![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
consists of a sample of examinees who are representative of the population |
norm group |
|
|
What approach can alleviate norms becoming outmoded in just a few years |
periodic renorming of tests should be the rule, not the exception. |
|
|
The most basic level of information provided by a psychological test is |
raw score. |
|
|
What are raw scores in personality testing? Ability testing? |
in personality testing, the raw score is often the number of questions answered in the keyed direction for a specific scale. In ability testing, the raw score commonly consists of the number of problems answered correctly, often with bonus points added |
|
|
raw scores, in isolation, are... |
absolutely meaningless |
|
|
How are norms empirically established? |
norms are empirically established by |
|
|
The vast majority of psychological tests are |
norm-referenced tests. |
|
|
These types of tests help determine whether a person can accomplish an objectively defined criterion such as adding pairs of two-digit numbers with 97 percent accuracy. |
criterion-referenced tests |
|
|
In the case of criterion-referenced tests, norms are... |
not essential. |
|
|
There are many different kinds of norms, but |
Each incorporates a statistical summary of a large body of scores. |
|
|
A very simple and useful way of summarizing data is to tabulate a |
frequency distribution |
|
|
A frequency distribution is |

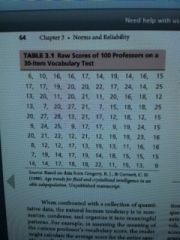
prepared by specifying a small number of usually equal-sized class intervals and then tallying how many scores fall within each interval. The sums of the frequencies for all intervals will equal N, the total number of scores in the sample.
|
|
|
It is common for frequency distributions to include |
between 5 and 15 class intervals. |
|
|
A __________ provides a graphic representation of the same information contained in the frequency distribution |
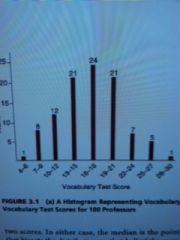
histogram |
|
|
A _________ is similar to a histogram, except that the frequency of the class intervals is represented by single points rather than columns. The single points are then joined by straight lines |
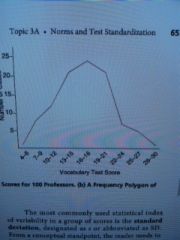
frequency polygon |
|
Can we designate a single, representative score for the 100 vocabulary scores in our sample? |
Yes. The mean (M), or arithmetic average, is one such measure of central tendency. |
|
|
How do you compute the mean? |
We compute the mean by adding all the scores up and dividing by N, the number of scores. |
|
|
Another useful index of central tendency |
the middlemost score when all the scores have been ranked. |
|
|
the mode is... |
simply the most frequently occurring score. |
|
|
The mean is sensitive to extreme values and can be misleading if a distribution has a few scores that are unusually high or low. If the mean is skewed what do you use? |
the median is a better index of central tendency |
|
|
The most commonly used statistical index |
standard deviation |
|
|
What is standard deviation? |
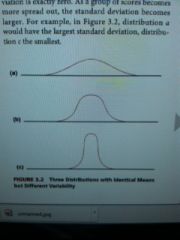
the standard deviation reflects the degree |
|
|
The standard deviation is symbolized how? |
S, it is simply the square root of the variance, designated as S2. |
|
|
The formula for the variance is... |
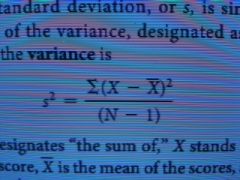
where g designates “the sum of,” X stands for each |
|
|
the variance and the standard |
interchangeable information |
|
|
What is the difference between the variance and the standard deviation? |
one can be computed from the other by squaring (the standard deviation to obtain the variance) or taking the square root (of the variance to obtain the standard deviation). The standard deviation is nonetheless the preferred measure of variance in psychological testing because of its direct relevance to the normal distribution |
|
|
the normal distribution is... |
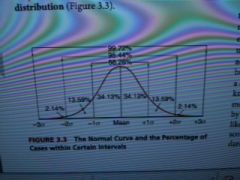
the distribution of scores that closely resemble a symmetrical, mathematically defined, bell-shaped curve |
|
|
Why would a normal distribution look skewed or asymmetrical? |
Small sample size |
|
|
Normal distribution is preferred because... |
1) the normal curve has useful mathematical features that form the basis for several 2) mathematical precision 3) the normal curve often arises spontaneously in nature |
|
|
________ refers to the symmetry or asymmetry of a frequency distribution |
Skewness |
|
|
If test scores are piled up at the low end of the scale, the distribution is said to be _____________ |
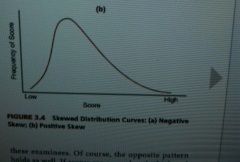
positively skewed |
|
|
when test scores are piled up at the high end of the scale, the distribution is said to be___________ |
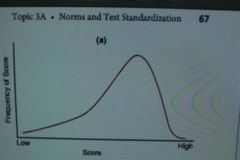
negatively skewed |
|
|
skewed distributions usually signify |
that the test developer has included too few easy items or too few hard items. |
|
|
A test has __________ validity if it looks valid to test users, examiners, and especially the examinees. |
face |
|
|
The proportion of examinees in a large tryout sample who get a specific item correct is called |
item-difficulty index |
|
|
For which of the below is it LEAST likely that we would find proportionate representation of race, social class, age groups, etc.? |
testing a small random sample |
|
|
When tests are used for purposes of ____________, it is necessary to develop a regression equation. |
predicting outcomes |
|
|
A(n) _____________ scale has a conceptually meaningful zero point. |
ratio |
|
|
A graphical display of the relationship between the probability of a correct response and the examinee's position on the underlying trait measured by the test is called |
item-characteristic curve |
|
|
According to the functionalist perspective on test validity, a test is valid if |
the test serves the purpose for which it is used |
|
|
Renorming of tests should |
be the rule, not the exception |
|
|
A factor loading is actually a(n) |
correlation |
|
|
In a frequency distribution, the sums of the frequencies for all intervals will ____________ the total number of scores in the sample. |
equal |
|
|
If the number of scores is even, the median |
is the average of the middlemost two scores |
|
|
The expression _____________ refers to the practice of using the original regression equation in a new sample to determine if the test predicts the criterion as well as it did in the original sample. |
cross-validation |
|
|
A(n) _____________ scale has a conceptually meaningful zero point. |
ratio |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT usually true of a norm group? |
it is homogeneous |
|
|
A factor loading is actually a(n) |
correlation |
|
|
An individual takes a new test for a medical disease, and the results indicate that she does not have the disease. In fact, it turns out that she did have the disease. This is an example of a |
false negative |
|
|
From a psychometric standpoint, _____________ questions are the weakest. |
matching |
|
|
The distribution of mental test scores in standardization samples typically |
approximates a normal curve |
|
|
Which coefficient has been used to gauge the degree to which a test measures a single factor? |
coefficient alpha |
|
|
Which scale construction method guarantees that all scale items correlate positively with each other and also with the total score for the scale? |
rational scale construction |
|
|
It is common practice in test development that the prepublication version of a new instrument might contain _____________ the number of items desired on the final draft. |
double |
|
|
Which of the following necessarily has a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 10? |
T-score |
|
|
In a ______________ validation study, test scores and criterion information are obtained simultaneously. |
concurrent |
|
|
T score scales are especially common for __________ tests. |
personality |
|
|
The distribution of mental test scores in standardization samples typically |
approximates a normal curve |
|
|
Unsystematic measurement errors behave like __________ variables. |
random |
|
|
In a sample of adults, correlations between reaction time and weight would most likely be |
close to zero |
|
|
A C scale consists of ____ units. |
11 |
|
|
The standard error of the estimate is an index of the error of measurement caused by the ______________ of a test. |
imperfect validity |
|
|
When are expert judges needed to determine the content validity of a test? |
when the trait being measured is ill-defined |
|
|
In his initial investigations, Wechsler considered the belief that mental measures must distribute themselves according to the normal curve to be |
mistaken |
|
|
What concept is best summed up by the question, "Does use of this test result in better patient outcomes or more efficient delivery of services?" |
test utility |
|
|
For which type(s) of scores are negative values possible? |
standard score |
|
|
_______________ validity is particularly relevant for entrance examinations and employment tests. |
Predictive |
|
|
If an examinee obtains a verbal score higher than his/her performance score, then the underlying true scores for verbal and performance abilities |
may or may not show the same pattern |
|
|
What statement best characterizes a "raw score"? |
it is useless by itself |
|
|
The item-discrimination index can vary from |
-1.0 to +1.0 |
|
|
Errors of measurement are |
positive or negative |
|
|
As noted by FairTest, what determines whether or not criterion-referenced tests are fair? |
how the cut-off scores are determined |
|
|
A construct possesses the following characteristic(s): |
A construct is a theoretical, intangible quality or trait in which individuals differ. 1. There is no single external referent sufficient to validate the existence of the construct; that is, the construct cannot be operationally defined |
|
|
For true-false items, the optimal level of item difficulty is |
.75 |
|
|
________________ are the most common type of raw score transformation encountered in psychological testing. |
Percentiles |
|
|
To know how well each preliminary test item contributes to accurate prediction of the criterion, we would use |
item-validity index |
|
|
Suppose the standard error of the estimate for predicted grade point average (GPA) is 0.2 grade units. Suppose a student has a predicted GPA of 2.90. Approximately what is the probability that the student will achieve a GPA of 3.3 or higher? |
2.5% |
|
|
primary goal of the Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children? |
1. Measure intelligence from a strong theoretical and research basis |
|
|
Suppose that a college freshman earned 125 raw score points on a vocabulary test where the normative sample averaged 100 points (with SD of 15 points). Suppose, in addition, he earned 110 raw score points on a spatial thinking test where the normative sample averaged 90 points (with SD of 20 points). In which skill area does he show greater aptitude, vocabulary or spatial thinking? |
vocabulary |
|
|
Errors of measurement are |
positive or negative |
|
|
Percentile ranks, age equivalents, grade equivalents, and standard scores are all examples of |
norms |
|
|
The Glasgow Coma Scale was developed by the method of |
expert rankings |
|
|
Factor loadings can vary between |
-1.0 and +1.0 |
|
|
A ________________ uses the standard deviation of the total distribution of raw scores as the fundamental unit of measurement. |
standard score |
|
|
Unsystematic measurement errors behave like __________ variables. |
random |
|
|
In a frequency distribution, the sums of the frequencies for all intervals will ____________ the total number of scores in the sample. |
equal |

