![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the main function of the lungs ? |
To circulate oxygen from the air and remove carbon dioxide from blood |
|
|
|
How is the RS related to cell energy? |
The cells obtain energy through mechanisms which use oxygen and produce CO2. |
|
|
|
What are the functions of the respiratory systems |
1. Gas exchange 2. protects respiratory surfaces from outside environment 3. sound Production 4. Olfactory sense
|
GOPS |
|
|
What does the conduction portion of the respiratory tract consist of ? |
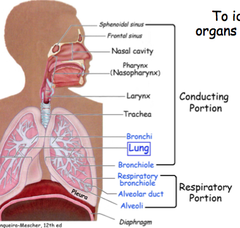
- the nasal cavity to the terminal bronchioles |
|
|
|
what structures are in the conduction part of the RT |
-Nasal cavity - Pharynx (nasopharynx) - Larynx -Trachea -Bronchi -Bronchi terminals |
|
|
|
what does the respiratory portion of the RT consist of |
alveoli and respiratory bronchioles |
|
|
|
What happens in the alveoli? |
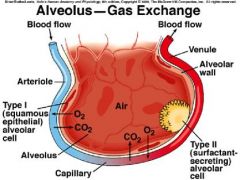
gas exchange
(there are about 300 million alveoli) |
|
|
|
what are alveoli |
air filled sacs |
|
|
|
what structure divides the upper and lower respiratory tracts ? |
the larynx |
|
|
|
What structures does the upper respiratory tract consist of ? |
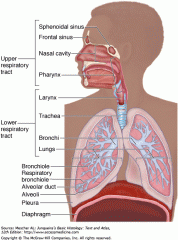
-Nose -Nasal Cavity -Pharynx |
|
|
|
What structures are in the lower RT ? |
-Larynx -Trachea -bronchi -lungs |
|
|
|
what are the 2 components of the nose |
-internal and external nose |
|
|
|
What structure forms the bridge of the nose? |
nasal bone |
|
|
|
whats the nasal bone an extension of? |
frontal and maxillary bones |
|
|
|
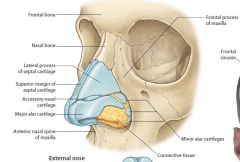
whats the external nose constructed from ? |
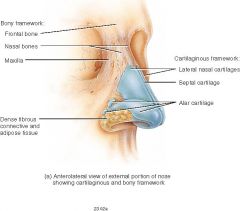
-Septal cartilage -Greater alar cartilage -Nasal bone |
|
|
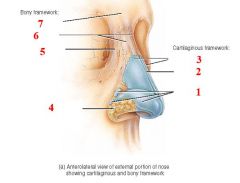
Name the labels 1-7 |
1. alar cartilages 2. septal cartilage 3. lateral nasal cartilages 4.fibrous connective tissue 5.maxilla 6. nasal bones 7. frontal bone |
|
|
|
What does the internal nasal cavity consist of ? |
-nares -vestibule -nasal conchae (internal nares ) -posterior region of the nasal cavity |
|
|
|
what material is the anterior portion of the nasal septum made from ? |
cartilage |
|
|
|
whats the more posterior region of the nasal septum made from |
Vomer bone and ethmoid bone |
|
|
|
what makes up the nasal floor cavity |
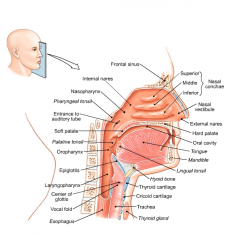
Hard palate |
|
|
|
what are the 3 bony ridges of the lateral wall of the NC |
superior, middle and inferiorchonchae |
|
|
|
what lies between the conchae |
Superior, middle and inferior meatuses |
|
|
|
what are the functions of the meatuses |
-air turbulance -warm and humidify air -trap particles |
|
|
|
within which meatuses do the openings paranasal sinuses lie ? |
superior and middle |
|
|
|
what lies between the superior and middle meatuses |
opening of paranasal sinus |
|
|
|
where is the opening of the nasolacrimal duct ? |
inferior meatus |
|
|
|
what lines the vestibule of the nasal cavity ? |
stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
|
what lines the posterior nasal cavity |
pseudo-stratified ciliated columnar epithelial cells and goblet cells |
|
|
|
which region of the nasal cavity does olfactory epithelium occur ? |
superior region |
|
|
|
the pharynx is shared by which two systems |
digestive and respiratory |
|
|
|
what 3 parts is the pharynx divided into ? |
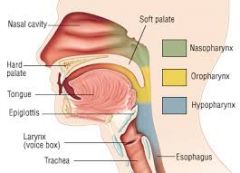
1.The nasopharynx 2.The oropharynx 3.The laryngopharynx |
|
|
|
what structurs lie in the nasopharynx |
-opening to auditory tubes (L+R) -pharyngeal tonsils |
|
|
|
which cacity does the oropharynx connect with |
oral cavity |
|
|
|
from what bone does the laryngopharynx extend from |
hyoid bone |
|
|
|
the oropharynx is considered as the junction point between what 2 structures |
-GI tract and respiratory tract |
|
|
|
what 2 things pass through the oropharynx ? |
food and air |
|
|
|
What part of the pharynx extends from the uvula to epiglottis |
oropharynx |
|
|
|
what lines the oropharynx |
stratified squamous epithelium
( Stratified * mechanical friction (e.g food) - rubbing and physical trauma from external sources* chemical damage - environmental and internal chemicals/compounds degrading epithelial lining) |
|
|
|
What tonsils occupy the oropharynx ? |
lingual and palatine tonsils |
|
|
|
what structure extends from the epiglottis to openings of the oesophagus and larynx |
laryngopharynx |
|
|
|
whats the larynx |
A cartilaginous structure that surrounds the glottis, which is a narrow opening |
|

