![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Give the reagents and conditions needed to produce an alkane from an alkene in the laboratory. |
React with hydrogen using a platinum catalyst at room temperature and pressure (RTP)
|
|
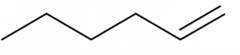
Name this alkene using systematic nomenclature rules |
hex-1-ene
|
|
|
Describe the effect on the C=C group in an alkene when the alkene is boiled under reflux with concentrated sulfuric acid and then with water.
|
The double C=C bond turns to a single C-C bond. An H atom bonds to one of the C atoms that were involved in the double bond and an -O-H group bonds to the other carbon atom. (an alcohol is produced) |
|
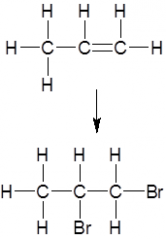
Give the reagents and conditions needed for this reaction
|
Mix with bromine or aqueous bromine solution at room temperature and pressure (RTP)
|
|
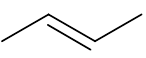
Give the structure of the product(s) when this alkene reacts with steam in the presence of phosphoric acid at high temperatures and pressures. |
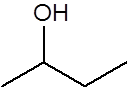
(or the same molecule flipped or rotated to any orientation)
|
|
|
Describe the effect on the C=C group in an alkene when the alkene is mixed with bromine at room temperature and pressure (RTP).
|
The double C=C bond turns to a single C-C bond. A Br atom bonds to each of the C atoms that were involved in the double bond. (a dibromoalkane is produced) |
|
|
Draw the full structure of methylpropene
|
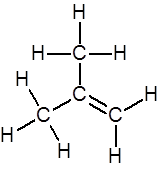
(bond angles are not important) |
|
|
Describe the colour change seen when bromine water is added to any alkene
|
The bromine water changes from orange to colourless. (Not 'clear'!) |
|
|
Give the reagents and conditions needed to produce an alcohol from an alkene in the laboratory. |
Boil the alkene 'under reflux' with concentrated sulfuric acid and then with water |
|
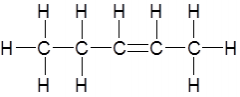
Name this alkene using systematic nomenclature rules |
pent-2-ene
|
|
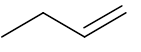
Give the structure of the product(s) when this alkene is reacted with concentrated hydrogen bromide (HBr) at room temperature and pressure (RTP) |
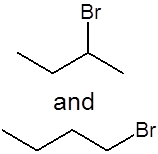
(or the same molecules flipped or rotated)
|
|
|
Ethene and bromine are mixed at room temperature. Give the colour change that would be observed |
The red-brown colour of the bromine disappears leaving a colourless product. (Not 'orange' initially - that only applies to bromine in solution / bromine water) |
|
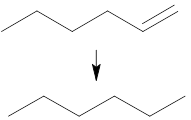
Give the reagents and conditions needed to carry out this reaction in industry
|
React with hydrogen using a finely divided nickel catalyst at high temperature and pressure.
|
|
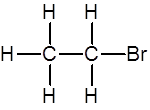
Give the reagents and conditions needed to produce this molecule from ethene
|
Mix the ethene with concentrated HBr at room temperature and pressure (RTP)
|
|
|
Describe the effect on the C=C group in an alkene when the alkene is mixed with steam in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst at high temperature and pressure.
|
The double C=C bond turns to a single C-C bond. An H atom bonds to one of the C atoms and an -O-H group bonds to the other carbon atom. (an alcohol is produced) |
|
|
Draw the skeletal structure of 4,6-dimethylhept-2-ene |
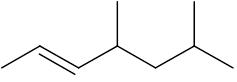
(Or this molecule flipped, rotated or twisted) |
|
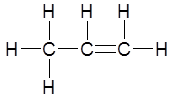
Draw the structure of the product(s) when this molecule reacts with hydrogen in the presence of a platinum catalyst at RTP
|
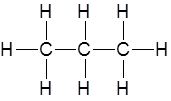
|
|
|
Give the reagents and conditions used to produce an alcohol from an alkene in industry
|
React the alkene with steam in the presence of a phosphoric acid catalyst at high temperature and pressure.
|
|
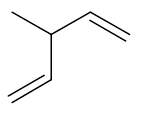
Draw the structure of the product formed when this molecule reacts with excess bromine at RTP
|
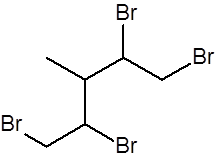
|
|
|
Give the reagents and conditions used to turn an alkene into an alkane in industry
|
React with hydrogen using a finely divided nickel catalyst at high temperature and pressure.
|
|
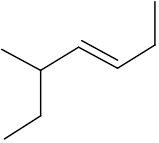
Name this alkene using systematic nomenclature
|
5-methylhept-3-ene
|
|
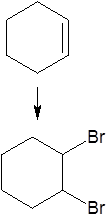
Give the reagents and conditions needed to carry out this reaction
|
Mix the alkene with bromine or (aqueous bromine solution) at room temperature and pressure (RTP)
|
|

Suggest what would be observed if bromine water was added to this substance
|
The orange colour of the bromine water would remain (The molecule is an alkane and alkanes do not react with bromine)
|
|
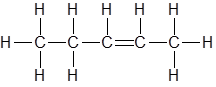
Draw the structure of the product(s) when this alkene is mixed with concentrated HCl at RTP
|
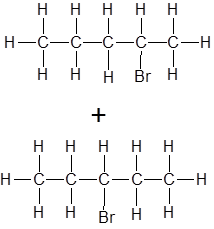
|
|
|
Describe the effect on the C=C group in an alkene when the alkene is mixed with hydrogen in the presence of a finely divided nickel catalyst at high temperature and pressure.
|
The double C=C bond turns to a single C-C bond. An H atom bonds to each of the C atoms that were involved in the double bond. (an alkane is produced) |
|
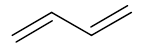
Suggest the structure of the product when one mole of the following alkene is mixed with one mole of bromine at RTP
|
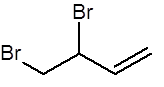
(either C=C can react but not both, due to the limited quantity of bromine)
|
|
|
Draw the structure of the product(s) when this alkene is mixed with generous quantities of hydrogen and finely divided nickel at high temperature and pressure
|
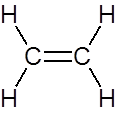
|
|
|
Describe the effect on the C=C group in an alkene when the alkene is mixed with concentrated HBr at room temperature and pressure (RTP).
|
The double C=C bond turns to a single C-C bond. An H atom bonds to one of the C atoms and a Br atom bonds to the other C atom (a bromoalkane is produced) |
|
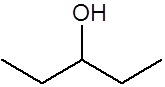
Suggest the structure of the alkene, and the reagents and conditions, that could be used to produce this substance in the laboratory
|
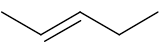
Boil 'under reflux' with concentrated sulfuric acid and then with water
|
|
|
Draw the skeletal structure of penta-1,3-diene
|
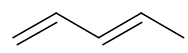
(or the same molecule flipped or rotated)
|
|
|
Describe the effect on the C=C group in an alkene when the alkene is mixed with hydrogen in the presence of a platinum catalyst at room temperature and pressure (RTP).
|
The double C=C bond turns to a single C-C bond. An H atom bonds to each of the C atoms that were involved in the double bond. (an alkane is produced) |

