![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What should be considered when a radiograph is interpreted?
|
-history
-clinical signs -physical exam findings -lab data |
|
|
Differential List is provided by:
|
Roentgen signs + History/PE/Lab
|
|
|
Is a specific diagnosis very possible with the use of radiography?
|
-no
-the radiographic signs are rarely pathognomonic |
|
|
Why is radiographic labeling important?
What labels should be included on a radiograph? |
-a radiograph is a medical legal document
Labels: -patient/owners name/owner case # -date -clinic name/doctor -R/L markers |
|
|
Billars Pillars to Successful Radiology
|
-normal anatomy
-systemic evaluation -description, description, description |
|
|
Reasons for different opacities
|
-x-rays have a potential to penetrate tissues
-x-rays pass through tissue and interact and ultimately expose film -x-rays are in part attenuated by tissues they pass through -absorption of x-rays as a function of: energy of x-ray, physical density of tissue, atomic number -thickness of tissue -differential absorption causing shades of grey between the black and whites |
|
|
How does the atomic number affect opacity?
|
-higher atomic number --> greater absorption --> fewer x-rays that reach the film --> more radiopaque
|
|
|
Effective atomic numbers of the different opacities
|
-gas = 1-2
-fat = 6-7 -soft tissue/fluid = 7-8 -bone = 14 -metal = 82 |
|
|
What is a benefit of the gas opacity?
|
-allows for contrast between structures
|
|
|
Fat opacity locations
|
-omentum
-mesentery -falciform ligament -retroperitoneal space |
|
|
What are some normal variations in opacity within the same bone and between bones?
|
-compact vs. spongy bone
-cortical vs. medullary bone |
|
|
Why is metal so radiopaque?
|
-absorbs all diagnostic x-rays
|
|
|
What is necessary in order to interpret radiographs?
|
-need at least 2 orthoganol views
-need a dark quiet room with at least 2 viewboxes -take your time -shield high intenstiy |
|
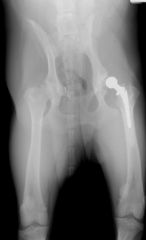
|
Luxated total hip replacement
|
|
|
How should one go about interpreting a radiography?
|
-use systemic evaluation
-ex) extrathoracic structures then intrathoracic |
|
|
A "high quality" radiograph has what characteristics?
|
-good exposure and processing
-good positioning -centering -no motion -collimation -free of artifacts |
|
|
What are the 3 phases of radiograph interpretation?
|
-recognition phase
-descriptive phase -analysis phase |
|
|
Recognition phase of radiographic interpretation
|
-compare all parts of the radiographic image to normal
-need to figure out if abnormality is a normal variant, artifacts or improper patient positioning |
|
|
Descriptive phase of radiographic interpratation
|
-describe how the lesion varies from the normal
-use LMNOSS&Function also describe the extent of the lesion ad the distribution |
|
|
Analysis Phase of Radiographic Interpretation
|
-take all of the information regarding radiographic changes from normal, history, and abnormalities from the PE and develop differential diagnoses
|
|
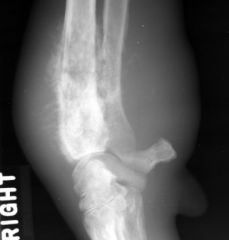
Descriptive Phase
|
-distal radius and ulna
-soft tissue swelling -aggressive bony lesion (lysis and irregular periosteum) |
|
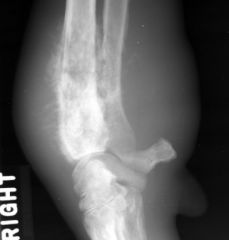
Analysis Phase
|
DDx:
-primary bone neoplasia -metastatic neoplasia -infection |
|
|
What does the ability to describe function often require?
|
-the use of contrast or multiple films over time
|
|
|
Summation
|
-a shadow of increased opacity due to areas of overlap
|
|
|
Border effacement
|
-loss of border between objects of similar opacity when in anatomic contact
|
|
|
Mock Line
|
-an optical illusion as a result of retinal physiology
-lateral inhibition to create edge enhancement is responsible for the light/dark lines at interfaces of dissimilar densities |
|
|
Magnification
|
-occurs when increasing object film distace
-exaggerate on short film at distance |
|
|
Distortion
|
-unequal magnification of an object due to its axis not being parallel to the film/cassette
|

