![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Paradox |
A statement or situation that seems contradictory. Ex: technology improved medicine, but makes it easier for misinformation to be spread |
|
|
Self realization programs |
EST Training Very draining (long hours) Large group Change your life around. Change belied system |
|
|
Self Help Books |
More motivational than explicit directions |
|
|
Codependency (3) |
Puts another persons needs first. Feeds into the dependent person. Anyone who let's another persons addictive behavior affect them, and is obsessed with controlling that behavior. |
|
|
Ego Boundaries. What is it and 2 examples |
What is and what is not me. Codependents dont have a good one and they move into someone else's life innapropriately. Physical/mental boundaries are off. You cant hit me, but you can verbally abuse me. |
|
|
Empiricism (2) |
The premise that knowledge should be acquired through observation. Advatage: Clarity and percision |
|
|
Independent variable |
The one that's manipulated |
|
|
Dependent variable |
The one that you measure when the experiment is over. Thought to be affected by the manipulations of the independent variable. |
|
|
If ____ then ____. |
IV (independent variable) DV (dependent variable) |
|
|
Experimental group with a control group |
Shows for certain cause/effect without nuisance variables |
|
|
Random sampling |
Advantage: random. Not special or different Disadvantage: need large numbers, so more expensive |
|
|
Correlation |
When two variables are related to one another. NOT CAUSE AND AFFECT. |
|
|
Positive correlation |
As one goes up, the other goes up |
|
|
Negative correlation |
As one goes up, the other goes down |
|
|
Zero correlation |
No relation |
|
|
Correlation strength |
Indicated by a correlation coefficient. -1.0➡️0➡️+1.0 |
|
|
Naturalistic observation |
Observing in the natural environment w/o affecting the results |
|
|
Case studies |
An in depth investigation on an individual |
|
|
Survey |
Large random samples. Representative samples |
|
|
Personality |
An individual's unique constellation of consistent behavioral traits |
|
|
Trait |
A durable disposition to behave in a particular way in a variety of situations |
|
|
The big 5 |
Extraversion, neurocentrism, openness to experience, agreeableness, conscientiousness |
|
|
Freud |
Psychodynamic. Most of your mind is unconscious |
|
|
The important ages? |
Age 1-5 |
|
|
What did Freud base most of his stuff on? |
Sexual urges |
|
|
Structure of the mind (Freud) |
Id, ego, superego |
|
|
Id |
Primitive instincts. Pleasure principle. Food, sex, ect. |
|
|
Ego |
Decision making in reality |
|
|
Super ego |
Morality. Makes you feel guilt |
|
|
Iceberg metaphor |
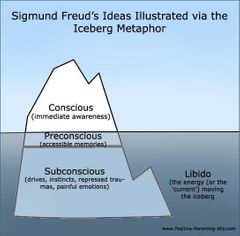
|
|
|
Defence mechanisms |
Unconcious reactions that protect a person from painful emotions |
|
|
Psychosexual stages |
Oral 0-1 Anal 2-3 Phallic 4-5 |
|
|
Oedipal complex (4) |
Sexual preference is resolved. Gives up longing for mom and identifies with dad. Gender identity is developed. If you dont make it past a stage you get fixated. |
|
|
Behaviorism |
Observable behavior. More scientific |
|
|
Classical conditioning (3) |
Aka respondent conditioning. Pavlov and Watson Involuntary behavior |
|
|
Generalization |
Dont just respond to the original stimulus, but also similar stimuli. |
|
|
Discrimination |
Only the original stimulus works |
|
|
Operant conditioning (2) |
Skinner Reinforcement and punishment |
|
|
Reinforcement |
Anything that strengthens behavior |
|
|
Punishment |
Anything that weakens behavior |
|
|
Positive reinforcement |
Strengthens by giving you something you like. |
|
|
Negative reinforcement |
Taking away something you don't like |
|
|
Escape |
Trying to get away from negative stimulus |
|
|
Avoidence |
Avoiding the negative stimulus before it even happens |
|
|
Extinction |
Conditioned stimulus is forgotten or unlearned |
|
|
Token economy |
Symbolic reward system |
|
|
Collective unconcious (2) |
Jung Contains traces of memories shared by the entire human race inherited from our ancestors |
|
|
Archetypes |
Emotionally charged images and thought forms that have universal meanings |
|
|
Alder (2) |
Believed in phases/stages Strive to be superior |
|
|
Evolutionary perspective |
We evolve physical and psychological characteristics that allow us to adapt, survive, and pass on our genes |
|
|
Biological perspective (2) |
Genetics Twin studies |
|
|
Humanism (4) |
Carl Rodgers Against frueds pessimism Rejected behaviorism We are all unique with free will and potential for growth |
|
|
Self concept |
Your beliefs about yourself |
|
|
Incongruence |
Difference between how you see yourself and how you really are |
|
|
Condition of worth |
Condition set by another person that I must meet in order for that person to treat me as worthy and loveable |
|
|
Hierarchy of needs |
Maslow Triangle shape with survival on the bottom |
|
|
Validity (2) |
The truth or accuracy of a measurement. Are you measuring what you are supposed to measure? |
|
|
Reliability |
Consistency over time |
|
|
Projective tests (2) |
Rorschak inkblots TAT pictures |
|
|
Self concept |
Set of beliefs you have about yourself |
|
|
Possible self |
Who you think you can be |
|
|
Self complexity |
How many different ways you see yourself. |
|
|
Self discrepancies |
A mismatching of self perceptions |
|
|
Actual self |
Who you actually are |
|
|
Ideal self |
The best you can be |
|
|
Ought self |
What you should be |
|
|
Positive ways of coping with discrepancies (2) |
Change habits. Acceptance. |
|
|
Negative ways of coping with discrepancies (3) |
Avoid situations that increase self awareness (ignorance is bliss). Drugs/alcohol Defence mechanisms |
|
|
Social comparison |
Comparing yourself to others |
|
|
Reference group |
Who you compare yourself to |
|
|
Individualism (2) |
My success depends on me. I put myself before the group. |
|
|
Collectivism |
I define myself with my family/social group |
|
|
Self efficacy |
Belief that you can achieve your goals |
|
|
Low self esteem (3) |
Low self efficacy. Put others down to make you feel high Unhappy |
|
|
High self esteem |
A good thing if realistic |
|
|
Narcissism |
Tendency to regard oneself and much better than you actually are |
|
|
Self attributions |
Inferences that people draw about the causes of their behavior |
|
|
Internal self attributions (5) |
Negative. Because I'm a loser! Stable (wont change) Uncontrollable Pessimistic |
|
|
External self attributions (5) |
Postitive. Blame something else. Unstable (can change) Controllable Optimistic |
|
|
Public self |
How you present yourself to the world |
|
|
Self monitoring |
The degree to which people attend to and control the impressions they make on others |
|
|
High self monitoring |
Concerned with making favorable impressions |
|
|
Low self monitoring |
More likely to express their true feelings/attitides |
|
|
Self verification theory |
People prefer to receive feedback from others that is consistent with their own self views |
|
|
Self serving bias |
Tendency to attribute ones successes to personal factors and ones failure to situational factors |
|
|
Self handicapping |
The tendency to sabotage ones performance to provide an excuse for possible failure |
|
|
Downward social comparison |
Defensive tendency to compare oneself with someone who's trouble is worse than ones own |
|
|
Self enhancement |
Tendency to maintain positive feelings about oneself |

