![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
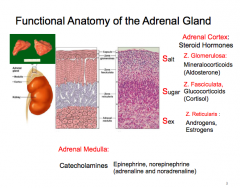
What are the layers of the adrenal cortex (four) and what is produced in each? |
|
|
|
What is the main action of mineral corticoids (aldosterone)?
|
Increase Na reabsorption and K secretion to maintain body fluid volume. |
|
|
What are the main actions of glucocorticoids (cortisol)?
Energy, glucose where, increased what for energy, immune and inflammation efffects |

|
|
|
What are the two functions of adrenal sex hormones? |
Growth, and developmental control |
|
|
What are the main functions of catecholamines? Increase what where? What type of response for fuel availability? |

|
|
|
How are adrenocortical hormones transported?
What is the transport globulins for each (corticosteroid, aldosterone, sex, progesterone)?
Which protein has low affinity reversible binding?
What two things is cortisol bound to?
What proteins is aldosterone bound to? How much is free? |

|
|
|
What are the purposes of transport binding proteins?
Activity, protection, life-time, delivery |

|
|
|
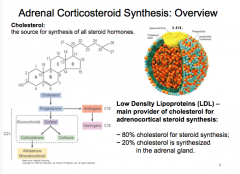
What is the source of all steroid hormones?
What is the main provider of cholesterol for adrenocortical steroid synthesis?
What is the pathway of cholesterol to aldosterone, androgens , and progesterone? |
|
|
|
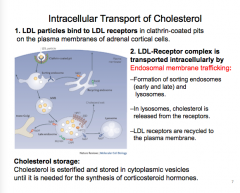
LDL particles bind to LDL receptors in ________ on plasma membranes of adrenal cortical cells.
LDL-receptor complex is transported intracellularly by ________________.
Formation of ________ and lysosomes. In lysosomes, __________ is release from the receptors. LDL receptors are ________ to the plasma membrane.
Cholesterol is ________ and stored in __________ until it is needed for the synthesis of _________ hormones. |
|
|
|
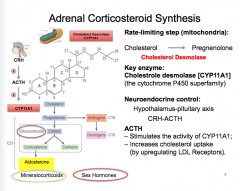
What is the rate limiting step (and where does it occur) in adrenal corticosteroid synthesis?
What is the key enzyme?
What controls this (which axis and which hormones)?
What are the two functions of ACTH? |
|
|
|
Draw out the adrenal steroid synthesis pathway, label the enzymes, label the zones of the adrenal cortex, and indicate the activators and inhibitor sod the pathway. |
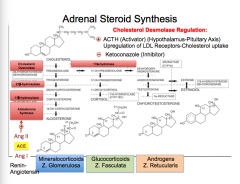
|
|
|
What are the target tissues for aldosterone (express MRs)?
What are two non-specific activation of MRs by glucocorticoids?
What is the enzyme that converts cortisol metabolite to cortisone? |
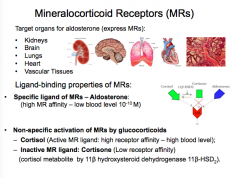
|
|
|
I. Genomic effects: Upregulation of Gene Expression (3-24 h, Delayed effects) = MINERALCORTICOIDS
Step 1: _________ penetrates the target cell, binds to MRs in the cytoplasm Forms a __________ complex;
Step 2: The hormone-receptor complex translocates to the __________; (transformation of the hormone-receptor complex)
Step 3: Binding to a _;
Step 4. Upregulation of gene expression (____________, _______________)
2. Non-Genomic Effects (<1h, _________ Effects) cAMP –, IP3 –, Ca2+– mediated signaling; |
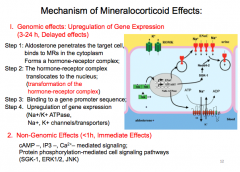
Non-genomic effects mediated via second messenger |
|
|
What are the effects of mineral corticoids on Na+, K+, and H+?
1. What pumps are affected? 2. What sodium channels? 3. What K channel in the kidney? 4. What kinase? What does this kinase activate resulting in what sodium and K levels? |
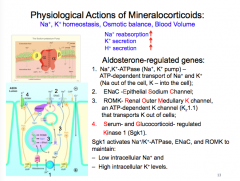
|
|
|
What is the main site of synthesis of glucocorticoids? Which GC is the most potent? Which has modest potency? What is the low active cortisol metabolite by 11-B-HSD2?
What are some synthetic glucocorticoids (in order of potency)? |
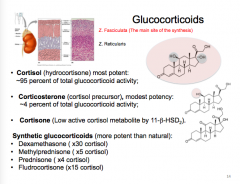
|
|
|
What re the key enzymes in cortisol biosynthesis? What are some drugs that can act on each? |
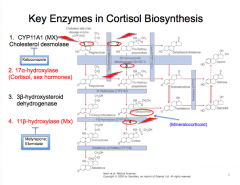
|
|
|
What type of rhythm is cortisol secretion? What two components is it regulated by?
When is cortisol production at its peak? Gradually declines by? When are the lowest levels? |
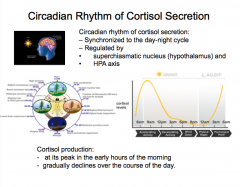
|
|
|
1. Glucocorticoids are _________. 5. Stimulation or _________ of gene expression (transactivation) 6. Suppression of genes via ___________factors (NFκB) (transrepression). |
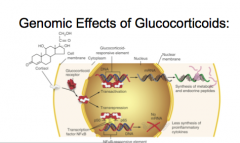
1. Glucocorticoids are cell-permeable 6. Suppression of genes via transcriptional factors (NFκB) (transrepression). |
|
|
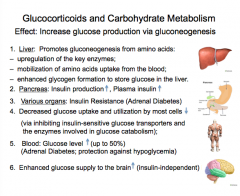
What is the overall effect of glucocorticoids? |
Increase glucose production via gluconeogenesis |
|
|
What are the target organs?
What happens in liver (promotes what from amino acids, up or down regulation of key enzymes, mobilization of what uptake from blood, enhanced ______ formation)?
What are the two effects in the pancreas (effects on insulin)?
|

|
|
|
What do many organs develop against in response to glucocorticoids?
What is the effect of glucose uptake and utilization by most cells? (increased or decreased)? How?
Does the blood glucose level go up or down?
Is glucose supply to the brain enhanced? |
|
|
|
What is the effect of glucocorticoids on protein metabolism?
1. Various Organs (Except the liver): __________ protein catabolism; __________ Protein Synthesis. – Increases _________ (catabolic effects) – Body weight __________ – Muscle __________
2. Liver: – __________ protein synthesis (upregulation of key enzymes); – __________ gluconeogenesis (convert amino acids to glucose) |

|
|
|
What is the overall effect of glucocorticoids on protein metabolism? |

|
|
|
Glucocorticoids and Fat Metabolism 1. Adipose tissue: _________ lipolysis, as an ___________ in the time of starvation: – Fat degradation to fatty acids ________
Result: ________ in gluconeogenesis, lipolysis and proteolysis
2. Food uptake _______ , Redistribution of body fat, paradoxical fat ________ in the body
3. High doses of oral cortisol can lead to _________ (deposition of fat in the chest and head, fat lump between the shoulders, rounded face); |

|
|
|
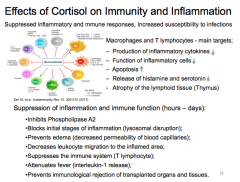
What is the effect of cortisol on immunity and inflammation?
__________ inflammatory and immune responses, ____________ susceptibility to infections Macrophages and _______ - main targets; – Production of inflammatory cytokines ______ – Function of inflammatory cells ______ - ______ of the lymphoid tissue (Thymus)
Suppression of inflammation and immune function (hours – days): • Inhibits Phospholipase ______ • Prevents ________ (_______ permeability of blood capillaries); • _________ leukocyte migration to the inflamed area; • _________ the immune system (T lymphocyte); |
|
|
|
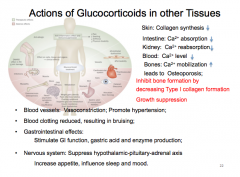
Actions of GC in other tissues: Skin: ________synthesis Intestine: Ca2+ absorption ____ Kidney: Ca2+ reabsorption _______ Blood: Ca2+ level ______ Bones: Ca2+ mobilization leads to ______; ________ bone formation by Growth suppression • Blood vessels:___________; Promote hypertension; • Blood clotting _______, resulting in bruising; • Gastrointestinal effects: • Nervous system: _______ hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis Increase appetite, influence ________ and mood. |
|
|
|
What are the male sex hormones?
What are the key enzymes?
What are two key enzyme deficiencies?
What are the female sex hormones?
The adrenal sex hormones have more of an effect for which sex? |
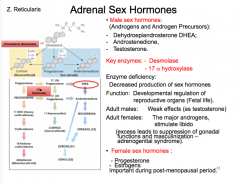
17-alpha-hydroxylase = decrease production of sex hormones??? 11-alpha-hydorylase= increased production sex hormones??? |
|
|
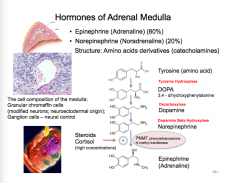
What are the hormones of the adrenal medulla?
What is the pathway of epinephrine synthesis starting with tyrosine?
It is increased by a high concentration of what? |
|
|
|
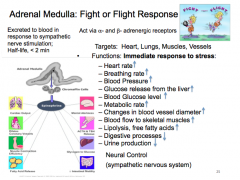
Adrenal medulla: Fight or Fligh Targets: What are the four? • Functions: Immediate response to _________: – Heart rate __ – Blood flow to skeletal muscles __ Neural Control |
|
|
|
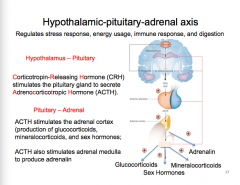
What is the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis? Draw it.
Regulates ______ response, ______ usage, _______ response, and _________. |
|
|
|
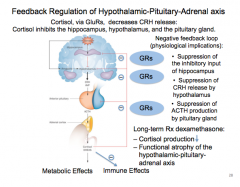
Cortisol effect on CRH release? What three areas of brain does cortisol inhibit?
• _______ of the inhibitory input of hippocampus • Suppression of _____ by hypothalamus • Suppression of ACTH production by _____
Long-term Rx dexamethasone: – Cortisol production ___ hypothalamic-pituitary- adrenal axis
Metabolic Effects ___ Immune Effects ___ |
|
|
|
What is stress?
What are some causes? |

|
|
|
What does moderate stress activate?
Acute Stress effects: – Energy production ___ |
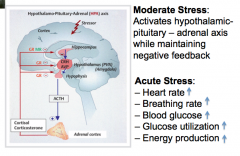
|
|
|
Effects of chronic stress:
– Excessive _____ and _____ of hypothalamic- pituitary – adrenal axis (overriding negative feedback); – Induces secrtion of – ________ of adrenal glands, adrenocortical hyperfunction; Major Health Problems: –Heart disease; –Immunosuppression; –Digestive problems; –Sleep disorders; –Anxiety, depression |
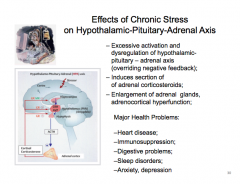
|

