![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the 6 structures that the vast majority of plants have |
Photosynthetic structures Support structures Nutrient uptake Reproductive structures Dispersal structures Alternation of generations |
|
|
What determines size, and what determines shape? |
Size - growth Shape - differential growth |
|
|
Early plant growth is primarily through what? |
Cell proliferation across primordium, and later only in subsets of cells known as meristemoids |
|
|
Describe the developmental process in plants |
Cells first have to acquire a new identity as leaf cells as opposed to meristem. The leaf then has to acquire polarity (outer and inner). Growth involves regulated patterns of cell division and expansion, as well as the differentiation of specialised cells |
|
|
What is made in the shoot apical meristem (SAM) and the root apical meristem (RAM)? |
SAM - stem, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds RAM - primary and lateral roots |
|
|
What is the name for the place where new branches/stems grow from? And where roots grow from? |
Branches/stems - axillary meristems Roots - basal meristems |
|
|
Describe the process of leaf formation |
1. SAM side cells are specified to change to a different state 2. Gives rise to leaf founder cells 3. Founder cell activation involves subsequent cell divisions to create a primordium that will develop into a leaf |
|
|
Describe what happens in the central and peripheral zones in the SAM |
Central zone: undifferentiated stem cells Peripheral zone: cells proliferate and differentiate into lateral organs Rib meristem: proliferate and differentiate into the stem |
|
|
Describe what each of the 3 layers do in the SAM |
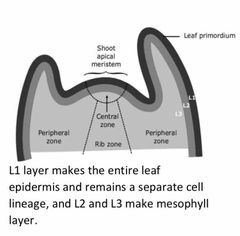
|
|
|
What are the different types of growth in plants? |
Linear - e.g. maize leaves, the primordium initially expands in all directions, and at later stages it grows by uni or bi-directional cell division Complex - in wider leaves, cell divisions contribute to the width of the blade. They are formed by persistent growth in isolated regions of the developing blade |
|
|
List the 4 different types of phyllotaxy |
Alternate Opposite Whorled Spiral |
|
|
Give examples of specialised cells within leaves |
Veins: transport water and nutrients Trichomes (hairs): can protect plants by deterring insects (e.g. stinging nettles) or even trap moist air around stomata to prevent water loss. Can be uni/multicellular, branched/unbranched or glandular/non-glandular. Guard cells: control stomata opening and closing |

