![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In an EKG, what does the T-wave measure? |
Repolarization of the ventricles |
|
|
In response to hemhorrage, what happens to the heart rate? |
Heart rate increases |
|
|
Which blood type is known as the universal acceptor? |
AB+ |
|
|
Which blood type is known as the universal donor? |
O- |
|
|
What effect does hypoxia have on EPO levels in the body? |
EPO levels increase |
|
|
In order to start the intrinsic pathway, what must be exposed in order to activate the clotting factor? |
Collagen |
|
|
What is the primary component of blood plasma? |
Water |
|
|
If hemhorraging is occurring, what is happening to blood volume? |
Decreases |
|
|
The term hypertrophy, when referencing skeletal muscle cells, refers to: |
Increase in size |
|
|
If the heart is undergoing ventricular diastole, what is occurring? |
Relaxation of the ventricles |
|
|
What ionic atom is found in the center of each hemoglobin subunit? |
Iron |
|
|
What are the large cells that break off fragments to form platelets? |
Megakaryocytes |
|
|
Identify the tissue layer that surrounds the outside of a skeletal muscle group. |
Epimysium |
|
|
What are the three phases of hemostasis (blood clotting)? |
Vascular-Platelet-Coagulation |
|
|
In an EKG, what does the QRS complex measure? |
Depolarization of the ventricles |
|
|
What is the specific structure on the sarcolemma of a muscle cell that has the receptors for neurotransmitters? |
Motor end plate |
|
|
Slow fibers, the type of skeletal muscle cells found in parts of the body responsible for long term, moderate tension contractions have much higher concentration of which molecule? |
Myoglobin |
|
|
Based on capillary hydrostatic pressure only, which direction will fluid move-into or out of the bloodstream? |
Out |
|
|
In an EKG, what does the P-wave measure? |
Depolarization of the atria |
|
|
When does isovolumetric contraction of the ventricles occur? |
Ventricle systole: 1st phase |
|
|
How does the anticoagulant Antithrombin-III act to prevent clotting? |
Inhibits thrombin |
|
|
The hormone Angiotensin II increases blood pressure by: |
Causing sodium retention |
|
|
Where in the body are most of the clotting factor proteins synthesized? |
The Liver |
|
|
Which vitamin is required by the liver for proper synthesis of clotting factors? |
Vitamin K |
|
|
Which molecule normally covers the active site in G-actin subunits to prevent myosin from binding? |
Tropomyosin |
|
|
During a secondary response to an immunogen, the production of antibodies occurs much quicker than during the primary response. What cells are present that allow this to happen? |
Memory B-Cells |
|
|
How many days does the average red blood cell last in the body? |
120 days |
|
|
Movement of skeletal elements by muscle is caused by: |
Pulling (tension) |
|
|
Based on Frank-Starling principle, if more blood is returned to the heart, what happens to the stroke volume? |
Stroke volume will increase |
|
|
What is the most prevalent type of white blood cell (leukocyte) found in the body? |
Neutrophil |
|
|
If a motor unit is stimulated to contract in order to generate movement and no movement happens, which muscular concept indicated the addition of more motor units to increase tension? |
Recruitment |
|
|
What effect does increasing the level of ADH ( antidiuretic hormone) have on blood pressure? |
Increases blood pressure |
|
|
During the initiation of contraction of skeletal muscle, what molecule does Ca2+ bind to? |
Troponin |
|
|
What physiologic aspect of the blood counteracts hydrostatic pressure at the level of the capillaries thus allowing a great amount of fluid to be reabsorbed? |
Blood colloid osmotic pressure |
|
|
If glucose is broken down in skeletal muscle to create ATP in the absence of O2, which by product is produced that commonly creates “sore” muscle? |
Lactic acid |
|
|
How many subunits compose the hemoglobin protein? |
4 |
|
|
Which type of skeletal muscle fibers are large diameter and create powerful contractions? |
Glycolytic |
|
|
Which type of white blood cell is primarily responsible for destroying mutated or cancerous cells within the body? |
NK lymphocytes |
|
|
What is the normal pH of human blood? |
7.4 |
|
|
What is the most prevalent protein found in blood plasma? |
Albumin |
|
|
Which type of white blood cell is primarily infected by the HIV/AIDS virus? |
T-cell lymphocytes |
|
|
Based on what was presented in class, which muscle would have the smaller motor units? |
Hands |
|
|
In a skeletal muscle cell, which organelle stores a high concentration of Ca2+? |
Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
In order for the thin filament to release their bond, what is required |
ATP |
|
|
The extrinsic pathway begins when which clotting factor is activated? |
Factor III |
|
|
When the thin and thick filament interact to form bonds for contraction, at what amount of overlap will the maximal amount of tension be able to be produced? |
Optimal resting length |
|
|
What is the maximum conduction rate through the AV node? Assume there is no damage or other stimulation from drugs. |
230bpm |
|
|
During excitation-contraction coupling, what is released by the sarcoplasmic reticulum when an action potential arrives at the muscle? |
Calcium |
|
|
If the heart is undergoing atrial systole, what is occurring? |
Contraction of the atria |
|
|
Which category of plasma proteins are antibodies of the immune system a part of? |
Globulins |
|
|
Which group of cells in the heart are considered to be the pacemaker cells which are responsible for initiating the cardiac cycle? |
Sino-atrial node |
|
|
Which type of white blood cell is responsible for producing antibodies? |
B-cell lymphocytes |
|
|
Which plasma protein is primarily responsible for binding to free iron in the bloodstream? |
Transferrin |
|
|
How long does it take electrical activity to conduct through the AV node? |
100msec |
|
|
Which organ in the human body is responsible for removing old/damaged red blood cells? |
Liver, Red bone marrow, Spleen. (All the above) |
|
|
The term “prepotential” refers to what physiologic feature of cardiac muscle cells? |
Membrane drifts toward threshold after repolarization |
|
|
Where in the body is the plasma protein albumin synthesized? |
Liver |
|
|
If muscle contracts and the tension increases but the overall length of the muscle does not, this type of contraction in known as: |
Isometric |
|
|
Which neurotransmitter is commonly responsible for stimulating skeletal muscle? |
Acetylcholine |
|
|
The Bainbridge (Atrial) reflux increases heart rate based on: |
Stretching of the atria due to increased venous return |
|

Identify the Z-line of the sarcomere |
C |
|

Identify the I-band of the sarcomere |
A |
|
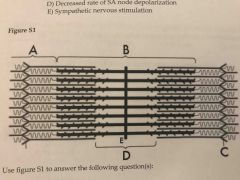
Identify the H-zone of the sarcomere |
D |
|

Identify the M-line of the sarcomere |
E |
|

At (2), why does blood flow from the atria into the ventricles? |
Pressure in the ventricles is lower than that of the atria |
|

What is occurring at (4)? |
Isovolumetric contraction of the ventricles |
|

At (8), why is there passive flow of blood from the atria into the ventricles? |
Pressure in the ventricles is lower then that of the atria |
|
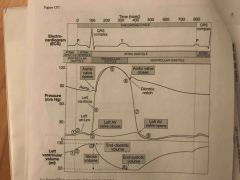
At (7), why does the volume inside the ventricles not change? |
Atrioventricular valves are closed |
|
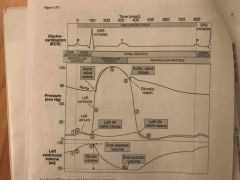
At which area does ventricular diastole (late) occur? |
8 |
|
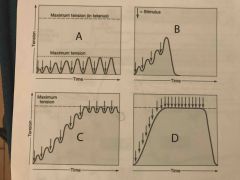
Which muscle contraction diagram shows a condition known as treppe? |
A |
|
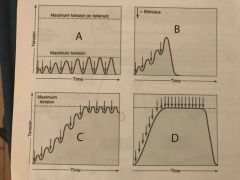
Which muscle contraction diagram shows a condition known as complete tetanus? |
D |
|
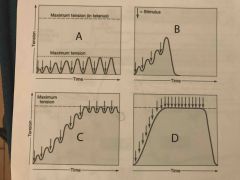
Which muscle contraction diagram shows a condition known as incomplete tetanus? |
C |
|
|
If a muscle contracts and the overall length of the muscle gets shorter while the tension remains constant, this type of contraction is known as? |
Isotonic |
|
|
What part of the thin filament does the myosin head bind to during contraction? |
Active site |
|
|
At what rate do the cells of the SA node spontaneously depolarize in the absence of any other input? |
80 to 100bpm |
|
|
Identify the inner most layer of a normal blood vessel |
Tunica intima |
|
|
Define Hypoxia |
Low oxygen levels in the tissue |
|
|
In order to maintain muscular tension over an extended period of time, many motor units must be utilized. What is this tension generation known as? |
Asynchronous motor unit summation |
|
|
Which type of capillary features large perforated regions to allow movement of large molecules out of the bloodstream and are found largely in the liver and spleen? |
Sinusoids |
|
|
What is the first to increase when a muscle contracts? |
Internal tension |
|
|
What is the defining characteristic of an artery? |
Carries blood away from the heart |
|
|
Which enzyme is responsible for converting fibrogen into fibrin? |
Thrombin |
|
|
At any given time, approximately what percent of the blood in the human body is within the venous vasculature? |
64% |
|
|
What is the primary protein that makes up the thin filament of the sarcomere? |
Actin |
|
|
Which metabolic cycle removes excess lactic acid from muscles? |
the Cori Cycle |
|
|
Fenestrated capillaries differ from continuous capillaries in that: |
Fenestrated capillaries have perforations |
|
|
What is the function of the T-tubules within skeletal muscle? |
Quickly disperse the muscle action potential throughout the cell |
|

At which area does Ventricular diastole (late) occur? |
8 |

