals that connect the central canal and lacunae, and lacunae to each other? |
The canaliculi |
|
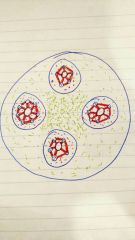
What does the central canal contain |
Blood vessels and nerves |
|
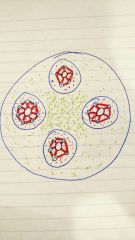
What are the smaller cavities within an osteon |
Lacunae |
|
|
What do lacunaes contain |
Osteocytes which form bones |
|
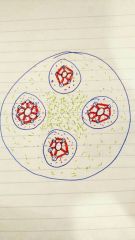
What is the purple matrix within the osteon |
The concentric lamella |
|

What is the less dense green matrix around the edge of the compact bone tissue |
Circumferential lamella |
|
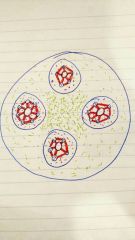
What is the dense green matrix in the center of the compact bone tissue |
The interstitial lamella |
|
|
What is another name for ostofication |
Osteogenesis |
|
|
What is the kind of ostofication that occurs when cartilage becomes hard tissue |
Intracondrall ossification |
|
|
What are the sponge like structures in spongy bone tissue |
Trabeculae |
|
|
Do trabeculae in spongy tissue contain osteons |
Nope |
|
|
What does the trabeculae in spongy bone contain |
Irregularly arranged lamellae, osteocytes, and canaliculi |
|
|
What is the organic part of the chemical composition of bone |
Osteoid |
|
|
What is osteoid (organic) part of the chemical composition of bone secreted by |
Osteoblasts that secrete matrix |
|
|
What is contained in the matrix that is secreted by Osteoblasts in organic bone |
Ground substances- proteoglycans and glycoproteins- and collagen fibers that provide strength and flexibility |
|
|
What are the inorganic chemicals that bones are composed of |
Mineral salts |
|
|
What are the kinds of inorganic mineral salts contained in bone |
65% of bone mass, mainly crystals of calcium phosphate, and responsible for hardness and resistance to compression |
|
|
What do osteoblasts do |
Secrete matrix- young cells |
|
|
Collagen fibers do what to bones |
Give it flexibility |
|
|
What is another name for ossification |
Osteogenesis |
|
|
Chondral |
Cartilage |
|
|
What does Intracondrall mean |
Within the cartilage |
|
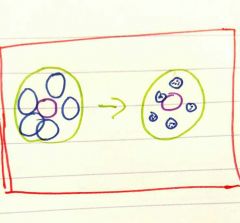
What is the red boarder supposed to represent |
The Mesenchyme- membrane in intramembranous ostofication |
|

What type of ostofication is this |
Intramembranous |
|

What are the larger blue circles before ossification |
Osteocytes- young cells |
|
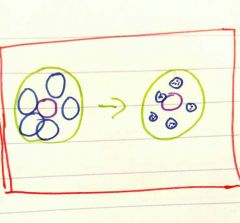
What are the smaller blue circles after ossification |
Osteocytes mature cels |
|
|
What is also contained within the mesenchyme membrane |
Fibroblasts |
|
|
What types of bones are made with intramembranous ossification |
Flat bones and the clavicles |
|
|
What types of bones are made with Intracondrall osteofication |
Everything besides flat bones and clavicals |
|
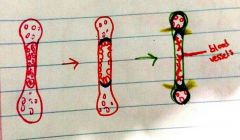
What are the small circles in the first bone |
Chondroblasts that convert to chondrocytes |
|
|
Are chondrocytes mature |
Yes! |
|
|
Blasts turn into what |
Cytes |
|
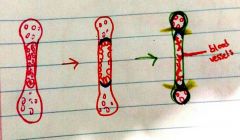
What is the center of the bone in the first picture called |
Primary ossification center |
|
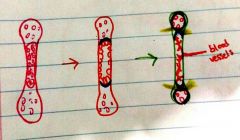
What do the cells do to destroy the primary ossification center |
Swell and get bigger |
|
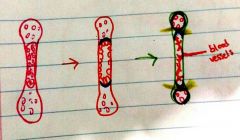
What are the cells within the bony collar of the second (red) bone |
Osteogenic cells (stem cells) |
|

What are the ends of the third (green) bone called |
Secondary ossification center |
|
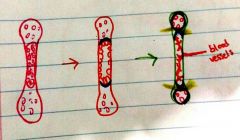
What are the yellow lines in the third (green) bone |
Growth plate. This becomes smaller and more compact as the bony collar expands |
|
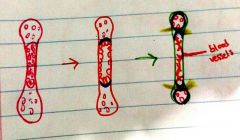
What is the growth plate/epiphyseal plate made of |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
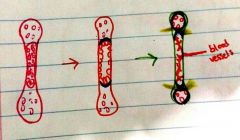
What is the drawback to the hypophyseal/growth plate |
Gives a greater chance of breaking since it is flexible and not calicified |
|
|
What is remodeling |
The destruction and production of bone tissue |
|
|
How many types of different sets of blood vessels develop |
3 |
|
|
What are the three types of different sets of blood vessels |
1) Nutrient artery and vein 2) metaphyseal vessels 3) periosteal vessels |
|
|
What is a nutrient artery/vein |
A pair of large blood vessels that enter through the nutrient foramen. The femur has two sets |
|
|
What is a metaphyseal vessel |
Supply epiphyseal cartilage so it can remain vascular, where bone growth occurs |
|
|
What are Periosteal vessels |
Supplies blood to periosteum and to superficial osteons |
|
|
How many types of hormones are there that work on bones |
2 types |
|
|
What are the two types of hormones that work on bones |
1) hormones that help in bone growth 2) calcium regulation |
|
|
What are the chemicals that help in bone growth |
Growth/pituitary hormone,Thyroid hormone, and sex hormones (testosterone and estrogen) |
|
|
What does the pituitary growth hormone do in growth of bones |
Stimulates the growth of the bones |
|
|
What does the thyroid hormone do in bone growth |
Modulates activity of the pituitary growth hormone; indirect |
|
|
What hormones help in calcium regulation |
Thyroid hormone, PTH (parathyroid hormone), and vitamin D |
|
|
What is the name of the hormone that is secreted by the thyroid |
Calcitonin |
|
|
What does the thyroid hormone calcitonin do |
Decreases the calcium levels in the blood because it inhibits the osteoclasts that break down the bones, no action is done by the intestines |
|
|
What does the parathyroid hormone do |
Increases the amount of calcium in the blood because it stimulates osteoclasts. Increases levels of vitamin D, reabsorption/retention of calcium in the intestines |
|
|
What does vitamin D do |
Increases the amount of calcium that will be retained from food |
|
|
What does calcitonin do to the kidneys |
Inhibits tubular reabsorption of calcium and phosphorus➡increased urination |
|
|
What is calcium necessary for |
1) transmission of nerve impulses 2) muscle contractions 3) blood coagulation and blood clot formation 4) secretion by glands and nerve cells 5) cell division |
|
|
How many kinds of fractures are there |
6 |
|
|
What is the kind of fracture that has multiple fractures in one location |
Comminuted, happens mostly in older people because of lessened bone density |
|
|
What is the kind of bone fracture that is caused by vertical pressure |
Compression, ex: compressed vertebral disc |
|
|
What type of fracture occurs when a bone is twisted |
Spiral: common sports fracture, a ragged break |
|
|
What kind of fracture occurs when a broken piece of bone is pressed inward |
Depressed; common head injury |
|
|
What is the fracture type that is only a partial break |
Greenstick, occurs mostly in kids since their bones are flexible |
|
|
What are the 4 steps in healing the bone |
1) a hematoma forms 2) an internal callous of fibrocartilage forms 3) a bony callous forms to bring the two parts of bone back together 4) bone remodeling |
|
|
What is a hematoma |
Clotting blood within a tissue |
|
|
When do blood vessels start to replace the old ones in healing a bone |
Step 2) when the fibrocartilage forms a callus, and after he hematoma forms |
|
|
What type of cell works like sand paper to remove the external structure of the bony callus |
Osteoclasts |
|
|
Rickets |
A bowing of the bones because calcium salts were not deposited into the bones. Caused by a vitamin D deficiency or insufficient calcium |
|
|
Acromegaly |
Thickened bones |
|
|
What is osteoporosis |
Loss of bone mass or tiny holes on the bone tissue |
|
|
What bones are most likely to be fractured in osteoporosis |
Spine and neck of femur since they are the most weight bearing sections |
|
|
What are the risk factors of osteoporosis |
Lack of estrogen, calcium or vitamin D, low levels of (TSH) thyroid stimulating hormone |
|
|
What is rheumatoid arthritis |
Inflammation of joints |
|
|
What bone covering layer is thicker |
Periosteum |

