![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Plant tissues |
Collection of cells performing a specific function |
|
|
|
Plant tissues are collectively called |
Plant tissue system With each tissue carrying out a different function |
|
|
|
Plant tissues are classified into 2 groups |
Meristematic tissues Permanent tissues |
|
|
|
Meristemactic tissues |
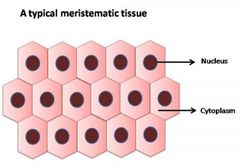
Cells in these tissue have the ability to divide ,describes as densely packed which continuously divide to create new cells Have a large nucleus with no vacuole
|
|
|
|
Functions of plant tissue |
.Provide support to the plant .Provides elasticity and flexibility allowing them to bend without damage .The xylem and phloem helps transport materials . Involved in process like photosynthesis and regeneration |
|
|
|
Meristematic tissues continously divide into 2 the new cell that remains the meisterm is called ........and the other cell the ..........
|
Initial (new )and derivative (old ) |
|
|
|
What happens As more cells are produced through mitosis |
The derivative (old) cells Pushed further away from the mitotic zone |
|
|
|
Characteristic of meristematic cells |
Ability to stretch enlarge &differentiate into other tissues as they manture. |
|
|
|
Meristematic tissues eventually give rise to |
Permanent tissues |
|
|
|
What are the 3 type of bases meristematic tissues are made up of Based on location... |
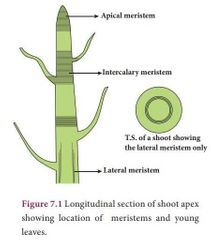
1.apical meristem 2.lateral meristems 3.inter calary meristems |
|
|
|
Where are Apical meristems located |
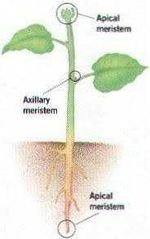
Polar ends of the plant Tips of roots Tips of shoots |
|
|
|
Apical Meristems are also known for |
Shaping how the plant grows responsible for initial growth and development |
|
|
|
Lateral meristem are located in the .... |
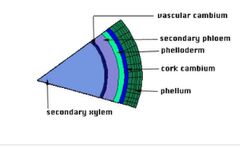
Root and stem |
|
|
|
Importance of lateral meristem |
Important for adding to the thickness or girth of the plant |
|
|
|
Lateral meristem are divided into 2 types |
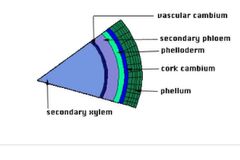
Vascular cambium Cork cambium |
|
|
|
vascular cambium |
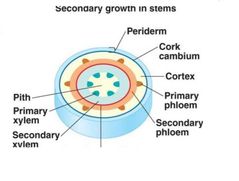
Entends throughout the tips and shooters of the plant as the plant grows in width new tissues are constantly produced by the cylindrical tissues called vascular cambium |
|
|
|
Cork cambium |
Found in the bark roots and stems of woody plants cylindrical Shape orinates under the epidermis of trees Runs parallel to the vascular cambium |
Phellogens |
|
|
Periderm consists of new living cells called |
Cambium cork Derived from cork cambium Replaces the epidermis in plants with secondary growth stages
|
|
|
|
Vascular and cork cambium |
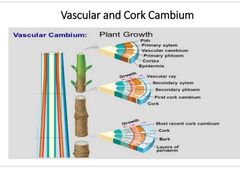
|
|
|
|
Intercalary meristems |
Instrumental in increasing the length of the inter node Mostly seen in moncots like grasses |
located at internodes are the base of the leaves |
|
|
Permanent tissues |
These are meristerm tissues that have lost their ability to divide and may further be classified into simple and complex tissues |
|
|
|
Simple permanent tissue |
Include parenchyma Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma |
|
|
|
Complex permanent tissues |
Include xylem and phloem |
|
|
|
Parenchyma |
These tissues are described as thin walled cells that are alive at maturity and make up the inside of non woody plants ...stems roots and leaves |
|
|
|
Parenchyma |
Parenchyma cells are not useful to the plant because of their thin walls ...they are useful in moving water and nutrients as well as healing and repair |
|
|
|
Parenchyma continues |
Based on location of the parenchyma cells they will vary in shape Found in the parenchyma cells are large central vacoules creating pressure between neighboring cells allowing the plant to store large amount of water and nutrients Its thin walls also permit the movement of sugars created in the leave |
|
|
|
Collenchyma cells |
These support the cells known for being alive at maturity, have thick walls composed of pectin. Hemicellouse and cellulose Very visable nucleus The tissues stored food Prevent tearing of leaves And performs the function of photosynthesis |
|
|
|
Sclerenchyma |
Known as dead tissues of plants because it's made up of hard wood Secondary walls of the cells are densely thick and contain lignin and hemcellulose. These cells are hard non growing and present in mature stems and barks |
|
|
|
Sclerenchyma |
the main types of sclenchyma are sclerosis and fiber Found in xylem ,phloem ,pith,cortes and peiderm Contribute to the hard covering of nuts fruits and other seeds Fibers add support to the plants as they elongate .especially important as plant continue to divide |
|
|
|
Complex permanent tissues |
Made up of more than one type of cells. 2 complex tissues are xylem and phloem |
|
|
|
Xylem and phloem |
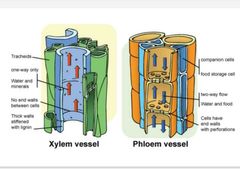
Found in the vascular bundles |
|
|
|
Xylem consist of |
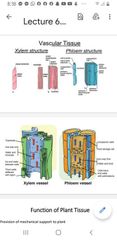
Tracheids Vessels Xylem Parenchyma Xylem fibers Main function to transport water and souble nutrients from root to plant |
|
|
|
Xylem cont |
Xylem conducts in one direction vertically The tracheids and vessels assist in transport of water while the xylem parenchyma stores the plant food |
|
|
|
Xylem fibers |
Xylem fibers act as support for the plant |
|
|
|
Phloem |
Consists of 4 elements sieve tubes ,companion cells. Phloem fibers and phloem parenchyma. Has the ability to conduct both directions |
|
|
|
Function of the phloem |
main function is transporting food from leaves to other parts of the plant |
|
|
|
Transport in plants |
Movement of water between cells occurs over a water potential gradient |
|
|
|
Movement of water in unobsturctive tube over a long distance eg xylem and pholem |
Is driven by a pressure potential gradient Water moves from a region of high pressure potential to a region of low water potential (bulk flow) |
|
|
|
Water potential |
The tendency of a solution to uptake water across a membrane water always moves across a selectively permeable membrane toward a region of lower of more negative water potential |
|
|
|
Water potential |
Water potential is measured by megapascals |
|
|
|
Importance of water potential |
Determines how water and minerals enter the roots and transported throughout the cells |
|
|
|
Solute potential |
Osmotic potential is the measure of the effect of dissolved solutes on the osmotic behaviour of the solution |
|
|
|
Water potential in plants |
Vacuole are filled with solutes sugar and minerals accumulation of solutes created pressure for water up take into vacuole |
|
|
|
Turgor pressure |
When cells are placed in water water moves into the cell based on negative solute potential ,this movement causes pressure in the cell because it can not expand due to the cell wall.this pressure is called turgor pressure |
|
|
|
Turgid |
When water enters the plant via osmosis and the pressure potential balances ,at this point the plant becomes turgid,plants will maintain turgidty until water is loss and the plants wilt |
|
|
|
Flaccid |
When the plant is not excerting pressure, osmotic potential is negative ,pressure potential is zero ,at this point the plant is flaccid |
|
|
|
Difference between bulk flow a d diffusion |
Bulk flow I'd driven by differences in pressure potential Whereas in diffusion it is driven by solute potential In bull flow flow occurs within hollow dead cells In diffusion occurs across plasma membrane of living cell In bulk flow moves entire solution..in diffusion moves either water or soulte |
|
|
|
Translocation |
Photosynthesis occurs in the leaves its products diffuse to the nearest small vein where they are actively transported into sieve tubes elements. This movement is called translocation |
|
|
|
Movement of products from photosynthesis |
Products are trans located from source to sinks... source an organ (eg mature leaf or storage root ) that produces more sugars than required . Sinks an organ eg root,flower ,developing friut,tuber,or immature leaf that consumes sugar for it's own growth and storage needs |
|
|
|
Sinks |
Sinks can turn into sources eg sweet potatoes which stores carbohydrates but can release these reserves need to nourish other organs |
|
|
|
Products translocated include...... |
Sugars Amino acids Some minerals Variety of solutes |
|
|
|
Loading and unloading |
The movement of products from the mesophyll to the sieve tubes occur eighter simplest of both symplasic and apoplast pathways depending on species of the plant |
|
|
|
Bulk flow |
Bulk flow is used to transport the products of photosynthesis |
|
|
|
Sinks |
Sometimes there are more. Sinks than can be supported by sources In such case plants may abort flowers,seeds or fruit in a phenomenon called self thining |
|

