![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is split brain |
A condition resulting from surgery that separates the brains two hemispheres by cutting the divers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) connecting them |
|
|
|
When does plasticity occur |
It happens all through your life but is more apparent during childhood and development |
|
|
|
What is the general structure of a neuron |
Soma, dendrites, axon, terminal crunches of axon (axon termina) and sometimes myelin sheath |
|
|
|
Function of cell body |
Back (Definition)the part of a neuron that contains the nucleus; the cell’s life-support system |
|
|
|
Function of Dendrites |
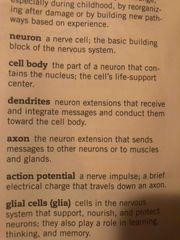
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Function of axon |
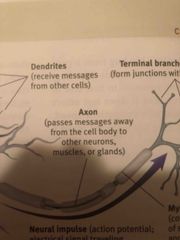
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Function of axon terminals |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Function of myelin sheath |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Define action potential |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is a glial cell |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Define synapse |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Define neural impulse |
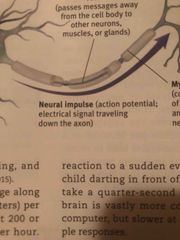
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
How does the message go through a neuron |
Through electrical signals receiving a message from the dendrites, processing through the cell body, and sending it through the axon, the message leaves through the axon terminal |
|
|
|
How do neurotransmitters affect our mood and behaviour |
Neurotransmitters have their own pathways carrying different but specific messages that affect our motions and emotions |
|
|
|
What type of neurotransmitters are there |
Acetylcholine (ACh), Dopamine, seretonin, norepinephrine, GABA (gammaaminobutyric acid), glutamate, and endorphins |
A,D,S,N,G,G,E |
|
|
Acetylcholine (ACh) |
Enables muscle action, learning and memory |
What aches |
|
|
Dopamine |
Influences movement, learning, attention and emotion |
An emo ADHD kid in school is dope |
|
|
Serotonin |
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal |
Sarah is a PMSing skinny tired hoe |
|
|
Norepinephrine |
Helps control alertness and arousal |
When driving through a pine forest, you need to be alert |
|
|
GABA (gammaaminobutyric acid) |
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter - undersupply linked to seizures tremors and insomnia |
|
|
|
Glutamate |
A major excitatory neurotransmitter involves in memory |
|
|
|
Endorphin |
Influences the perception of pain or pleasure |
End or feel? |
|
|
What are the parts of the Central nervous system |
Spine and brain |
|
|
|
What are the parts of the peripheral nervous system |
Neurons |
|
|
|
What is Autonomic nervous system |
The part of your peripheral nervous system that controls your glands and the muscles in your i thermal organs. You cannot override this system |
|
|
|
What is your somatic nervous system |
The part of your peripheral nervous system that monitors sensation and triggers motor output. |
|
|
|
What are the parts of the autonomic nervous system |
Sympathetic nervous system that arouses you when you are nervous Parasympathetic nervous system that calms you to conserve energy. |
|
|
|
What is sensory input and motor output |
Sensory input is when your nerves sense something that requires action Motor output is the reaction to a sensory input Ex: touching a hot stove. The burning sensation is sensory input and your motor output makes you pull your hand away |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the endocrine system. |
To send chemical messages (hormones) to tissues via the blood stream |
|
|
|
Where is the pituitary gland |
In the brains core near the hypothalamus. |
|
|
|
Why is the pituitary gland called the master gland |
It releases hormones as well as directions for other endocrine glands to release hormones. |
|
|
|
What are the parts of the brain stem |
Medulla, pons, reticular formation |
|
|
|
Where is the thalamus |
Above the brain stem |
|
|
|
Function of the brain stem |
The brain stem contains the m’exila that controls heartbeat and breathing, and the pons that helps control movement and sleep. A cat that has just a brain stem will walk and climb but not for food |
|
|
|
The reticular formation |
Extends from the spinal cord to the base of the thalamus that filters through information to send to important parts of your brain. |
|
|
|
Where is the cerebellum |
At the rear of the brain stem |
|
|
|
Function of cerebellum |
Helps judge time, textures, sound, and controls emotion. Reading vocabulary and information storage. It also coordinates voluntary movement |
Cere-ballerina |
|
|
What are the parts of the limbo system |
Amygdala, the hypothalamus, and hippocampus |
|
|
|
Function Amygdala |
Allow agression and fear |
Our friend Amy |
|
|
Function of hypothalamus |
Helps body maintain homeostasis Regulate hunger body temperature sexual behaviour by reading your blood chemistry or picking up signals from other parts of the brain. |
|
|
|
Function of the Hippocampus |
Processes conscious explicit memories of facts and events |
|
|
|
What is the cerebral cortex |
The ultimate control center of the brain. Pink stuff on top |
|
|
|
What are the 4 lobes in the cerebral cortex |
Frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal |
|
|
|
What is the corpus Callosum |
Axon fivers connecting the two cerebral hemispheres |
|
|
|
Function of thalamus |
Receives information about all senses except smell then forwards these messages to their final destination |
|
|
|
Where is the frontal lobe located |
At the front of the head |
|
|
|
Where is the parietal lobe located |
In the top of the head |
Parents |
|
|
Where is the temporal lobe located |
At the side of the head. By your ears |
|
|
|
Where is the occipital lobe located |
At the back of the head |
|
|
|
What is neuron genesis |
The formation of new neurons |
|

