![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are several factors that make it difficult to determine how much radiation a patient has recieved
|
include the many quantities that can be used to express the amount of radiation, the different units that are used, and the generally uneven distribution of the radiation within the patients body.
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 main ways radiation quantities can be expressed
|
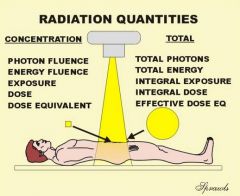
Concentration and total
|
|
|
|
What is being looked at when units of concentration are being used
|
photon fluence
energgy fluence exposure dose dose equivalent |
|
|
|
What is being looked at when the total radiation units are being used
|
total photons
total energy integral exposure intregral dose effective dose equivalent |
|
|
|
What is concentration of radiation mostly concerned with
|
the concentration of radiation at some point (such as exposure) , or to a specific tissue or organ ( absorbed dose)
|
|
|
|
What is total radiation concerned with
|
total radiation delivered to the body
|
|
|
|
What are the two types of Units of measurements of quantities of radiation
|
conventional
SI (metric) |
|
|
|
What are the quanities of radiation measured
|
concentration
total radiation |
|
|
|
What are the units
|
conventional
SI |
|
|
|
What are the conventional units of radiation measurement
|
the three R's
roentgen rad rem and coloumbs |
|
|
|
What units make more sense
|
the conventional (old will often have nice rounded numbers) the SI units where made for the sake of having one unifying system of measurment
|
The SI units are
C/kg (=roetgens) sieverts (rem) greys (rads) |
|
|
Why do the conventional units sometimes still get used today
|
However, because of their practicality and familiarity, some of the conventional units, especially the roentgen, will continue to be used by many.
|
|
|
|
How is all forms of electromagnetic radiation packaged
|
into small units of energy called photons
|
|
|
|
What is the physical differentce between different types of radiation
|
he physical difference between the different types of radiation, like light and x-rays is the amount of energy packed in each photon
|
|
|
|
What are 2 useful ways of expressing the radiation delivered to the body
|
total number or the concentration of the photons
|
|
|
|
graphic representation of how much energy is contained in sunlight and x ray radiation
|
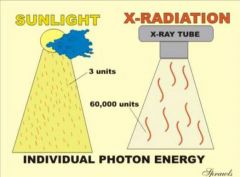
note how the total amount of photons or concentration is not related to the energy
|
|
|
|
Why is expressing the amount of radiation delivered to an object in terms of either the total number or the concentration of photon
|
There are several reasons. One is that the number of photons in a typical x-ray beam is such a large number, like in the billions or more, that it is not a practical quantity to work with
|
|
|
|
Do we have a practical instrument for counting large quanitites of photons in an X-ray bem
|
no
|
|
|
|
What is a good way to think of radiation
|
a shower of photons
|
|
|
|
What are 2 situations in medicine where the number of photons is important
|
Total photon (measure of radioactivity in curies or becquerels
Photon Concentration (fluence in photons/unit area) |
|
|
|
Where do photon fluence and total photons fit in the quantities chart
|
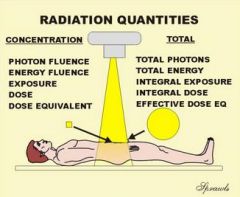
|
|
|
|
What is total photons
|
a measure of radioactivity (curies or becquerels)
|
|
|
|
How is the total photons measured
|
One method used to measure the radioactivity of a sample is to count the photons that are emitted. Then, with proper calibration factors, the counts per minute (CPM) can be converted into units of radioactivity, curies or becquerels.
|
|
|
|
What does photon concentration (fluence) determine
|
a factor of image quality
|
|
|
|
What is critical in medical imaging
|
the concentration of photons absorbed in the image forming process is a very critical factor (fluence= photons/unit area)
|
|
|
|
Why is the quantity of radiation absorbed so important
|
this is the principle factor that determines the amount of visual noise in the image. That is the so-called quantum (photon) noise
|
|
|
|
In projection imaging (radiography, fluoroscopy, gamma camera) the critical quantity is the concentration (photons/unit area) absorbed by the image receptor that determines the noise leve
|
yes
|
|
|
|
Is energy commonly used for expressing the amount of radiation delivered to the body
|
yes, rad or Gy (absorbed dose)
|
|
|
|
What is the concentration of energy absorbed in tissue
|
the concentration of energy absorbed in tissue is the quantity, Absorbed Dose (rad or Gy)
|
|
|
|
What is the total energy absorbed in a body
|
the total energy absorbed in a body is the Integral Dose (Joule in SI and conventional unit is the gram-rad)
|
|
|
|
What are 2 quantities we have talked about
|
Photons (total [curies or becquerels] and concentration[photon per unit area])
Energy (absorbed dose [Gy or Rad] and intergral dose [Joule in SI and conventional unit is the gram-rad]) |
|
|
|
Is Exposure a 3rd radiation quantity
|
yes
|
|
|
|
What is exposure
|
Exposure is a radiation quantity that expresses the concentration of radiation delivered to a specific point, such as the surface of the human body
|
|
|
|
d
|
d
|
|
|
|
Surface Exposure
|
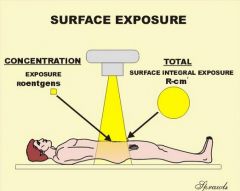
this is expressed as either surface intergral exposure or exposure
|
|
|
|
Surface Exposure
|
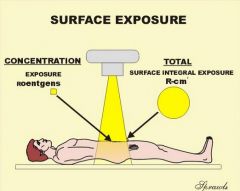
this is expressed as either surface intergral exposure or exposure
|
|
|
|
Where is Exposure and Surface intergral exposure located in the quantities chart
|
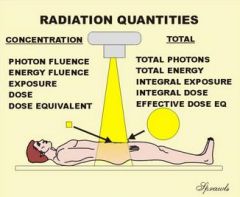
|
|
|
|
What are the units of exposure
|
roentgens
|
|
|
|
What are the units of surface integral exposure
|
R-cm^3
|
|
|
|
Is exposure a measure of concentration
|
yes
|
|
|
|
Is surface intergral exposure a measure of total dose
|
yes
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 units for expressing exposure
|
roentgen and SI coulomb/kg of air (C/kg of air)
|
|
|
|
What is the most common quantitiy used to express the amount of radiation at a given point
|
exposure
|
|
|
|
What is the more common term for photon concentration
|
photon fluence
MOVE |
|
|
|
How is total photons related to photon concentration or fluence
|
This quantity depends on the size of the exposed area and the radiation concentration. If the radiation is uniformly distributed over the exposed area, the total number of photons entering the patient can be found by multiplying the concentration (fluence) by the exposed area
|
|
|
|
What are the units of exposure
|
R (conventional)
Coloumbs/kg (SI) |
|
|
|
What is the conversion for roentgens to C/kg
|
1 R = 2.58 x 10-4 C/kg
|
|
|
|
What is the conversion factor for C/kg to R
|
1 C/kg = 3876 R
|
|
|
|
Exposure is the quantity most commonly used to express the amount of radiation delivered to a point.
|
yes
|
|
|
|
Why is exposure commonly used
|
The reason exposure is such a widely used radiation quantity is that it can be readily measured (total photons and photon fluence are very difficult to measure and that is one reason why that is not used)
|
|

