![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
136 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Central Nervous System |
the division of the nervous system that is located in the skull and spine |
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System |
The division that is located outside the skull and spine |
|
|
Brain and spinal cord |
Two parts of the Central Nervous System |
|
|
Somatic Nervous System and Autonomic Nervous System |
Two parts of the Peripheral Nervous System |
|
|
Somatic Nervous System |
The part of PNS that controls external environment |
|
|
Afferent nerves |
Nerves that carry sensory signals from the skin, skeletal muscles, joints, eyes, ears so on to the CNS |
|
|
Efferent Nerves |
The nerves that carry motor signals from the CNS to the skeleteal muscles |
|
|
Autonomic Nervous System |
Regulates the body's internal environment |
|
|
Afferent Nerves |
Carry sensory signals from internal organs to CNS |
|
|
Efferent Nerves |
Carries motor signals from CNS to internal organs |
|
|
Sympathetic Nerves and Parasympathetic Nerves |
Two parts of Autonomic Nervous System |
|
|
Sympathetic Nerves |
Motor nerves that project from the CNS in the lumbar and thoracic regions of the spinal cord |
|
|
Parasympathetic Nerves |
Motor nerves that project from the brain and sacral region of the spinal cord |
|
|
Parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves |
Two stage neural paths |
|
|
Sympathetic systems |
The second stage of this nerve requires neurons to go for a substantial distance from their target organs |
|
|
Cranial Nerves |
Nerves that project from the brain |
|
|
I. Olfactory (Sensory) |
Cranial nerve that is responsible for smelling |
|
|
II. Optic(Sensory) |
Cranial nerve repsonsible got vision |
|
|
IV. Trochlear(Motor, Sensory) |
Cranial nerve for Eye Movement and sensory isgnals from certain eye muscles |
|
|
V. Trigeminal (Sensory, Motor) |
Cranial nerves for facial sensations and chewing |
|
|
VI. Abducens (Motor, Sensory) |
Eye movement and sensory signals from certain eye muscles |
|
|
VII. Facial (Sensory, Motor) |
Taste from anterior two-thirds of tongue and facial expression, secretion of tears, salivation, and cranial blood vessel dilation |
|
|
VIII. Auditory-Vestibular (Sensory) |
Audition; sensory signals from the organs of balance in the inner ear |
|
|
IX. Glossopharyngeal (Sensory, Motor) |
Taste from posterior third of tongue, Salivation and swallowing |
|
|
X. Vagus (Sensory & Motor) |
Sensations from abdominal and thoracic organs, control over abdominal and thoracic regions and muscles of the throat |
|
|
XI. Spinal Accesory (Motor, Sensory) |
Movement of neck, shoulders and head, sensory signals fron muscles of the neck |
|
|
XII. Hypoglossal (Motor & Sensory) |
Tongue Movements & sensory signals from tongue muscles |
|
|
Vagus nerves |
The longest cranial nerves |
|
|
What are the three meninges that protects the brain and spinal cord |
dura mater meninx, (arachnoid and subarachnoid membrane), pia mater meninx |
|
|
Dura mater membrane |
The first meninx found located below the skull |
|
|
Arachnoid membrane |
The membrane next to dura mater |
|
|
Subarachnoid space |
The space located beneath the arachnoid membrane that contains blood vessels and cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid |
The fluid that fills the subarachnoid space, the central canal and cerebral ventricles |
|
|
Central canal |
The small central channel that runs the length of the spinal cord |
|
|
Unipolar neuron |
A neuron with one process extending from its cell body |
|
|
Bipolar neuron |
A neuron with two processes extending from its cell body |
|
|
Interneuron |
Neurons with short axons or no axons at all |
|
|
Interneuron |
Its function is to integrate(unite) neural activity within single brain structure |
|
|
Nuclei |
The clusters of cell body in the CNS |
|
|
Ganglia |
The clusters of cell bodies in the PNS |
|
|
Tracts |
Bundles of axons in the CNS |
|
|
Nerves |
Bundles of axons in the PNS |
|
|
Glial cells |
__ outnumber neurons by 10 to 1 |
|
|
Oligodendrocytes |
This class of glial cells send out extensions, rich in myelin, that wrap around the axons of some neurons in the CNS |
|
|
Myelin sheaths |
This increase the speed on the and efficiency of axonal conduction |
|
|
Myelin |
This is a fatty insulating substance |
|
|
Schwann Cells |
This class of glial cells send out extensions, rich in myelin, that wrap around the axons of some neurons in the PNS |
|
|
Schwann cells |
This glial cell guide axonal regeneration(regrowth) after damage exclusive in the PNS |
|
|
Astrocytes |
Largest glial cell and star shaped. Play a roles in the passage of chemicals from the blood to the CNS found in the outer surfaces of blood vessels. |
|
|
Glue |
Glia from GLIAl cells means |
|
|
Golgi Stain |
Done by exposing neural tissue to potassium dichromate + silver nitrate = silver chromate that stained each neuron entirely black and produced a silhoutte of the neuron |
|
|
Camillo Golgi |
Who discovered golgi stain |
|
|
Franz Nissl |
The developer of Nissl Stain |
|
|
Cresyl Violet |
The most common dye used in the Nissl method |
|
|
Electron Microscopy |
A neuroanatomical technique that provides information about the details of neuronal steucture that has 1,500 magnification that is insufficient to reveal the fine anatomical details of a neuron |
|
|
Electron micrograph |
The result of coating the slices of a neural tissue with an electron absorbing substance then passing a beam of electrons through the tissue onto a photographic film |
|
|
Scanning electron microscope |
This tool provides spectacular electron micrographs in three dimension |
|
|
Antenograde tacing method & Retrograde tracing method |
The two types of neuroanatomical tracing techniques |
|
|
Anterograde tracing methods |
Used when an investigator wants to trace the paths of axons projecting away from the cell bodies using chemicals transported to the axons and terminal buttons |
|
|
Retrograde tracing methods |
Used when an investigator wants to trace the paths of axons projecting into an area using cheminals that are taken up by the terminal buttons and then transported backward to the cell bodies |
|
|
Anterior-posterior, dorsal-ventral, medial-lateral |
The three axes of the vertebrate nervous system |
|
|
Anterior |
This means toward the nose end |
|
|
Posterior |
This means toward the tail end |
|
|
Ventral |
This means toward the surface of the chest or the bottom of the head |
|
|
Dorsal |
This means toward the surface of the back or the top of the head |
|
|
Lateral |
This means away from the midline of the body |
|
|
Superior, inferior |
__ and __ used to refer to the top and bottom of the primate head |
|
|
Proximal |
With regards to PNS, this means closer to the CNS |
|
|
Distal |
With regard to the PNS, this means father from the CNS |
|
|
Midsagittal section |
A section cut down the center of the brain between the two hemispheres |
|
|
Cross section |
A section cut at a right angle to any long, narrow structure, such as spinal cord or a nerve |
|
|
Sagittal plane |
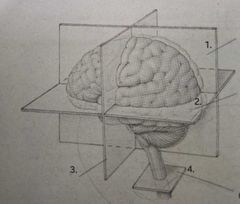
1. |
|
|
Horizontal Plane |
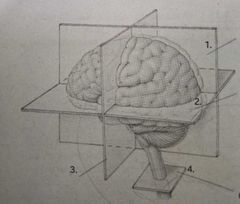
2. |
|
|
Coronal plane |
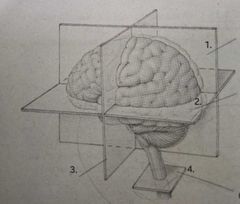
3. |
|
|
Cross section |
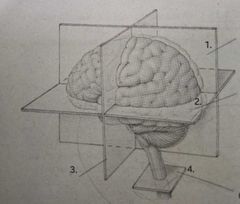
4. |
|
|
Gray matter and white matter |
This spinal cord comprise two different areas |
|
|
Gray matter |
The inner H-shaped core |
|
|
White matter |
The surrounding area of gray matter |
|
|
Gray matter |
Composed largely of cell bodies and unmyenalinated interneurons |
|
|
Gray matter |
Composed largely of cell bodies and unmyenalinated interneurons |
|
|
Dorsal horns |
The two dorsal arms of the spinal gray matter are called |
|
|
Dorsal root and ventral root |
Two roots of the spinal nerves found on the left and right side of the spine |
|
|
Spinal nerves |
These arw attached to thw spinal cord on the left and right |
|
|
Dorsal root |
Their cell bodies are grouped together outside the cord to form the dorsal root ganglia |
|
|
Forebrain, midbrain, & hindbrain |
The three swellings that occur at the anteior end of the tube found in the verterbrae embryo |
|
|
Telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metensephalon & myelencephalon |
The five swellings that compose the developing brain at birth |
|
|
Mesencephalon |
This swelling is also called the midbrain |
|
|
Myelencephalon |
Also called medulla. The posterior division of the brain |
|
|
Myelencephalon |
Composed of large tracts that carry signals between the brain and the body |
|
|
Reticular formation |
A complex network of about 100 tiny nuclei that occupies the cebtral core of the brain stem fron the posterior boundary of myelencephalon and the anterior boundary of the midbrain |
|
|
Reticulum |
It means little net |
|
|
Reticular activating system |
The reticular formation is also referred to as ___ as it also plays a vital role in arousal |
|
|
Reticular formation |
This involves a variety of functions— including sleep attention, movement, the maintenance of muscle tone, and various cardiac, circulatory, and respiratory reflexes. |
|
|
Pons & Cerebellum |
The two divisions of the Metencephalon |
|
|
Pons |
The bulge structure found in the brain's ventral surface |
|
|
Cerebellum |
It is the large convoluted structure on the brain stem's dorsal surface. Cerebellar damage eliminates the ability to precisely control one's movements and adapt to changing conditions. |
|
|
Tectum & tegmentum |
The two divisions of the mesencephalon |
|
|
Tectum |
The dorsal surface of the midbrain |
|
|
Colliculi |
The two pair of bumps found in the tectum |
|
|
Inferior colliculi |
The posterior pair with an auditory function |
|
|
Superior colliculi |
The anterior pair with the visual function |
|
|
Optic tectum |
In lower vertebrates, the function of the tectum is entirely vision thus it is referred as __. |
|
|
Periaqueductal gray, substantia nigra, red nucleus |
The three colorful structures found in the tegmentum |
|
|
Periaqueductal gray |
The gray matter situated around the cerebral aqueduct |
|
|
Cerebral aqueduct |
The duct connecting the third snd fourth ventricles; has the role in mediating the analgesic(pain reducing) effects of opiate drugs |
|
|
Substantia niagra |
Also called the black substance |
|
|
Thalamus & hypothalamus |
The two parts of diencephalon |
|
|
Thalamus |
The large two lobed structure that constitutes the top of the brain stem |
|
|
Massa intermedia |
The two lobes in the thalamus are joined by __ |
|
|
White lamina |
This is visible layer on the surface of the thalamus composed of myelinated axons |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Located below the anterior thalamus. It helps to regulate several motivated behaviors such as the hormones release by the pituitary gland |
|
|
Hypo |
It means "below" |
|
|
Pituitary gland |
The literal meaning is snot gland |
|
|
Optic chiasm |
The point at which the optic nerves from each eye come together |
|
|
Decussate, Contralateral, Ipsilateral |
The X shape is created because some of the axons of the optic nerve __ via the optic chiasm. The fibers are siad to be ___ and the nondecussaying fibers are said to be ___. |
|
|
Mammillary bodies |
Pair of spherical nuclei located on the inferior surface of the hypothalamus |
|
|
Telencephalon |
The largest brain division that mediates the brain's comolex function. |
|
|
Cerebral cortex |
The layer of tissue found in the cerebral hemispheres |
|
|
Cerebral cortex |
Also known as cerebral bark |
|
|
Lissen-cephalic |
Also known as smooth brained |
|
|
True |
The number and size of the cortical convolutions appear to be related more to body size. True or False |
|
|
Fissures |
The large furrows in the convoluted cortex |
|
|
Sulci |
The small furrows in the convoluted cortex |
|
|
Gyri |
The ridges between fissures and sulci |
|
|
Longitudinal fissures |
The largest fissures is called found in the cerebral hemispheres |
|
|
Cerebral commissures |
It is the hemisphere connecting tracts |
|
|
Corpus callosum |
The largest cerebral commissure |
|
|
Central fissure and lateral fissure |
The two major landmarks on the lateral surface of each hemisphere |
|
|
Frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe |
The four lobes of the brain |
|
|
Precentral gyri |
The largest gyri that contain motor cortex |
|
|
Postcentral gyri |
The largest gyri that contain somatosensory cortex |
|
|
Superior temporal gyri |
The largest gyri that contain the auditory cortex |
|
|
Occipital cortex |
The function of this cortex is entirely visuap |
|
|
Neurons & Glial cells |
Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells |
|
|
III. Oculomotor (Motor, Sensory) |
Cranial nerve responsible for eye movement and PUPILLARY CONSTRICTION and sensory signals from certain eye muscles |
|
|
https://embryo.asu.edu/pages/david-h-hubel-and-torsten-n-wiesels-research-optical-development-kittens |
Additional Reading |

