![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
|
|
|
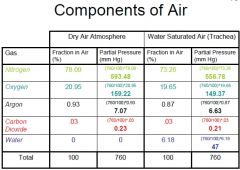
What are the PO2 & PCO2 values for the normal airway, alveolus, pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein?
|
Airway:
PO2: 149 mmHG PCO2: 0 mmHg Alveolus: PO2: 100 mmHg PCO2: 40 mmHg Pulmonary artery: PO2: 40 mmHg PCO2: 45 mmHg Pulmonary vein: PO2: 100 mmHg PCO2: 40 mmHg |
|
|
What is the normal pulmonary artery & vein O2 saturation, [HCO3-] & pH?
|
Pulmonary artery:
O2 sat.: 75 mmHg [HCO3-]: 22-28 mmHg pH: 7.35-7.45 Pulmonary vein: O2 sat.: 97 mmHg [HCO3-]: 22-28 mmHg pH: 7.35-7.45 |
|
|
Define anatomic dead space?
Define alveolar dead space? Define physiological dead space? |
Anatomic dead space is a volume of air that doesn't contribute to gas exchange (mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles - all conducting airways)
Alveolar dead space is the air volume within alveoli which are poorly ventilated or ventilated but w/ no or poor perfusion. Physiological dead space is anatomic dead space + alveolar dead space. |
|
|
Define wasted ventilation?
Define minute ventilation? Define alveolar ventilation? |
Wasted ventilation is the air volume within the physiological dead space.
Minute ventilation is the volume of air moved into the lungs per unit time...tidal volume x frequency [ V(E) = V(T) x f ] Alveolar ventilation [V(A)] is minute ventilation [V(E)] minus ventilatory dead space [V(d)]. [ V(A) = V(E) - V(d) ] |
|
|
What are the (2) methods for measuring dead space?
Which one is more accurate? |
1) Fowler's single breath N2 washout
& 2) Bohr method The Borh method is more accurate b/c it accounts for the total physiological dead space whereas the Fowler method only accounts for anatomical dead space and NOT alveolar dead space |
|
|
On a Fowler method graph when determining dead space, where do we estimate total dead space?
|
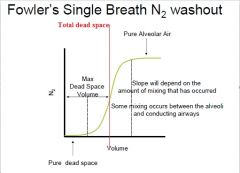
1/2 way point of the slope
|
|
|
How do you calculate dead space using the Bohr method? (equation)
How do you interpret the results? |
V(d) / V(t) = [ P(a)CO2 - P(E)CO2 ] / [ P(a)CO2 ]
V(d): physiological dead space volume V(t): tidal volume P(a)CO2: partial pressure of arterial CO2 P(E)CO2: partial pressure of expired CO2 The normal V(d) / V(t) ratio is ~0.3 which is about 1/3 of ventilation not-participating in gas exchange. (150 ml of 500 ml total) This value can increase significantly w/ disease. |
|
|
What is the relationship between alveolar ventilation and alveolar partial pressures/blood partial pressure of CO2?
|
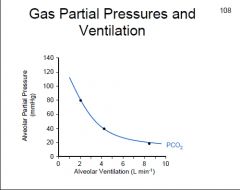
↑ventilation = ↓P(A)CO2...increase ventilation rate by 2 will decrease P(A)CO2 by 1/2
|
|
|
What is the alveolar gas equation used to calculate the mean partial pressure of O2 in the alveoli?
|
P(A)O2 = P(I)O2 - [ P(A)CO2 / R ]
P(I): inspired partial pressure O2 R: ~0.8 in normal conditions |
|
|
A patients alveolar partial pressure of O2 is 99 mmHg & a partial pressure of CO2 at 40 mmHg. What is their Inspired partial pressure of O2? (just know how to set the equation up)
|
P(A)O2 = P(I)O2 - [ P(A)CO2 / R ]
99 = P(I)O2 - [40 / 0.8 ] P(I)O2 = 149 |
|
|
Plotting alveolar partial pressures for PO2 & PCO2 on one graph will show what relationships?
|
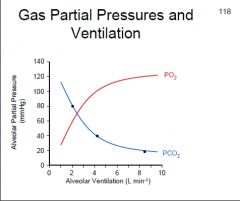
↑ventilation = ↓PCO2
↑ventilation = ↑PO2 |
|
|
Define:
Hypoventilation? Hyperventilation? Hypercapnia? Hypocapnia? Eupnea? Hypopnea? Hyperpnea? |
Hypoventilation: ↓alveolar ventilation w/ ↑P(a)CO2
Hyperventilation: ↑alveolar ventilation w/ ↓P(a)CO2 Hypercapnia: ↑CO2 in blood Hypocapnia: ↓CO2 in blood Eupnea: normal breathing Hypopnea: ↓ventilation in response to ↓metabolic CO2 production Hyperpnea: ↑ventilation in response to ↑CO2 production |

