![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Test I. Multiple Choice (1-50) 1. According to CHED Memo Order #20, s.2014, what outcomes should all HEI's observe alignment in order to ensure quality graduates?
A. Institutional Outcomes B. Course Outcomes C. Program Outcomes D. Student Learning Outcomes |
C. Program Outcomes |
|
|
2. Based on the same memo, students should be able to communicate effectively in which language? A. Mother Tounge B. Tagalog and English C. English, Filipino, Mother Tongue D. English and Filipino |
D. English and Filipino |
|
|
3. Which of the following are mentioned in the same memo? I. ethical responsibility II. historical and cultural heritage III. latest developments IV. independence and teamwork A. I, II, III, IV B. I and II C. I and III D. II, III, IV |
A. I, II, III, IV |
|
|
4. Which statement/s is/are TRUE about the contributions of Bloom in the field of education? I. Education should be holistic II. In writing the objectives, behavioral verbs should be used. III. Each Taxonomy is organized into levels. IV. The levels are given equal importance. A. I and II B. I, II and III C. I and III D. I, II,III and IV |
B. I, II and III |
|
|
5. In the revised taxonomy, why is there a need to change the nouns into verbs? A. Verbs suggest active teacher engagement B. Verb suggest active student engagement C. Verbs suggest thinking, feeling and doing are active. D. Verbs suggest that learning is doing. |
B. Verb suggest active student engagement |
|
|
6. Which of the following does NOT belong? A. Understanding B. Analyzing C. Evaluating D. Applying |
A. Understanding |
|
|
7. Which of the following verb is behavioral? A. Describe B. Know C. Understand D. Learn |
A. Describe |
|
|
8. Which of the following does NOT belong? A. Explain B. Define C. List D. Recognize |
A. Explain |
|
|
9. Which behavioral verb involves declaring information, facts and ideas?
A. List B. Identify C. Define D. State |
D. State |
|
|
10. Which behavioral verb involves drawing an image or writing a scenario that's represents the concept? A. Infer B. Discuss C. Draw D. Illustrate |
D. Illustrate |
|
|
11. You want your students to give examples of a concept. Which is the best behavioral verb for this? A. Explain B. Exemplify C. Classify D. Discuss |
B. Exemplify |
|
|
12. You want students to display their knowledge visibly and publicly. Which is the best behavioral verb for this? A. Exhibit B. Use C. Dramatize D. Demostrate |
A. Exhibit |
|
|
13. You want your students to identify the similarities between two concepts. What are asking of them to do? A. Contrast B. Examine C. Compare D. Agree |
C. Compare |
|
|
14. You want your students to examine both pros and cons of something. What are asking of them to do? A. Defend B. Argue C. Critique D. Criticize |
C. Critique |
|
|
15. You want your students to assign a score to a given work based on criteria. What are asking them to do? A. Assign B. Rate C. Conclude D. Number |
B. Rate |
|
|
16. Which diagram is best when requiring students to compare and contrast? A. Ishikawa B. Concept map C. Venn D. Gantt |
C. Venn |
|
|
17. Which cognitive level is tapped in the given scenario? Teacher Dina Macuja creates a memory game where students have to label the parts of a flower on the board. A. Remembering B. Understanding C. Applying D. Analyzing |
A. Remembering |
|
|
18. Which cognitive level is tapped in the given scenario? Teacher Halina Tayo requires her student to watch the president's SONA of the previous year, argue whether or not his promises have been accomplished, and rate his overall performance at the present. A. Applying B. Analyzing C. Evaluating D. Creating |
C. Evaluating |
|
|
19. Which cognitive level is tapped in the given scenario? Teachers Anne Bajo and Dina Lego teach English and computer, respectively. They collaborated and required their students to design a simple program which they will present to a group of young audiences. A. Evaluating B. Creating C. Applying D. Understanding |
B. Creating |
|
|
20. Which outcome is of the lowest level of cognitive domain? A. Compare the results of experiment A with experiment B. B. Illustrate the different ways to recycle. C. Define recycle, reuse, and reduce. D. Discuss the different levels of thinking. |
C. Define recycle, reuse, and reduce. |
|
|
21. Which outcome is of the highest level of cognitive domain? A. Generate new mathematical model to address novel problem. B. Make judgment about the effectiveness and efficiency of two mathematical strategies. C. Utilize mathematical concept to solve real-world problems. D. Interpret mathematical charts to draw conclusion. |
A. Generate new mathematical model to address novel problem. |
|
|
22. Which does NOT belong? A. Imitation B. Set C. Adaptation D. Mechanism |
A. Imitation |
|
|
23. Which statement is true about SET of the psychomotor domain level? A. It is use of sensory cues to guide motor activity. B. It is the ability to convert learned simple responses into habitual actions. C. It refers to readiness to act. D. It refers to the ability to skillfully perform a task. |
C. It refers to readiness to act. |
|
|
24. Which psychomotor domain level is tapped when students make their first attempt at a physical activity? A. Mechanism B. Guided Response C. Perception D. Adaptation |
B. Guided Response |
|
|
25. Which psychomotor domain levels according to Simpson is the lowest and highest respectively? A. Perception; Origination B. Imitation; Origination C. Guided Response; Complex overt response D. Perception; Non-discursive |
A. Perception; Origination |
|
|
26. Which statement/s is/are TRUE? I. Reflex movements are learned, voluntary reactions. II. The highest level of Harrow's taxonomy is the ability to play sports. III. Physical abilities highlight fitness which comprises stamina, strength, agility, etc. A. I and II B. I and III C. III only D. I, II, III |
C. III only |
|
|
27. Who among the following made taxonomies for the psychomotor domain? I. Simpson II. Bloom III. Dave IV. Harrow V. Anderson A. I and III B. II and IV C. I, III, IV D. I, II, III, IV ,V |
C. I, III, IV |
|
|
28. Which of the following shows the highest level of psychomotor domain according to Harrow? A. Advance learned movements as one would find in acting. B. Development of fitness with focus on areas like flexibility and core strength. C. Response to stimuli such as visual and auditory. D. Use effective body language such as gestures and facial expressions. |
D. Use effective body language such as gestures and facial expressions. |
|
|
29. Harrow's psychomotor domain starts with _______. A. Fundamental movements B. Non- discursive communication C. Reflex movement D. Perception |
C. Reflex movement |
|
|
30. Which of the following does NOT belong? A. Imitation B. Articulation C. Precision D. Mechanism |
D. Mechanism |
|
|
31. Which statement is TRUE about the affective domain? A. It emphasizes thinking processes. B. Learner's emotional experiences are considered at the highest levels of taxonomy. C. Outcomes of this domain include fostering enthusiasm and development of positive attitudes. D. The affective domain is less relevant in education compared to the cognitive domain. |
C. Outcomes of this domain include fostering enthusiasm and development of positive attitudes. |
|
|
32. What does assessment of student start with? A. Institution's vision, mission, and core values. B. Student Learning Outcomes C. CHED recommendations as stated in the memo. D. Institutional, Program and Course outcomes. |
A. Institution's vision, mission, and core values. |
|
|
33. Which of the following exemplifies good practice of assessing learning outcomes?
A. Arranging standalone activities to address immediate needs. B. Informing students of the SLO's at the beginning, middle, and end of instruction. C. Having the content as basis of one's assessment task. D. Setting criteria or standard of success to help interpret results.
|
D. Setting criteria or standard of success to help interpret results. |
|
|
34. Which of the following is NOT ideal in assessing learning outcomes? A. Using real-world application. B. Allowing students to practice self assessment. C. Providing specific feedback. D. Emphasizing both LOTs and HOTs |
D. Emphasizing both LOTs and HOTs |
|
|
35. In the instructional cycle, which a phase concludes the cycle? A. Summative Assessment of Outcomes B. Formative Assessment of Outcomes. C. Mastery Learning D. Institutional Vision- Mission |
A. Summative Assessment of Outcomes |
|
|
36. Which of the following phases is first? A. Deciding the lesson focus B. Supporting student activities C. Diagnostic Assessment D. Formative Assessment |
C. Diagnostic Assessment |
|
|
37. What does diagnostic assessment identify? A. Strengths B. Weaknesses C. Both A and B D. Levels |
C. Both A and B |
|
|
38. Based on the instructional cycle, how can we ensure mastery Learning? A. Review/ Reteach B. Lesson Focused C. Clear desired SLOs D. Summative Assessment |
A. Review/ Reteach |
|
|
39. The SLO is " to interpret a given a poem." Which assessment task aligns? A. A multiple- choice test where student selects the correct meaning of specific words in the poem. B. An essay where students analyze the theme and symbolism based on their own understanding. C. A recitation exercise where students memorize and recite the poem. D. A quiz that requires them to remember the poem's author, tittle and publication date. |
B. An essay where students analyze the theme and symbolism based on their own understanding. |
|
|
40. The SLO is " to express opinion on the current issue related to West Philippine Sea." Which assessment is least preferred? A. a vlog B. performance C. an essay D. editorial cartoon |
B. performance |
|
|
For items 41-43, identify the type of portfolio needed in the given scenarios. 41. You wish to see your students' progress in writing from the beginning of the school year till the end. So, you require that they compile all their outputs, drafts, revisions, and final products. A. Development B. Process C. Product D. Showcase |
A. Development |
|
|
42. To help your graduating students become more bankable in the industry you require them to gather all their outputs that are commendable and exemplary. You then instruct them that they need to bring this in their interviews. This may include their lesson plans, their rubrics, and their seat work activities in the practicum, etc. A. Process B. Showcase C. Evaluation D. Product |
B. Showcase |
|
|
43. You inform your class that they are to stage a dramatic performance using the model of Viola Spolin. You then require them to document the entire procedure starting with the planning, then the performance, and the aftermath which may comprise audience's and performer's feedback. A. Evaluation B. Development C. Product D. Process |
D. Process |
|
|
44. Which element of a portfolio is most important and is found in all types of portfolios?
A. dates B. self- assessment C. cover sheet D. work samples |
D. work samples |
|
|
45. What element differentiates evaluation portfolio from other types of portfolios? A. stating the course outcomes and the corresponding activities to meet them. B. the evaluation and comment of the teacher on the provided work. C. the best work of the students based on the evaluation of the teacher. D. including the steps in achieving desired output. |
A. stating the course outcomes and the corresponding activities to meet them. |
|
|
46. When using authentic assessment methods, how do we ensure reliable measurement? A. Set criteria for grading B. Use rubrics C. Involve experts in evaluating work D. Refer to standards in evaluating tasks. |
B. Use rubrics |
|
|
47. Which of the following statements is TRUE about rubrics? A. Holistic rubrics provide specific feedback. B. Holistic rubrics is best when dealing with time constraint and a large number of students. C. Analytic rubric is easy to create. D. Analytic rubric fails to identify strengths and weaknesses. |
B. Holistic rubrics is best when dealing with time constraint and a large number of students. |
|
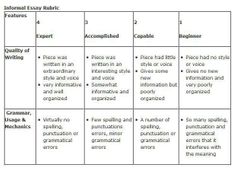
For items 48-50, refer to the given rubric.
48. What type of rubric is this?
A. Holistic rubric B. Analytic rubric C. Hybrid between analytic and holistic D. Essay rubric |
A. Holistic rubric |
|
|
49. What is missing in the rubric? A. Performance descriptors B. Criteria C. Performance level D. Task description |
D. Task description |
|
|
50. Which Statement is FALSE about this rubric? A. The highest overall score for this rubric is 4. B. The student who does well in all criteria is considered an expert. C. Both criteria are given equal weight. D. The lowest possible score is 2. |
A. The highest overall score for this rubric is 4. |
|
|
Test II. Matching Type. (1-10) Choose the letter that best corresponds to the statements. Some options may be used twice.
1. This is the epitome and goal of learning.
a. Analyzing b. Applying c. Creating d. Evaluating e. Remembering f. Understanding |
c. Creating |
|
|
2. This involves separating concepts into components and elements. a. Analyzingb. Applyingc. Creatingd. Evaluatinge. Rememberingf. Understanding |
a. Analyzing |
|
|
3. This level is achieved when learners state information in their own words. a. Analyzingb. Applyingc. Creatingd. Evaluatinge. Rememberingf. Understanding |
f. Understanding |
|
|
4. This is all about judging the worth or value of something. a. Analyzingb. Applyingc. Creatingd. Evaluatinge. Rememberingf. Understanding |
d. Evaluating |
|
|
5. This is all about making sense of texts and images. a. Analyzingb. Applyingc. Creatingd. Evaluatinge. Rememberingf. Understanding |
f. Understanding |
|
|
6. It requires producing definitions and facts from memory. a. Analyzingb. Applyingc. Creatingd. Evaluatinge. Rememberingf. Understanding |
e. Remembering |
|
|
7. This is also known as the transfer of learning. a. Analyzingb. Applyingc. Creatingd. Evaluatinge. Rememberingf. Understanding |
b. Applying |
|
|
8. This level involves using what was learned in similar but new situations. a. Analyzingb. Applyingc. Creatingd. Evaluatinge. Rememberingf. Understanding |
b. Applying |
|
|
9. This is the foundational level that starts the process of learning. a. Analyzingb. Applyingc. Creatingd. Evaluatinge. Rememberingf. Understanding |
e. Remembering |
|
|
10. This involves synthesizing elements to produce something new. a. Analyzingb. Applyingc. Creatingd. Evaluatinge. Rememberingf. Understanding |
c. Creating |
|
|
Test III TRUE or FALSE. (1-10)Read the statements carefully. Write TRUE if the statement is true, and FALSE if Not.
1. In blooms taxonomy, evaluating is deemed most complex of all skills.
|
TRUE |
|
|
2. Critical thinking skills and higher order thinking skills are different from one another. |
FALSE |
|
|
3. HOTS are most useful in spelling, vocabulary learning, and syntax coding. |
FALSE |
|
|
4. The four categories of knowledge focus on how you learn and use what you know while the types of learning focus on what you know. |
FALSE |
|
|
5. The highest level of processing according to Kendall and Marzano is self-system. |
TRUE |
|
|
6. The sixth level of processing involves thinking about thinking. |
FALSE |
|
|
7. Knowledge utilization is higher than retrieval and analysis. |
TRUE |
|
|
8. Self-system includes monitoring one's learning process and clarifying the accuracy of one's learning. |
FALSE |
|
|
9. Pestalozzi believes that children ought to learn by head, hand,and heart. |
TRUE |
|
|
10. MELCs, which stands for most essential learning competencies aims to guide educators in designing their class instruction. |
TRUE |
|
|
Test IV. IDENTIFICATION A. Categories of Knowledge. Read the statements carefully and identity what the statements refer to. Write F for factual Knowledge, C for Conceptual, P for Procedural and M for Metacognitive. 1. Gerald knows what metacognitive knowledge is. |
F |
|
|
Write F for factual Knowledge, C for Conceptual, P for Procedural and M for Metacognitive.2. Felicidad has a clear idea about the many definitions of love. |
F |
|
|
Write F for factual Knowledge, C for Conceptual, P for Procedural and M for Metacognitive. 3. Thelma follows the steps by John Muller in conducting authentic Assessment. |
P |
|
|
Write F for factual Knowledge, C for Conceptual, P for Procedural and M for Metacognitive. 4. Esther outlines the principles in assessing learning. |
C |
|
|
Write F for factual Knowledge, C for Conceptual, P for Procedural and M for Metacognitive. 5. Mario knows what photosynthesis is. |
F |
|
|
Write F for factual Knowledge, C for Conceptual, P for Procedural and M for Metacognitive. 6. Yelina is aware of her learning gaps in trying to grasp the concept of relativity. |
M |
|
|
Write F for factual Knowledge, C for Conceptual, P for Procedural and M for Metacognitive. 7. Oliver identifies which strategies can help him best in reading ten papers in a week. |
M |
|
|
Write F for factual Knowledge, C for Conceptual, P for Procedural and M for Metacognitive. 8. Walter can explain the theoretical model of his research paper. |
C |
|
|
Write F for factual Knowledge, C for Conceptual, P for Procedural and M for Metacognitive. 9. Philip knows that the tasks is difficult for him so he chunked it into manageable bits. |
M |
|
|
Write F for factual Knowledge, C for Conceptual, P for Procedural and M for Metacognitive. 10. Rene follows the scientific method in conducting his research. |
P |
|
|
B. Affective Domain. Read the statements carefully and Identity what statements refer to. A. Characterizing B. Receiving C. Responding D. Organizing E. Valuing 1. The ideal behavior of this level is showing enjoyment or pleasure in an activity. |
C. Responding |
|
|
2. This is the highest level of the affective domain. A. CharacterizingB. ReceivingC. RespondingD. OrganizingE. Valuing |
A. Characterizing |
|
|
3. This level involves prioritizing values and resolving conflicts between them. A. CharacterizingB. ReceivingC. RespondingD. OrganizingE. Valuing |
D. Organizing |
|
|
4. It involves being aware of a phenomenon due to attentiveness. A. CharacterizingB. ReceivingC. RespondingD. OrganizingE. Valuing |
B. Receiving |
|
|
5. The ultimate goal of this level is commiting or assuming responsibility. A. CharacterizingB. ReceivingC. RespondingD. OrganizingE. Valuing |
E. Valuing |
|
|
6. This level requires consistency and that values become part of one's lifestyle. A. CharacterizingB. ReceivingC. RespondingD. OrganizingE. Valuing |
A. Characterizing |
|
|
7. The learner actively participates in group discussion. A. CharacterizingB. ReceivingC. RespondingD. OrganizingE. Valuing |
C. Responding |
|
|
8. " I listen attentively and pay close attention." A. CharacterizingB. ReceivingC. RespondingD. OrganizingE. Valuing |
B. Receiving |
|
|
9. Example of an outcome in this level is " to strike balance between work and leisure." A. CharacterizingB. ReceivingC. RespondingD. OrganizingE. Valuing |
D. Organizing |
|
|
10. Learners rally in support of a minority group that faces discrimination. A. CharacterizingB. ReceivingC. RespondingD. OrganizingE. Valuing |
E. Valuing |
|
|
C. Authentic Assessment. Read the statements carefully and identify what the statements refer to. A. Performance B. Portfolio C. Product D. All of the Above 1. Examples include diagrams, research, advertisement. |
C. Product |
|
|
2. It involves identifying task criteria. A. PerformanceB. PortfolioC. ProductD. All of the Above |
D. All of the Above |
|
|
3. This is a purposeful collection of student work. A. PerformanceB. PortfolioC. ProductD. All of the Above |
B. Portfolio |
|
|
4. This pertains to all actual concrete creations. A. PerformanceB. PortfolioC. ProductD. All of the Above |
C. Product |
|
|
5. This is used to present student growth over time. A. PerformanceB. PortfolioC. ProductD. All of the Above |
B. Portfolio |
|
|
6. Examples include experiments, simulations, recitals. A. PerformanceB. PortfolioC. ProductD. All of the Above |
A. Performance |
|
|
7. Choosing this goes through a process that starts with identifying standards. A. PerformanceB. PortfolioC. ProductD. All of the Above |
D. All of the Above |
|
|
8. This is a demonstration of one's knowledge. A. PerformanceB. PortfolioC. ProductD. All of the Above |
A. Performance |
|
|
9. This is an example of alternative assessment. A. PerformanceB. PortfolioC. ProductD. All of the Above |
D. All of the Above |
|
|
10. It requires the use of rubrics. A. PerformanceB. PortfolioC. ProductD. All of the Above |
D. All of the Above |

