![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are hazardous materials? |
Any items or agents that have the potential to cause harm to humans, animals or the environment either by itself or interaction with other agents |
|
|
|
Risks posed by hazardous materials can depend on which factors? |
Type of material
Quantity
Concentration
Context
|
CCTQ |
|
|
What are the 4 different types of hazards? |
Chemical
Physical
Radioactive
Biological |
CPRB |
|
|
What are chemical hazards? |
Substances that cause harm or damage to the body, property or environment |
|
|
|
List 5 examples of chemical hazards |
Toxic
Corrosive
Flammable
Explosive
Oxidising agents |
|
|
|
What are physical hazards? |
Conditions or situations that cause the body physical harm or intense stress |
|
|
|
Name 3 examples of physical hazards |
Very cold
Very hot
Pressurised vessels |
|
|
|
What are radioactive hazards? |
Hazards that harm or damage the human body by directly affecting cells |
|
|
|
What are biological hazards? |
Biological agents that cause harm to the human body
E.g.
Viruses Parasites Bacteria Fungi |
|
|
|
How can hazmats lead to death, acute or chronic injury? |
Inhalation of toxic substances
Ingestion of toxic substances
Chemical or heat/cold burns
Absorption of toxic substances through skin
Injection |
|
|
|
What elements may appear in hazard warning sign? |
Pictogram
UN number
UN classification
Hazard warning diamond
Emergency action code
ADR code |
|
|

What hazard does this pictogram illustrate? |
Substances which will harm the environment |
|
|

What hazard does this pictogram illustrate? |
Substances which may explode |
|
|

What hazard does this pictogram illustrate? |
Oxidising substances |
|
|

What hazard does this pictogram illustrate? |
Very toxic or toxic substances |
|
|
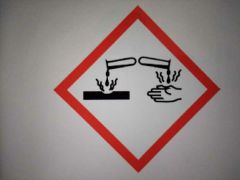
What hazard does this pictogram illustrate? |
Corrosive substances |
|
|
|
What are the different types of classes for hazardous materials? |
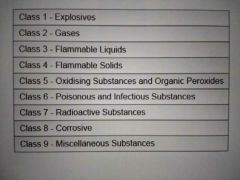
|
|
|
|
What is the EAC? |
Emergency action code:
(number followed by letters) Provides emergency services information on what initial actions should be taken at an incident involving hazmats
|
|
|
|
What is an ADR code? |
A hazard identification number which uses UN classifications to identify hazards associated with different substances |
|
|
|
What 2 sections make up an ADR placard? |
ADR code
UN number |
|
|
|
All wagons on the national rail network are recorded on which database? |
TOPS
Train operations processing system |
|
|
|
What is the highest level FF chemical protection clothing? |
A gas tight suit used with self-contained BA |
|
|
|
What protection can a gas tight suit offer? |
Protection from hazard solids, liquids or gases
Not protected against fire |
|
|
|
How many GTS are found on an appliance? |
2 |
|
|
|
What are the specs of a GTS? |
Orange 10.5kg Made from Polyester fabric Coated with orange Viton Black butyl undercoat Inside coated with black Viton over black butyl undercoat |
|
|
|
What is the recommended max time for an individual to wear a GTS? |
20mins |
|
|
|
What does HMEPO stand for? |
Hazardous Materials and Environmental Protection Officer |
|
|
|
What is the primary role of the HMEPO? |
Provide advice to the IC ASSIST IC |
Provide advice to the IC Assist the IC in determining the EAC, decontamination codes and appropriate PPE Manage the rapid response unit Liaise with the SA Evacuate all available intelligence (to avoid conflicting advice to IC) |
|
|
What should be considered when selecting a safe position for the IC to assess a HAZMAT incident? |
Type of material, hazards and risks
Cordon off a minimum of 25m from the hazard
Crews upwind from the hazard
Crews/appliances uphill from hazard (if in a form that can flow) |
|
|
|
How can the IC gather information at a HAZMAT incident? |
Using defensive tactical mode Observation Safety triggers for emergency personnel ORD Witnesses Package labels, placards, signs Chemdata and hazardous materials database On site specialist advice |
|
|
|
What are the 3 working areas at a HAZMAT incident? |
Hot zone (inner cordon)
Warm zone (inner cordon)
Cold zone (outer cordon) |
Zones |
|
|
What is the hot zone? |
Greatest risk area
Risk of gross contamination (direct contact) |
|
|
|
What is the warm zone? |
Area surrounding hot zone Risk of cross contamination Outside edge is the inner cordon (min 25m) |
|
|
|
What is the cold zone? |
Safe working area for control points and emergency services |
|
|
|
What is decontamination? |
Procedure used to remove hazardous materials from people and equipment |
|
|
|
Who is responsible for carrying out decontamination? |
Crew from the attending FRU |
|
|
|
What is the decontamination zone? |
Area where decontamination takes place
Shout be set up in the Cold zone (at least 25m from the Hot zone), but once established it is considered part of the Warm zone Must established using warning tape and traffic cones
|
|
|
|
What must the IC and HMEPO consider before establishing the decontamination zone? |
Type and scale of contamination
Weather conditions and wind direction
Available drainage
Slope of ground
Access for oncoming vehicles |
|
|
|
What are the 4 decontamination codes? |
Emergency decontamination Code 1 Wet decontamination Code 2 Wet decontamination Code 3 Dry decontamination |
|
|
|
What is the Hughes Shower MD4? |
A rapidly inflatable decontamination shelter fitted with showers for firefighter use |
|
|
|
What is Asbestos? |
A mineral found in 2/3 of the earth's crust
Used extensively as a building material in the 1950s due to its excellent heat insulation properties |
|
|
|
Why is Asbestos a hazard? |
There is a risk of inhalation airborne fibres Can lead to terminal lung disease |
|
|
|
What are the typical uses for asbestos? |
Ceiling/floor tiles Fireboard Insulation (pipes, boilers etc.) Spray insulation Gaskets Brake linings Cement asbestos sheeting |
|
|
|
What are the operational procedures when dealing with asbestos? |
Observe any warning signs Use the ORD Priority message stating 'asbestos reported' Minimum personnel committed GTS for non-fire situations Minimum cutting to avoid airborne fibres Risk assessment Keep asbestos damp to prevent airborne fibres No eating/drinking/smoking at incident until after decontamination Contaminated fire gear to be double bagged and labelled for specialist cleaning |
|
|
|
What is a biological risk? |
Any circumstance that may present a risk of infection and illness to firefighters |
|
|
|
What is a biohazard? |
A biological risk category as defined in specific legislation |
|
|
|
Name 6 premises that may contain biohazards: |
Pathology laboratories Veterinary and pharmaceutical research establishments Medical schools/universities Commercial premises Food research establishments Hospitals |
|
|
|
Name 6 examples of clinical waste: |
Human/animal tissue Blood/bodily fluids Excretions Drugs or pharmaceutical products Swabs/dressings Syringes/needles/other sharp instruments |
|
|
|
What is the definition of a CBRN event? |
A deliberate attack using chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear agents with the intent of killing people, disrupting society, business or economy |
|
|
|
Name some examples of CBRN events: |
Potential for mass casualties Potential for large loss of life Potential for long term health and environmental effects Extremely hazardous environment that may persist Mass decontamination Use of a combination of CBRN materials |
|
|
|
What are the 3 phases to a CBRN event? |
Response
Recovery
Restoration |
|
|
|
How is radiation measured? |
Millisieverts (mSv)
Microsieverts (uSv) (Micro is 1000th of a Milli) |
|
|
|
What are the 2 ways a radiation dose is received? |
Absorbed dose
Dose rate |
|
|
|
What are the different types of radiation? |
Alpha - large particles that do not travel far or penetrate barriers Beta - smaller particles which travel further in air Gamma - electromagnetic waves which can travel immense distances X-ray - also electromagnetic waves at lower dose (dentist/Dr surgeries) |
|
|
|
What is the difference between sealed and unsealed radioactive materials? |
Sealed - no contamination risk as it is contained Unsealed - risk of contamination (solids, powders, liquids, gases) |
|
|
|
What is a EPD? |
Electronic personal dosimeter Provides staff with a warning of any radiation present and will also measure the absorbed dose |
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of alarm on the EPD? |
Initial dose rate alarm (100micro) Fast tone - radioactivity present
Dose constraint alarm (5milli) Slow tone - withdraw immediately
Exceptional dose alarm (100milli) Continuous tone - maximum dose, withdraw |
|

