![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Theory:
|
an explanation of natural phenomena based on observation and accepted fundamental principles
|
|
|
"acceleration of a falling body is independent of its weight" who was the first to think of this idea?
|
galileo galilei
|
|
|
Physics:
|
the process by which we arrive at general principles that describe how the physical universe behaves.
- the study of all aspects of the universe. - about understanding how everything works |
|
|
range of validity:
|
it applies to a range of how valid a theory is.
|
|
|
Problem solving strategy 1.1: solving physics problems
|

|
|
|
Model:
|
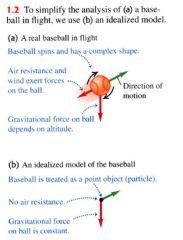
a simplified version of a physical system that would be too complicated to analyze in full detail.
|
|
|
Physical quantity:
|
any # that is used to describe a physical phenomenon quantitatively.
|
|
|
time:
|
based on an atomic clock which uses the energy difference between the two lowest energy states of the cesium atom
|
|
|
second (s):
|
the time required for 9,192,631,700 cycles of cesium atom's microwave radiation
|
|
|
meters (m):
|
the distance that light travels in a vaccum in 1/299,792,458 sec.
|
|
|
kilograms (kg):
|
the mass of a particular cylinder of platinum-iridium alloy kept at the international bureau of weights and measures.
|
|
|
formula for distance:
|
d = vt
v= velocity t= time |
|
|
Problem-solving strategy 1.2: unit conversions:
|

|
|
|
uncertainty: (aka: error):
|
b/c it indicates the max. difference there is likely to be between the measured value and the true value.
|
|
|
accuracy:
|
how close it is likely to be the true value.
|
|
|
Using significant figures:
|

|
|
|
velocity:
|
the speed combined with its direction of motion
|
|
|
force:
|
a push/pull exerted on a body
|
|
|
scalar quantity:
|
a single number
|
|
|
vector quantity:
|
has magnitude ("how much" or "how big") & a direction in space.
|
|
|
Displacement:
|
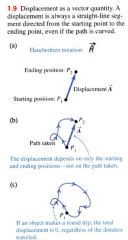
- simply a change in position of a point.
- is a vector quantity because we must state no only how far the particle moves, but also in what direction it is moving. |
|
|
What does negative of a vector mean?
|
a vector having the same magnitude as the original vector but the opposite direction "antiparallel"
|
|
|
Components of a vector:
|
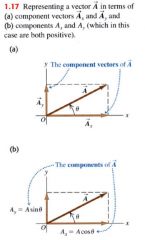
are just numbers, not vectors themselves.
|
|
|
definition of vector components from that of the trig. functions:
|
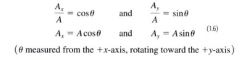
|
|
|
Finding the magnitude of a vector:
|
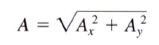
|
|
|
Finding the direction of a vector:
|

|
|
|
Unit Vector:
|
- a vector that has a magnitude of 1 with no units.
- only purpose is to point... to describe a direction in space. - (^) "hat/caret" symbol for a unit vector to distinguish it from ordinary vectors whose magnitude may/ maynot = 1 |
|
|
Unit Vector:
|
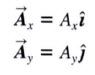
- a vector that has a magnitude of 1 with no units.
- only purpose is to point... to describe a direction in space. - (^) "hat/caret" symbol for a unit vector to distinguish it from ordinary vectors whose magnitude may/ maynot = 1 |
|
|
Scalar product (dot product):
|
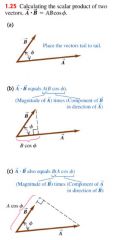
- draw the two vectors with their tails at the same point.
- angle between their direction ranges from 0 - 180. |
|
|
definition of the scalar (dot) product:
|
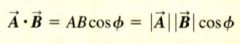
|
|
|
The scalar product of two parallel vectors is always equal to?
|
0
|
|
|
The scalar (dot) product in terms of components:
|
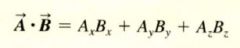
the scalar product of two vectors is the sum of the products of their respective components.
|
|
|
Vector product (cross product):
|
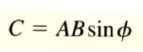
- denoted by vector A x vector B
- draw the two vectors with their tails at the same point. - a vector quantity with a direction parallel to this plane (parallel to both vector A and B). - the angle from vector A to vector B and take it to be the smaller of the two possible angles from 0 - 180 then sin of the angle is greater than or equal to 0 and C is never negative. |
|
|
The vector product of two parallel or antiparallel vectors is always = ?
|
0
|
|
|
The vector product of any vector with itself is ?
|
0
|
|
|
cross product (vector product) not commutative..
|
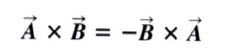
|
|
|
the right hand rule:
|
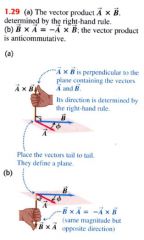
|
|
|
vector product can also be expressed in determinant form as:
|
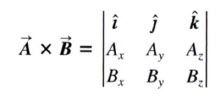
|
|
|
law of nature:
|
represents our best understanding of how nature behaves given certain limiting assumptions.
|
|
|
Summary:
|

|

