![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The major site of resistance in renal blood flow is what?
|
afferent arteriole
|
|
|
How are resistance and pressure related?
|
Resistance is correlate with a drop in pressure
Low resistance in large vessels because not much change in pressure from one end to the other |
|
|
Vessels in the kidney are arranged in __________ and thus cause progressive drops in blood pressure as blood flows from beginning to end
|
series
|
|
|
What substances are excluded from glomerular filtration?
|
large proteins and blood cells
|
|
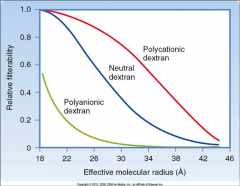
What does this graph tell us about glomerular filtration?
|
-both size and charge determine filtration
-positive/cationic substances filter more freely than negative/anionic substances |
|
|
What are the three components of the glomerular filtration membrane? Which portions have negative charge?
|
-fenestrated endothelium (negative charge from GAGs)
-GBM (negative charge from GAGs) -epithelial slit pores (between podocyte foot processes) |
|
|
The podocyte slit pore is made up of what proteins? Mutations in these proteins cause what?
|
-nephrin
-Neph 1 -Neph 2, etc -mutations --> proteinuria |
|
|
How are most proteins reabsorbed?
|
As amino acid components in the proximal tubule
|
|
|
What constitutes heavy proteinuria? What is its consequence
|
>3.5 g/day
-causes edema |
|
|
What two things determine GFR?
|
-number of glomeruli
-GFR of each glomerulus |
|
|
What drives filtration? What opposes it?
|
-drives - Pressure difference between glomerular capillary and Bowman's space
-opposes - oncotic pressures in Glomerular capillary and Bowman's space |
|
|
Single nephron GFR (single nephron glomerular filtration rate) also takes into account what two things?
|
-water permeability
-surface area |
|
|
GFR = RPF x ______
|
FF
|
|
|
The most important physiological determinant of GFR is what?
|
RPF
|
|
|
As RPF increases, _____ also increases. Why?
|
-GFR
-filtration pressure increases because of a decrease in colloid osmotic pressure in the glomerulus (same amount of protein but in a larger volume) -FF unchanged unless big increase in RPF |
|
|
What effect does increasing delta P have on FF? GFR?
|
-increases FF and increases GFR
-i.e. if you increase the blood pressure in the glomerular capillary you will increase FF |
|
|
What effect will a decrease in plasma protein have on GFR?
|
-increase it
(doesn't really occur in practice) |
|
|
Relaxation of the afferent, efferent, or both arterioles will have what effect on RPF?
|
All increase flow
|
|
|
Increasing resistance on the afferent arteriole will have what effect on pressure in the glomerulus?
|
decrease it
(flow will also be decreased) |
|
|
Increasing resistance in the efferent arteriole will have what effect on pressure in the glomerulus?
|
Increase it
(flow will decrease though) |
|
|
Increasing resistance of both the afferent and efferent arterioles will have what effect on pressure in the glomerulus?
|
-no effect - they counteract one another
(flow will fall, however) |

