![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the uses for CFCs
|
-Refrigerants
-Propellants in aerosols -Blowing agents |
|
|
What happens when CFCs reach the stratosphere?
|
They undergo photodissociation to produce chlorine radicals, which go onto remove ozone
|
|
|
Advantage of HCFCs (a CFC replacement)
|
H-C bonds are broken down in troposphere before the compounds have chance to reach the stratosphere
|
|
|
Disadvantage of HCFCs
|
Greenhouse gasses that contribute to global warming
|
|
|
how can the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere he reduced?
|
-Reducing the consumption of fossil fuels
-using alternate energy fuels -increasing photosynthesis -burying or reacting CO2 |
|
|
When molecules absorb infrared radiation what happens?
|
-Vibrational energy increases
-Energy is transfered to other molecules through collisions -This increases their kinetic energy raising the average temperature of the atmosphere |
|
|
What is diamonds structure?
|
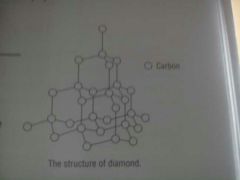
Each C atom is joined tetrahedrally to four other C atoms by strong covalent bonds
|
|
|
Why is CO2 a gas at room temperature, while SiO2 is a solid?
|
-CO2 has weak intermolecular bonds
-SiO2 has a giant network structure = more energy to overcome bonds |
|
|
why is CO2 soluble in water, while SiO2 is insoluble?
|
-CO2 has polar bonds
-Water can't break the giant structure of SiO2 |
|
|
What are the three part of the atmosphere?
|
Ionosphere
Stratosphere Troposphere |
|
|
To convert ppm to % you...
|
÷10000
|
|
|
What are the different types of energies in order of increasing energy?
|
Translational
Rotational Vibrational Electronic |
|
|
What are type of radiation is associated with each type of energy?
|
Translational-
Rotational- Microwave Vibrational- Infrared Electronic- ultraviolet |
|
|
E = hv
what does each letter represent |
E = energy
h = planck constant (6.63×10^-34) v = frequency |
|
|
One of the things that can happen when a molecule absorbs visible or UV radiation
|
Electrons can be excited to a higher electronic energy level; the electrons will return to their original energy levels in time, releasing the energy that has been absorbed
|
|
|
Another thing that can happen when a molecule absorbs visible or UV radiation
|
Chemical bonds can break and radicals form (this is called photodissociation)
|
|
|
The last things that can happen when a molecule absorbs visible or UV radiation
|
An electron is ejected from a molecule which then becomes ionised
|
|
|
What does a curly arrow represent
|
Indicates the movement of two electrons
|
|
|
What is a radical
|
A species with one or more unpaired electrons
|
|
|
What is heterolytic fission
|
Both the electrons of the shared pair goes to just one of the atoms when the bond breaks
|
|
|
What is homolytic fission
|
-One of the two electrons in he shared pair goes to each of the atoms
-both atoms now have one unpaired electron -radicals have been formed |
|
|
An initiation reaction is when...
|
There are no radicals at the beginning of this stage but radicals are formed by the end of the stage
|
|
|
A propagation reaction is when...
|
There are radicals at the start of this stage, and new radicals are formed by the end of the stage
|
|
|
A termination reaction is when...
|
The reaction is terminated when two radicals collide
|
|
|
An equation for the formation of ozone
|
O + O2 ---> O3
|
|
|
Two equations that show ozone being lost
|
X + O3 ---> XO + O2
XO + O ---> O2 + X |
|
|
Why is the depletion of ozone a problem?
|
-Ozone absorbs UV radiation
-this is very damaging to the skin -a lot of the UV radiation us absorbed by ozone in the stratosphere -reducing skin damage |
|
|
Define dynamic equilibrium
|
When the rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of the backwards reaction
|
|
|
Two equations for the production and destruction of ozone
|
Production O + O2 ---> O3
Destruction O3 --(hv)-> O2 + O Destruction O + O3 ---> O2 +O2 |
|
|
What does Le Chatelier's principle state
|
If a system is at equilibrium, and a change is made in any of the conditions, then the system responds to counteract the change as much as possible
|
|
|
Where will the equilibrium shift if the concentration of the reactants increases
|
To the right (decreases the reactants)
|
|
|
Where will the equilibrium shift if the concentration of the products increases
|
To the left (decreases products)
|
|
|
Where will the equilibrium shift if the concentration of the reactants decreases
|
To the left (increases reactants)
|
|
|
Where will the equilibrium shift if the concentration of the products decreases
|
To the right (increases products)
|
|
|
If the pressure increases where will the equilibrium shift
|
To the side with fewer gas molecules
|
|
|
If the pressure decreases which way will the equilibrium shift
|
To the side with more has molecules
|
|
|
If the temperature increases which way will the equilibrium shift
|
Shift in the direction of the endothermic reaction
|
|
|
If the temperature decreases which way will the equilibrium shift
|
Shift in the direction of the exothermic reaction
|
|
|
There are seven ways to affect a rate of reaction, name some
|
-Concentration
-Pressure -A catalyst -Intensity of reaction -Surface area -particle size -temperature |
|
|
What is the collision theory
|
Reactions occur when particles of reactants collide with a certain minimum kinetic energy
|
|
|
How does increasing concentration and pressure affect rate of reaction
|
The particles are in closer proximity to each other encouraging more frequent collisions
|
|
|
How does increasing temperature affect the rate if reaction
|
-A higher proportion of colliding particles have sufficient energy to react
-More particles are able to overcome the activation enthalpy barrier |
|
|
How does increasing surface area affect rate of reaction
|
Larger surface area on which the reactions can take place, greater chance of successful collisions
|
|
|
The activation enthalpy is...
|
the minimum kinetic energy required by a pair of colliding atoms or molecules before a reaction will occur
|
|
|
How do catalysts work?
|
By providing an alternate pathway for the breaking and making of bonds. This alternate pathway has a lower activation enthalpy
|
|
|
How does a homogeneous catalyst work?
|
-The activation enthalpy barrier is overcome and an intermediate is formed
-The intermediate breaks down to give a product and reform the catalyst |
|
|
How does a heterogeneous catalyst work?
|
They provide a surface on which the reaction may take place, thus lowering the energy needed for a successful collusion
|

