![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is CDTI
|
The Computed Tomography Dose Index, CTDI, is the special dose quantity that is used extensively to express absorbed dose in CT.
|
|
|
How is exposure converted to absorbed dose
|
you most know the ratio at a given photon energy. the ratio is called f
|
|
|
What does CDTI take into account
|
the direct radiation and the radiation from adjacent slices that result from scatter
|
|
|
What is the mean glandular dose
|
The Mean Glandular Dose (MGD) is the special dose quantity used in mammography.
|
|
|
What is the definition of mean glandular dose
|
It is defined as the mean, or average, dose to the glandular tissue within the breast.
|
|
|
Why is glandular tissue considered important
|
The assumption is that the glandular tissue, and not the fat, is the tissue at risk from radiation exposure
|
|
|
Is it possible to determine the radiation dose to glandular breast on a case by case basis
|
it is just about impossible to determine the actual dose to the glandular tissue during a specific mammographic procedure because of variations in breast size and distribution of glandular tissue within the breast.
|
|
|
What is MGD based on
|
The MGD is based on some standard breast parameter
|
|
|
What is the first step when measuring MGD
|
The first step is to determine the entrance surface exposure, or air kerma, to the breast. This can be measured directly with small dosimeters placed on the breast or calculated from the known calibration factors for the mammography equipment
|
|
|
What is the second step when measuring MGD
|
Then, the MGD is determined by multiplying the surface exposure value by published dose factors. The dose factor values are tabulated according to breast size and composition and the penetrating characteristics of the x-ray beam as determined by the anode material, filtration, and KV.
|
|
|
What standardized breast is used for for comparison of imaging techniques, evaluation of equipment performance, general dose management, and regulatory and accreditation purposes
|
A "standard" breast is used. The standard is a 4.2cm thick compressed breast consisting of 50% glandular tissue and 50% fat.
|
|
|
What does the standard breast correspond to
|
This corresponds to the standard phantom that is used for image quality evaluation and comparative dose determinations
|
|
|
What is the integral dose
|
Integral dose is the total amount of energy absorbed in the body. It is determined not only by the absorbed dose values but also by the total mass of tissue exposed
|
|
|
What are the conventional unites of integral dose
|
The conventional unit for integral dose is the gram-rad, which is equivalent to 100 ergs of absorbed energy
|
|
|
Theoretically how is the intergral dose calculated
|
The concept behind the use of this unit is that if we add the absorbed doses (rads) for each gram of tissue in the body, we will have an indication of total absorbed energy
|
|
|
What is the SI unit of integral dose
|
Since integral dose is a quantity of energy, the SI unit used is the joule
|
|
|
What is the conversion of integral dose from SI to conventional units
|
1 J = 1,000 gram-rad
|
|
|
Why is integral dose the the radiation quantity that most closely correlates with potential radiation damage during a diagnostic procedure.
|
This is because it reflects not only the concentration of the radiation absorbed in the tissue but also the amount of tissue affected by the radiation.
|
|
|
How is the integral dose calculated
|
There is no practical method for measuring integral dose in the human body. However, since most of the radiation energy delivered to a body is absorbed, the integral dose can be estimated to within a few percent from the total energy delivered to the body
|
|
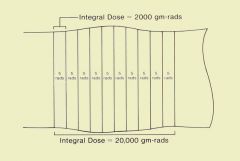
|
Computed tomography can be used to demonstrate integral dose, as illustrated below. We begin with a one-slice examination and assume that the average dose to the tissue in the slice is 5 rad. If there are 400 g of tissue in the slice, the integral dose will be 2,000 gram-rad. If we now perform an examination of 10 slices, but all other factors remain the same, the dose (energy concentration) in each slice will remain the same. However, the integral dose (total energy) increases in proportion to the number of slices and is now 20,000 gram-rad. In this example we made the simplifying assumption that no radiation is scattered from one slice to another. In reality, some radiation is exchanged between contiguous slices but that does not affect the concept presented.
|
|
|
What are dose equivalents used for
|
Dose equivalent (H) is the quantity commonly used to express the biological impact of radiation on persons receiving occupational or environmental exposures. Personnel exposure in a clinical facility is often determined and recorded as a dose equivalent.
|
|
|
What is the dose equivalent proportional to
|
Dose equivalent is proportional to the absorbed dose (D), the quality factor (Q), and other modifying factors (N) of the specific type of radiation
|
|
|
What is the quality factor for most stuff in radiology
|
Most radiations encountered in diagnostic procedures (x-ray, gamma, and beta) have quality and modifying factor values of 1
|
|
|
What is a major exception to this rule
|
For example, alpha particles have a quality factor value of approximately 20
|
|
|
continue with this if necessary
|
http://www.sprawls.org/ppmi2/RADQU/#ABSORBED DOSE
|
|
|
What is equivalent dose
|
equivalent dose, is a computed average measure of the radiation absorbed by a fixed mass of biological tissue, that attempts to account for the different biological damage potential of different types of ionizing radiation.
|
|
|
What are the units of equivalent dose
|
Equivalent dose is dimensionally a quantity of energy per unit of mass, and is usually measured in sieverts or rems.
|
|
|
What is the reason for effective dose
|
The concept of effective dose is used in radiation protection as an estimate of the stochastic effect that a non-uniform radiation dose has on a human.
|
|
|
What quantity is used to express relative risk to patients
|
Effective dose is becoming a very useful radiation quantity for expressing relative risk to humans, both patients and other personnel
|
|
|
What does effective dose take in to consideration
|
It takes into account the specific organs and areas of the body that are exposed
|
|
|
Why is important to consider organs individually
|
The point is that all parts of the body and organs are not equally sensitive to the possible adverse effects of radiation, such as cancer induction and mutations
|
|
|
How are different organs weighted differently
|
For the purpose of determining effective dose, the different areas and organs have been assigned tissue weighting factor (wT) value
|
|
|
What is the formula for effective dose
|
Effective Dose (Gy) = Absorbed Dose (Gy) x wT
|
|
|
What happens if more than one organ is irradiated during a procedure
|
f more than one area has been exposed, then the total body effective dose is just the sum of the effective doses for each exposed area.
|
|
|
Is effective dose useful for comparing different types of radiologic exams
|
There is often a need to compare the amount of radiation received by patients for different types of x-ray procedures, for example, a chest radiograph and a CT scan. The effective dose is the most appropriate quantity for doing this. Also, by using effective dose it is possible to put the radiation received from diagnostic procedures into perspective with other exposures, especially natural background radiation
|
|
|
effective dose
|
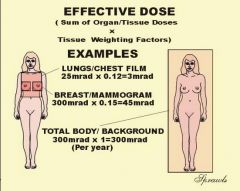
|
|
|
sample weighting factors
|
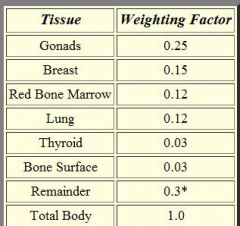
|

