![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Plant stress |
Any change in environmental conditions that might reduce or adversely change and plants growth or development - changes in colouration - necrotic or dead tissue - changes in normal development |
|
|
Internal and external stressors |
Internal stressor - Endogenous - water, chemical/nutritional, systemic pathogenic disease - External stressors - Exogenous - environmental, temperature, light intensity, humidity, air movement, pollution, herbivory, physical damage, non systemic pathogenic disease |
|
|
Biotic factors |
Insects Fungi Bacteria Viruses |
|
|
Abiotic factors |
Environmental stress Mechanical stress |
|
|
Biotic Symptoms and signs |
Damage pattern non uniform Damage spreads over time (infectious) Signs visible |
|
|
Abiotic symptoms and signs |
Damage pattern uniform Damage does not spread over time No visible signs |
|
|
Physical plant disease |
Disorder not caused by pathogen Water stress, nutritional disease, temperature, light, phytotoxicity |
|
|
Symptoms vs Signs |
- symptom equals a change in appearance, no direct evidence of stress causing agent Sign - visible evidence of stress causing causing agent |
|

Front (Term) |
Anthocyanescence - nutrition - phosphorus deficiency, pH, cold |
|

Front (Term) |
Bronzing - cold, nutrition |
|

Front (Term) |
Chlorosis - nutrition: N, Mg, Fe common |
|

Front (Term) |
Mosaic virus |
|

Front (Term) |
Mottling - virus, nutrition |
|

Front (Term) |
Blotching - fungus |
|

Front (Term) |
Leaf spot - fungus |
|

Front (Term) |
Scorch - nutrition, salinity, UV |
|

Front (Term) |
Oedema |
|
|
Examples of signs |
Frass (excrement), slime trails, exoskeletons, actual pest, webbing, fungus |
|
|
Endogenous vs Exogenous stress |
Endogenous - stress from within Exogenous - stress from without |
|
|
Water related plant stress (Most common reason for plant stress - not enough/too much) Symptoms of low water stress |
Stunted growth, small leaves, older leaves yellow/red, leaves blueish, flagging, wilting, leaf drop |
|
|
Symptoms of excess water stress |
Leaf drop, leaf yellowing, tips/leaves turn brown, oedema/edema, wilting |
|
|
Examples of signs |
Frass (excrement), slime trails, exoskeletons, actual pest, webbing, fungus |
|
|
Endogenous vs Exogenous stress |
Endogenous - stress from within Exogenous - stress from without |
|
|
Water related plant stress (Most common reason for plant stress - not enough/too much) Symptoms of low water stress |
Stunted growth, small leaves, older leaves yellow/red, leaves blueish, flagging, wilting, leaf drop |
|
|
Symptoms of excess water stress |
Leaf drop, leaf yellowing, tips/leaves turn brown, oedema/edema, wilting |
|
|
Secondary pest/disease related to over watering |
Root rot, damping off, vascular wilt, container pest/fungus |
|
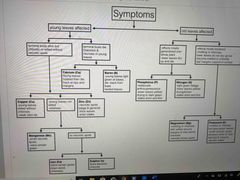
Front (Term) |
Study |
|
|
Mobile nutrients |
Nitrogen N Phosphorus P Potassium K Magnesium Mg Zinc Zn |
|
|
Immobile nutrients |
Calcium Ca Boron B Copper Cu Sulphur S Iron Fe |
|
|
Types of cold injury |
Desiccation, water soaking, split bark, Southwest injury, wilting/flagging, tissue necrosis, plant death |
|
|
Endogenous factors contributing to plant hardiness |
Cell turgor, size of cell (smaller cells more hardy), nutrition (deficiency k, excess N) dehydrated cells more desiccated by cold wind, pear/disease |
|
|
Exogenous factors contributing to plant hardiness |
Min/max temperature Rainfall/snow/wind Seasonal duration Climate hardening |
|
|
Three categories of cold sensitivity |
Chilling sensitive - injured with exposed to temperatures still above 0 Frost sensitive - able to withstand a light frost for a short time Cool hardy - able to withstand extended exposure to temperatures below 0 |
|
|
Cold protection strategies in plants |
Tissues block ice development Supercooling (ability of a liquid to reach a temp below it’s freezing point without becoming solid Dehydration |
|
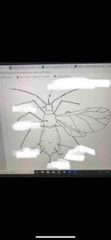
Front (Term) |
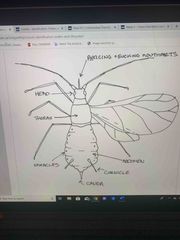
Hemiptera - aphids, leafhoppers, stink bugs, whiteflies, lace bugs |
|
|
Endogenous factors contributing to plant hardiness |
Cell turgor, size of cell (smaller cells more hardy), nutrition (deficiency k, excess N) dehydrated cells more desiccated by cold wind, pear/disease |
|
|
Exogenous factors contributing to plant hardiness |
Min/max temperature Rainfall/snow/wind Seasonal duration Climate hardening |
|
|
Three categories of cold sensitivity |
Chilling sensitive - injured with exposed to temperatures still above 0 Frost sensitive - able to withstand a light frost for a short time Cool hardy - able to withstand extended exposure to temperatures below 0 |
|
|
Cold protection strategies in plants |
Tissues block ice development Supercooling (ability of a liquid to reach a temp below it’s freezing point without becoming solid Dehydration |
|
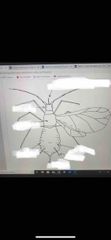
Front (Term) |
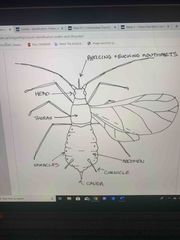
Hemiptera - aphids, leafhoppers, stink bugs, whiteflies, lace bugs |
|

Front (Term) |
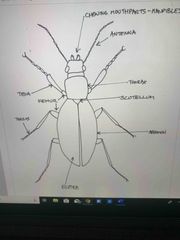
Coleoptera - beetles |
|

Front (Term) |
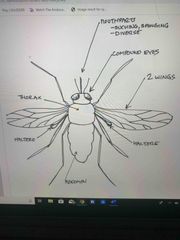
Diptera - flies |
|

Front (Term) |
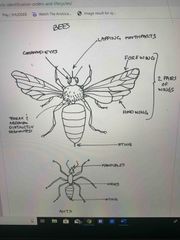
Hymenoptera - ants, bees, wasps |
|

Front (Term) |
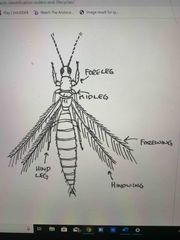
Thysanoptera - thrips |
|

Front (Term) |
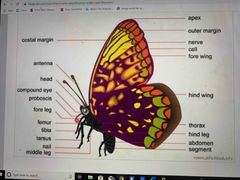
Lepidoptera - moths, butterflies |
|
Front (Term) |
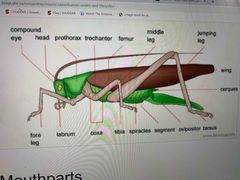
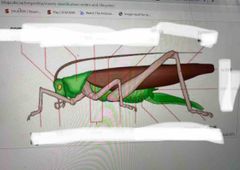
Orthoptera - grasshoppers |
|

Front (Term) |
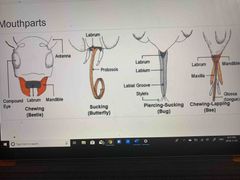
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Acidic soils can cause.. |
Aluminum toxicity (iron and aluminum tie up phosphorus) |
|
|
Excess phosphorus can tie up.. |
Iron and zinc |
|
|
Nutrient deficiencies can be caused by.. |
Low soil nutrition pH Water deficiency |
|
|
Yellowing on new leaves |
Sulphur deficiency |
|
|
Reddening of older leaves |
Phosphorus deficiency |
|
|
Dead terminal bud |
Calcium deficiency |
|
|
Interveinal chlorosis on old leaves |
Potassium deficiency |
|
|
Intervienal chlorosis on new leaves |
Iron deficiency |
|
|
Yellowing on old leaves |
Nitrogen deficiency |
|
|
7 climatic factors |
Daily minimum/max temperature on monthly average Frost free days Rainfall Winter factor (cold rain) Snow depth Wind |

