![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What process occurs in the proximal tubule? |
Bulk isosmotic reabsorption |
|
|
Draw an annotated graph showing the osmolarity of tubular fluid as it passes through the nephron |
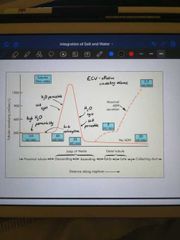
|
|
|
What might cause a change in the osmolarity of blood? How is this fixed? |
Ingestion of excess salt - fixed by modulating water secretion by ADH |
|
|
What might cause a change in volume of the blood? What is done to fix this? |
Dehydration - modulation of Na excretion by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone cascade |
|
|
Why do changes in volume tale hours to affect urine flow? |
Because the hormone responsible for fixing it is aldosterone, a steroid hormone which alters transcription. This takes hours |
|
|
Why do changes in osmolarity take minutes to fix? |
Because the hormone responsible for fixing it is ADH, which is a fast-acting peptide hormone |
|
|
Describe the pathway of osmolarity regulation |
- increased blood osmolarity or decreased ECV leads to activation of Baroreceptors/osmoreceptors - leads to: 1. Increased thirst, fluid intake and fluid volume 2. ADH release, vasoconstriction, increased water retention, increased fluid volume |
|
|
Where are baroreceptors located? |
In the carotid/aortic sinuses |
|
|
Where are osmoreceptors located? |
In the OVLT and SFO of the hypothalamus |
|
|
What does OVLT and SFO stand for? |
Organum vasculosoum laminae terminalis Subfornical organ |
|
|
What are the specific triggers for ADH release? |
A 2% rise in osmolarity A 15% drop in volume |
|
|
Describe the pathway of ADH-mediated AQP2 insertion |
- ADH occupies V2 receptors on basolateral membrane - activates AC via Gs, to stimulate cAMP production - activates PKA, which phosphorylates cytoskeletal elements to promote fusion of AQP2 vesicles into the apical membrane |
|
|
Which AQPs are expressed on the basolateral membrane? |
AQP3/4 |
|
|
How was it discovered that ADH had an effect on the apical membrane of kidney cells? |

Experiments on Brattleboro rats showed that, on freeze-fracturing the apical membrane of a rat principal cell, a different arrangement could be seen depending on ADH presence |
|
|
What are the 4 actions of ADH? |
Stimulate AQP2 insertion Activate urea carriers in CD Stimulate NKCC in Thick Ascending Limb Vasoconstrictor effect |
|
|
Describe the NKCC pathway of ADH |
- ADH acts on V1 receptors which stimulates PLC to produce IP3 - IP3 causes calcium release, which activates PKC - PKC phosphorylates and stimulates NKCC |
|
|
Give some factors that would stimulate renin release |
- Increased Cl- reabsorption across macula densa - reduced Ang2 - reduced ADH - increased SNS and catecholamines - increased prostaglandins - increased stretch of JG cells
|
|
|
What does the macula densa release and why? |
Cl- mediated release of ATP, which is broken down to adenosine to inhibit renin release |
|
|
Describe the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone cascade |
Renin catalyses angiotensinogen => angiotensin 1
ACE catalyses angiotensin 1 => angiotensin 2
Angiotensin 2 receptors on adrenal cortex stimulates aldosterone release |
|
|
Which drug can block renin's conversion of angiotensinogen to A1? |
Enalkiren |
|
|
Which drug can block ACEs conversion of A1 to A2? |
Captopril |
|
|
Which drug antagonises the Ang2 receptor on adrenal cortex cells |
Saralasin |
|
|
What are the 5 actions of angiotensin 2? |
- Aldosterone release from adrenal cortex - Renal vasoconstriction - enhanced PT reabsorption - heightened sensitivity of macula densa to distal flow rate - stimulated thirst and ADH release |
|
|
How does aldosterone stimulate Na reabsorption? |
Aldosterone dimerises with a mineralocorticoid receptor, which acts as a transcription factor to stimulate production of Na-K-ATPases and promote reabsorption |
|
|
Which drug antagonises the aldosterone receptor? |
Spironolactone |
|
|
What is the purpose of Ang2's renal vasoconstriction? |
It constricts efferent more than afferent, so increases GFR and restores it to normal levels |
|
|
Describe the pathway allowing Ang2 to promote proximal Na reabsorption |
Ang2 acts on Gq coupled receptor to promote PLC's production of IP3 IP3 increases calcium, which activates PKC PKC phosphorylates and promotes the NHE on the apical membrane, promoting Na absorption |
|
|
Describe the function of ANP |
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide antagonises the renin-A2-aldosterone axis, and causes vasodilation by raising cGMP levels |

