![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the MCC of erythema palmare? |
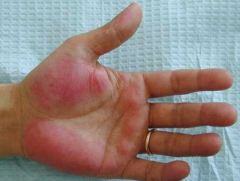
1. Elevated estrogen 2. Cirrhosis 3. Metastatic liver CA 4. Pregnancy |
|
|
What are the ssx of erythema toxicum neonatorum? |
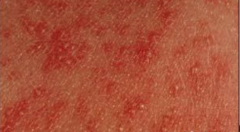
1. Occurs in newborns on 2-3 day 2. Multiple papules that rapidly evolve into pustules 3. Can become confluent |
|
|
What will a bx yield in erythema toxicum neonatorum? |
1. Folliculitis with eosinophils and neutrophils |
|
|
What are the ssx of erythema multiforme minor? |
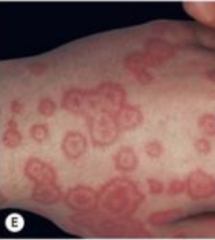
1. Associated with orolabial HSV 2. Major=SJS 3. Central dusky purpuric area |
|
|
What will EM show in erythema multiforme minor? |
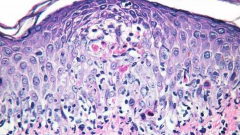
1. Vacuolar interface with tagging of lymphocytes along DEJ |
|
|
What are the MC sites for erythema multiforme minor? |
1. Dorsal feet and limbs 2. Elbows 3. Knees 4. Palms and soles |
|
|
What is the tx for erythema multiforme minor? |
1. Supportive 2. HSV== antivirals |
|
|
What must you r/o in case of oral erythema multiforme? |
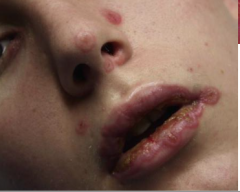
1. Candida--- can guide tx (use of antifungals indicated) |
|
|
What are the ssx of erythema annulare centrifugum? |
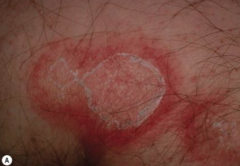
1. Polycyclic 2. Trailing scale at inner border 3. Eccentric growth |
|
|
What will EM show in erythema annulare centrifugum? |
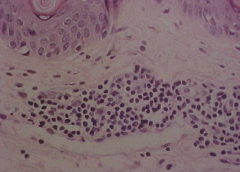
1. Lymphocytes tightly associated with vessels |
|
|
How do you tx erythema annulare centrifugum? |
1. Topical steroids 2. R/o tinea |
|
|
What are the ssx of erythema gyrated repens? |
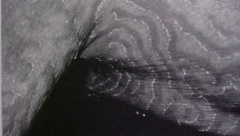
1. Undulating bands of slightly elevated wavy erythema over the entire body 2. Wood grain with trailing scale 3. Severe pruritus |
|
|
What is the MC underlying malignancy associated with erythema gyratum repens? |
1. Lung CA |
|
|
With what is necrolytic migratory erythema associated? |
1. AA precursor and uptake decarboxylation tumor of the pancreas |
|
|
What are the ssx of necrolytic migratory erythema? |
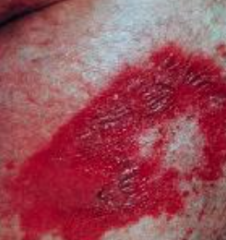
1. Papulovesicular lesions coalesce 2. Form pustules, then erode 3. Hyperglycemia, weight loss, diarrhea (glucagonoma ssx) |
|
|
How do you tx necrolytic migratory erythema? |
1. Removal of tumor |
|
|
What other disorder has identical pathology to NME? |
1. Zinc deficiency |
|
|
What are the ssx of Wells syndrome (recurrent granulomatous dermatitis with eosinophilia)? |
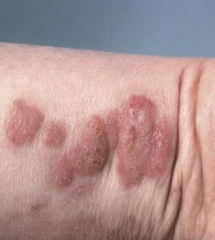
1. Hybrid between cellulitis and urticaria 2. Reaction to many antigens: viruses, parasites, drugs, etc. |
|
|
How do you tx Wells syndrome? |
1. TCN 2. UVB 3. PUVA 4. Dapsone |
|
|
What is the microscopic appearance of Wells syndrome? |
1. Flame figures: dermal eosinophils and histiocytes surrounding central masses of bright pink collagen |
|
|
What are the ssx of erythema nodosum? |
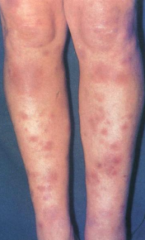
1. Crops of bilateral deep tender nodules 2. Overlying skin is shiny and red 3. Acute onset arthralgia, malaise, and edema |
|
|
What are the ssx of Lofgren's syndrome? |
1. Erythema nodosum with fever, arthralgia, hilar LAD, and fatigue |
|
|
What will histology show in erythema nodosum? |
1. Septal panniculitis |
|
|
What are the ssx of Sweet syndrome? |
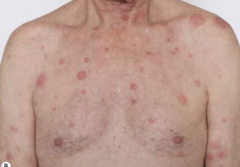
1. Sudden onset fever 2. Leukocytosis 3. Tender, erythematous, well-demarcated papule and plaques 4. Pathergy |
|
|
How do you tx Sweet syndrome? |
1. Systemic corticosteroids |
|
|
What are the ssx of Marshall syndrome? |
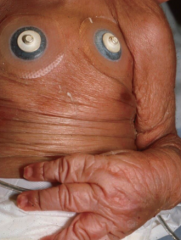
1. Simliar to Sweet, but followed by cutis lax changes 2. Primarily in children 3. Small red papule expand to urticarial tagetoid plaques |
|
|
What are the ssx of pyoderma gangrenosum? |
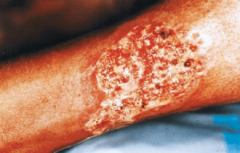
1. Recurrent ulcerative disease 2. Pathergy 3. Atrophic scarring 4. Rolled edges |
|
|
What is the MC underlying conditions associated with pyoderma gangrenosum? |
1. UC 2. Chron's disease |
|
|
How do you tx pyoderma gangrenosum? |
1. Excise colon segment 2. Steroids 3. Hyperbaric O2 4. Immunosuppressants |
|
|
How long does urticaria last? |
1. <24 hours=acute 2. >6 weeks=chronic |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis behind chronic urticaria? |
1. Functional histamine-releasing autoantibodies that bind to high-affinity IgE receptor 2. Fc epsilon RI 3. Eosinophilia |
|
|
When should you bx a urticarial lesion? |
1. If it has lasted >24 hours |
|
|
How do you tx urticaria? |
1. Oral antihistamines 2. Cool bathing 3. Food elimination |
|
|
How do you tx anaphylaxis? |
1. 0.3-0.5 mL dose of 1:1000 dilution of epi 2. Diphenhydramine |
|
|
What are the ssx of hereditary angioedema? |
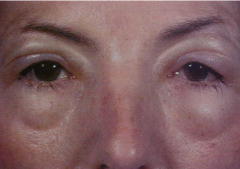
1. AD 2. Minor trauma causes swelling of affected area 3. No pruritus or urticaria |
|
|
How do you tx HAE? |
1. FFP 2. Stanazol 3. Tranexamic acid |
|
|
What are the different types of HAE? |
I- low serum of normal C1EINH II- normal levels of dysfunctional C1 EINH |
|
|
What is the best screening test for HAE? |
1. C4 |
|
|
What are the ssx of Schnitzler's syndrome? |
1. Chronic non-pruritic urticaria 2. Fever 3. Disabling bone pain 4. Macroglubulinemia |
|
|
How do you tx Schnitzler's syndrome? |
1. Oral steroids |
|
|
What are the MCC of dermatographism? How do you tx? |
1. PCN, pepcid, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, infectious disease, DM, menopause 2. Tx= oral antihistamines |
|
|
What are the ssx of cholinergic urticaria? |
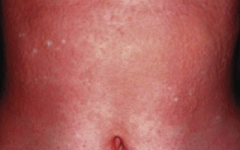
1. Tiny punctate extremely pruritic wheals 2. Surrounded by urticaria 3. Triggered by exercise and heat |
|
|
How do you tx cholinergic urticaria? |
1. Cold shower 2. Oral antihistamines |
|
|
What are the ssx of adrenergic urticaria? How do you tx? |
1. Small papule with pale halo 2. 10-15 minutes after emotional upset, coffee, or chocolate 3. Propranolol |
|
|
What are the ssx of cold urticaria and AE? How do you tx? |
1. Face/hands 2. Occurs with rewarming 3. Tx with periactin |
|
|
What are the ssx of heat urticaria? How do you tx? |
1. Heat >109.4 2. Burns, stings, red, swollen, indurated 3. Tx= heat desensitization |
|
|
How do you tx pressure urticaria? |
1. Oral steroids |
|
|
How do you tx exercise-induced urticaria? |
1. OAH 2. Avoid celery and gliadin |
|
|
How do you tx vibratory AE? |
1. OAH |
|
|
How do you tx aquagenic urticaria? |
1. Petrolatum 2. OAH 3. PUVA |

