![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
General Formula |
CnH2n |
|
|
|
Saturated or Unsaturated hydrocarbon |
Unsaturated hydrocarbon |
|
|
|
What hybridisation? |
sp2 hybridised Carbon-carbon double bond. |
|
|
|
Prefix(es)- stem - suffix |
Parent chain is longest continuous chain that contains carbon-carbon double bond. Suffix ‘ene’ Name of alkyl substituents arranged in alphabetical order and position of substituent is numbered. |
|
|
|
What type of isomerism do alkenes exhibit? |
Constitutional Isomerism- chain isomerism & positional isomerism Cis-Trans isomerism •restricted rotation about C-C double bond ( presence of pi bonds). •each C of double bond bonded to two diff groups |
|
|
|
Do alkenes have high melting point? |
Alkenes have slightly lower melting point boiling point than corresponding alkanes. |
|
|
|
Is boiling point of branched alkene lower or higher than its straight chain alkene? |
Branching lowers boiling point. Bpmp increases with increasing total number of electrons. |
|
|
|
1. What is the trend of density of alkenes? 2. Are alkenes more or less dense than water? |
1. Density increases with increasing Mr. 2. Liquid alkenes are less dense than water. |
|
|
|
Solubility of alkenes? |
Alkenes soluble in non-polar solvents & insoluble in polar solvents. |
|
|
|
What is the reactivity of alkenes? |
Alkenes are much more reactive than alkanes. Double bond is composed of a strong sigma bond and a weaker pi bond. Pi electrons are more loosely held than sigma electrons, thus more susceptible to reactions ( loosely held pi electrons serve as source of electrons ) Alkenes are susceptible to reaction with electrophilic reagents or electrophiles. |
more or less than alkanes? |
|
|
What are electrophiles? |
Electron pair acceptors. Electron deficient which contains a full or partial positive charge to accept an electron pair. |
|
|
|
Reactions alkenes undergoes? |
Electrophilic addition, Hydration, Reduction, Oxidation , Dehydration. |
|
|
|
What is addition reaction? |
Two molecules react together to form a single large product moelcule. |
|
|
|
Addition of bromine reagent and condition? Observation? |
1.Br2(l) (reddish brown), room temp Decolorisation of reddish brown bromine to a colourless solution. 2. Br2 dissolved in CCL4 (orange-red), room temp Decolorisation of orange-red bromine to a colourless solution 3. Br2 (aq) (orange) , room temp. Decolorisation of orange bromine to a colourless solution. |
|
|
|
Steps of electrophilic addition using Br2 (l) and Br2 dissolved in CCl4. |
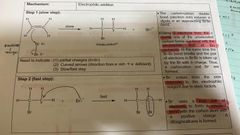
|
|
|
|
Electrophilic addition using Br2 (aq), room temp |

|
Two products are formed due to presence of H2O which competes with Br- |
|
|
Addition of HBR to symmetrical alkene. Reagent and condition? |
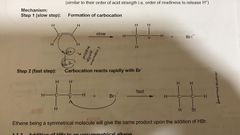
HBr (g) or HBr dissolved in CCL4, room temp. |
|
|
|
Addition of HBr to an unsymmetrical alkene |

|
|
|
|
When is Markovnikov’s rule used? What is the rule? |
Used in addition of HX to an unsymmetrical alkene. Hydrogen atom becomes attached to unsaturated C atom with higher number of H atoms |
|
|
|
Electrophilic addition involves formation of ____ carbocation |
MORE STABLE |
|
|
|
What does relative stability of carbocation depend on? When does stability of a charged system increase? |
How well it disperses the positive charge on the central carbon atom. Stability increases with an increase in number of electron donating groups which disperses positive charge. |
|
|
|
What does relative stability of carbocation depend on? When does stability of a charged system increase? |
How well it disperses the positive charge on the central carbon atom. Stability increases with an increase in number of electron donating groups which disperses positive charge. |
|
|
|
What are electron withdrawing groups? |
Eg. Halogens Intensify the positive charge on central carbon atom, destabilising carbocation. |
|
|
|
What is racemic mixture? |
Equal quantities of each enantiomer is formed ( 2 mirror images which are non-superimposable ) optically inactive ... cancel out rotating capacity. |
|
|
|
What is racemic mixture? |
Equal quantities of each enantiomer is formed ( 2 mirror images which are non-superimposable ) optically inactive ... cancel out rotating capacity. |
|
|
|
How is a racemic mixture formed from electrophilic addition reactions? |
In stage 2 of mechanism, there is a planar arrangement. Carbocation attached by Br- either from top of plane or bottom of plane with equal probability. |
|
|
|
Direct Hydration reagent and conditon? |
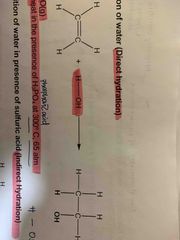
H2O (g), heat in presence of H3PO4 at 300 degree celsius, 65 atm |
|
|
|
Indirect hydration reagent and condition? |
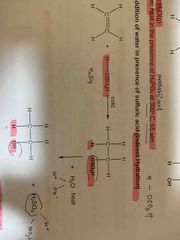
Use cold, concentrated H2SO4, followed by H2O (l), heat |
|
|
|
What are the reagents and conditions for reduction of alkene? |
Reagent: H2 (g) Condition: Pt or Pd catalyst at rtp. Ni catalyst in presence of heat and slightly elevated pressure. |
|
|
|
What are the two types of oxidation? |
Mild oxidation & Strong oxidation |
|
|
|
Reagent and Condition and Observation for mild oxidation ? |
Cold, alkaline KMnO4 —> decolourisation of purple KMnO4 & formation of brown ppt Cold, dilute acidic KMnO4 —> decolourisation of purple KMnO4 to a colourless solution |
|
|
|
What does mild oxidation of alkene form? |

Diol |
|
|
|
Reagent and Condition and Observation for strong oxidation? |
Alkaline conditions —> decolourisation of purple KMnO4 & formation of brown ppt of MnO2 Acidic conditions —> decolourisation of purple KMnO4 to a colourless solution. |
|
|
|
What does strong oxidation form? What are the products formed dependent on? |

1. Terminal Alkene : CO2 + H2O 2. C attached to 1 R group and H: Carboxylic acid 3. C attached to 2 R groups: Ketone |
The products from the oxidation depen on degree of substitution of C-C double bond. |
|
|
What cannot be used for oxidation of alkenes? |
Acidified K2Cr2O7 |
|
|
|
Does combustion of alkene result in a more or less smoky flame than alkanes? Why? |
Combustion occurs with a more smoky flame than alkanes because alkenes have a higher % of carbon than corresponding alkanes. Thus alkenes not used as fuels. |
|
|
|
How are alkenes prepared in the lab? |
1. Elimination of water from alcohols (dehydration) 2. Elimination of HX from a halogenoalkane |
|
|
|
What is elimination reaction? |
Removal of atoms or groups of atoms from two adjacent carbon atoms to form a multiple bond. |
|
|
|
Reagent and Condition and Equation for elimination of water from alcohols? |
Reagent and Condition: Excess concentrated H2SO4, 180 degrees celcius Al2O3, 400 degrees celcius |
|
|
|
Trend for ease of elimination ? |
Tertiary alcohols (3 R groups) > Secondary alcohols (2 R groups) > Primary alcohols |
no. of R groups |
|
|
Which is the major product for elimination of water from alcohols? |
Major product is the alkene with the greatest no. of R groups attached to doubly bonded carbon. |
|
|
|
Reagent and Condition for elimination of HX from a halogenoalkane? |

Alcoholic KOH, heat |
|

