![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name three functions of a plasma membrane |
1. encloses contents of a cell 2. controls movement of substances in/out of cells 3. cell recognition/communication |
|
|
Describe what is meant by the fluid mosaic model |
1. two layers (bilayer) of phospholipids 2. molecules not in a fixed position |
|
|
Phospholipid structure |
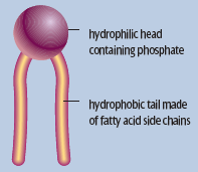
hydrophobic: polar hydrophilic: non-polar |
|
|
Factors that affect the fluidity of the plasma membrane |
1. phospholipid composition - fluid: more kinked tails - less fluid: straight tails, no kinks 2. temperature - ⬆ more fluid -⬇ less fluid 3. presence of cholesterol - only found in animal cell membranes - maintain membrane fluidity - prevents membrane becoming too fluid, restrics movement of phospholipids (high temp) - prevents from too solid, prevent tight packing (low temp) |
|
|
Define passive movement |
- movement that doesn't require energy - high to low concentration |
|
|
Define diffusion |
- form of passive movement - water, air, plasma membranes - small polar molecules (gases, water, lipids) soluble - large proteins (polar) and charged ions repelled by tails |
|
|
Define Osmosis |
- form of passive diffusion across semi-permeable membrane - high to low concentration of water |
|
|
Define facilated diffusion |
- passive: polar molecules, charged ions across plasma membrane - requires channel proteins, carrier proteins |
|
|
Define active movement |
- requires energy in form of ATP Includes - active transport (substance movement against concentration gradient via carrier channels) - bulk transport (endocytosis, exocytosis) |
|
|
Endocytosis |
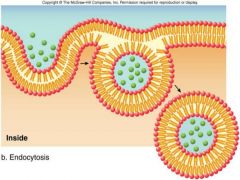
- material goes into the cell - membrane folds and reates a vesicle containing the substance |
|
|
Exocytosis |
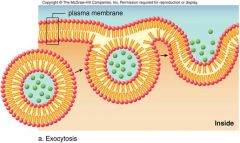
- vesicle containing the molecules fuses with the membrane - secretes substance out of the cell |

