![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of reaction is the addition of hydrogen halides |
Electrophilic addition |
|
|
Electrophile |
Positively/ partially positively charged reagent which attacks an electron rich area of a molecule |
|
|
Electrophilic addition of HBr diagram |
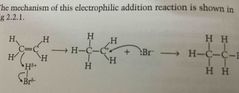
(E.g) HBr -HBr is a polar molecule with a partial +ve charge on the H atom and a partial -ve charge on the br atom - the HBr acts as an electrophile attacking the electron rich area of the molecule (double bond) - the H atom bonds with an electron from the double bond and a carbocation is formed - a Br- ion is formed which attacks the +vely charged carbocation and a bromoalkane is formed |
|
|
Reaction with bromine steps |
- the br-br molecule is polarized by the high electron density of the c=c bond. - the partially positive br molecule attacks the electron rich double bond -And electron pair from the double bond forms a bond with the +vely charged br and a carbocation is formed -a br- ion is formed which attacks the carbocation -the br molecules add to the two adjacent C atoms where the double bonds were |
|
|
Addition of steam conditions |
-concentrated phosphoric acid - temp 330 degrees C -pressure 60 atm |
|
|
Hydrogenation conditions |
- finely divided nickel catalyst - 150 degrees C |
|
|
Hydrogenation is used to |
Turn edible oils into margarine and spreads |
|
|
Reactions with acidified potassium manganate (cold) is used to test for |
C=C |
|
|
Alkenes rxn with acidified KMnO4 cold |
- involves addition and oxidation -product is a diol -solution turns from purple to colourless |
|
|
Hot acidified KMnO4 |
- double bond broken - diol formed -diol oxidized to carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) -if aldehydes are formed they get further oxidized to carboxylic acids |
|
|
Double bond in rxn with hot KMnO4 is broken via |
Oxidative cleavage |
|
|
Rule for reacting HBr and other electrophiles with alkenes |
The more electronegative atom in the bond adds to the C atom in the alkene which is connected to the least number of H atoms. This is in order to form stable forms of the molecule which is influenced by the stability of the intermediate (carbonation) formed. (Tertiary carbocation > secondary > primary) . In these reactions, secondary carbocations are formed more than primary ones. |
|
|
Reaction with conc H2SO4 |
- sulphuric acid is used as a catalyst in this rxn -the final product is an alcohol - the OSO3H group adds to the alkene via electrophilic addition (H2SO4 is an electrophile) - water is then added to the product and it is heated - the OH group in H2O kicks out the OSO3H group and adds to the molecule - the extra H from water adds to the OSO3H group to reform H2SO4 |

