![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does Invasive mean?
|
Into the brain
|
|
|
What does noninvasive mean?
|
Not into the brain
|
|
|
What is a brain lesion?
|
Abnormal brain tissue
|
|
|
What is brain stimulation?
|
High-frequency electrical stimulation of the brain. There are two forms: Electrical & Chemical.
|
|
|
What odes ICS stand for?
|
Intracranial Stomulation (Electrical)
|
|
|
What does EEG stand for?
|
Electroencephalograph
|
|
|
What is an electroencephalograph (EEG)?
|
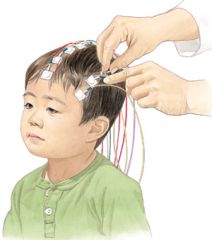
A brain-imaging technique that records "waves" of electrical activity in the brain using metal electrodes placed on a person's scalp.
|
|
|
What does CAT stand for?
|
Computerized Axial Tomography
|
|
|
What is a computerized axial tomography (CAT)?
|
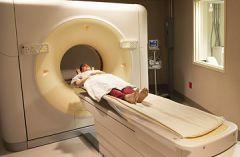
A brain-imaging technique that combines thousands of X-ray brain photographs to construct a cross-sectional picture of the brain.
|
|
|
What does MRI stand for?
|
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
|
|
|
What is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)?
|
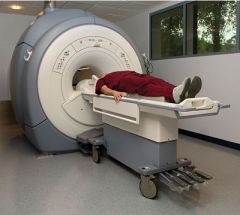
A brain-imaging technique that produces 3D images of the brain's soft tissues by detecting magnetic activity from nuclear particles.
|
|
|
What does PET stand for?
|
Positron Emission Tomography
|
|
|
What is a positron emission tomography (PET)?
|
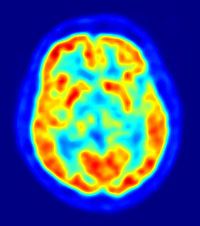
A brain-imaging technique that measures over several MINUTES the average amount of neural activity in different brain regions by showing each region's consumption of glucose.
|
|
|
What is an fMRI?
|
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
|
|
|
What is a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)?
|
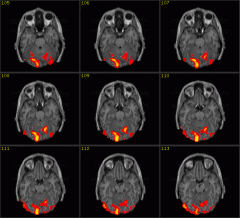
A brain-imaging technique that measures over a few SECONDS the average amount of neural activity in the brain regions by showing fluctuations in blood-oxygen levels.
|
|
|
What is frequency?
|
The number of cycles in one second. (Hz)
|
|
|
What is amplitude?
|
The size of the waves.
|
|
|
What are BETA waves?
|
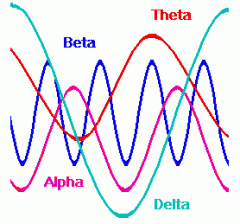
The normal brainwave of a person who is awake and alert. (14 - 35+ Hz)
|
|
|
What are ALPHA waves?
|
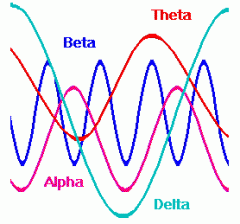
The normal brainwave of person who is awake but in a relaxed state. (8 - 14 Hz)
|
|
|
What are THETA waves?
|
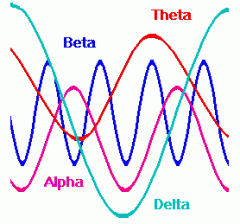
The normal brainwave of a person who is awake but relaxed AND drowsy. (Low waves & amplitude)
(4 - 8 Hz) |
|
|
What are DELTA waves?
|
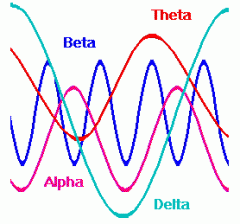
The normal brainwave of a person who is in DEEP dreamless sleep. (0 - 4 Hz)
|
|
|
What is magnetoencephalography?
|
Magnetic fields from the brain.
|
|
|
What are the 3 major regions of the brain?
|
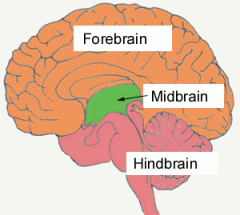
Hindbrain, Midbrain, and Forebrain
|
|
|
What is the Hindbrain?
|
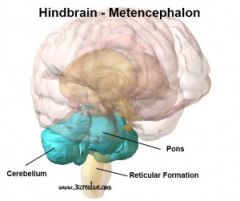
Region of the brain above the spinal cord that contains the medulla, pons, and cerebellum.
|
|
|
What is a medulla?
|
A part of the Hindbrain that controls breathing, heart rate, swallowing and digestion, as well as allowing us to maintain an upright posture.
|
|
|
What is a pon?
|
A part of the Hindbrain that is concerned with sleep and arousal.
|
|
|
What is a cerebellum?
|
A part of the Hindbrain that regulates and coordinates basic motor activities and plays a role in learning.
|
|
|
What is the Midbrain?
|
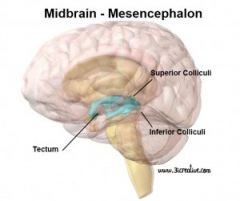
Region of the brain above the Hindbrain that contains the reticular formation.
|
|
|
What is the Midbrain reticular formation?
|
A part of the Midbrain involved in the regulation and maintenance of consciousness. (E.g. eye movements, reflexes and the sleep-wake center)
|
|
|
What is the Forebrain?
|
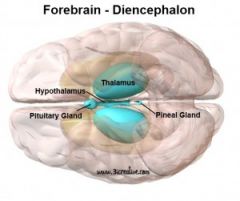
Region of the brain above the Midbrain that contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, and limbic system.
|
|
|
What is the thalamus?
|
A part of the Forebrain that is the brain's sensory relay station, sending messges from the senses to the higher parts of the brain.
|
|
|
What is the hypothalamus?
|
A part of the Forebrain involvedi n regulating basic biological processes, such as eating, drinking, sexual activity, emotion and stable body temperature. (Homeostasis)
|
|
|
What is the limbic system?
|
A part of the Forebrain consisting of structures that influence fear, aggression, the acquisition of new information in memory.
|
|
|
What is does the amydala do?
|
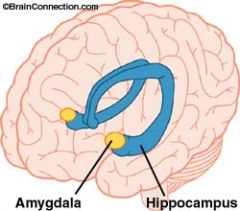
Influences fear and aggression.
|
|
|
What does the hippocampus do?
|
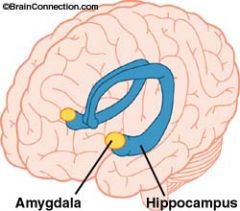
Is the acquisition of new information in memory.
|
|
|
What is the Cerebral Cortex?
|
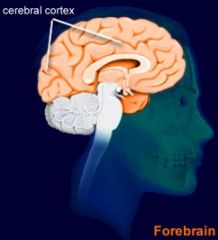
The thin outer surface of the cerebrum. Contains about 80% of the brain's total mass. Also responsible for higher-order mental processes.
|
|
|
What are convolutions (gyrus)?
|
Numerous folds or ridges on the surface of the brain.
|
|
|
What are the cerebral hemispheres?
|
Two main parts of the cerebral cortex.
|
|
|
What is the corpus callosum?
|
A thick band of nerve fibers connecting the right and left cerebral hemispheres, transmitting information between them.
|
|
|
What are the four lobes called?
|
Occipital, Parietal, Temporal and Frontal.
|
|
|
What are the Occipital Lobes?
|
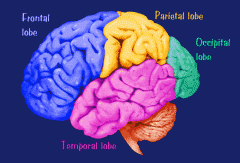
One of the four major sections of the cerebral cortex, located at the back of the cerebral hemispheres. Responsible for visual processing.
|
|
|
What are the Parietal Lobes?
|
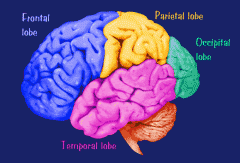
One of the four major sections of the cerebral cortex, located in the front of the Occipital lobes. Responsible for touch sensation and body's position.
|
|
|
What are the Temporal Lobes?
|
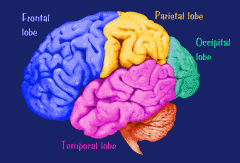
One of the four major sections of the cerebral cortex, located below the Parietal lobes and near the temples. Responsible for hearing and language.
|
|
|
What are the Frontal Lobes?
|
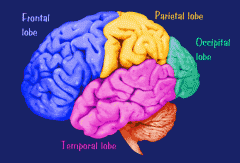
One of the four major sections of the cerebral cortex, located in the front of the cerebral hemispheres, behind the forehead. Responsible for coordination and higher mental processes.
|
|
|
What is the basal gangalia?
|
Controls cognition and voluntary movement.
|
|
|
What is the Association Cortex?
|
Areas that are neither motor or sensory but are thought to be involved in higher processing of information.
|
|
|
What is a Sulcus?
|
A groove on the surface of the brain.
|
|
|
What is the Hindbrain Reticular Formation?
|
A sensory gate that alerts higher brain centers to incoming info.
|
|
|
How many neurons are there in the human brain?
|
100 Billion
|
|
|
What is Aphasia?
|
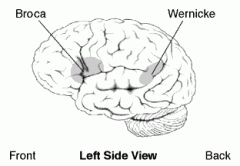
The inability to recognize or express language as a result of damage to brain tissue, such as after a stroke. (Broca Area & Wernicles Area)
|
|
|
What is Lateralization?
|
Degree to which a mental process is handled only by the left or right hemisphere.
|
|
|
Left-Brain Vs. Right-Brain
What is the left brain associated with? |

Verbal skills. (E.g. reading, writing, math, science, letters, language sounds, speech, grammar, explanations and logic)
|
|
|
Left-Brain Vs. Right-Brain
What is the right brain associated with? |

Nonverbal skills (E.g. spatial tasks, music, art, creativity, emotions, non-language sounds, directions, judgements, rotation of objects and face recognition).
|
|
|
What is plasticity?
|
The ability of the brain to alter its neural connections following damage.
|

