![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Light |
Form of electromagnetic radiation travels as waves |
|
|
Photon |
A packet of light |
|
|
Equation for photosynthesis |
Carbon dioxide + water + energy = glucose + oxygen |
|
|
Chlorophyll |
Green pigment Light absorbing Begins photosynthesis |
|
|
What is the primary absorbing pigment in all photosynthetic organisms? |
Chlorophyll |
|
|
Chlorophyll a |
Blue-green Primary absorbing pigment Absorbs dark blue and orange Transfers energy from sun to reactions of photosynthesis |
|
|
Chlorophyll b |
Yellow-green Accessory pigment Absorbs light blue and dark yellow Absorbs photons that "a" absorbs poorly or not at all |
|
|
Chloroplast |
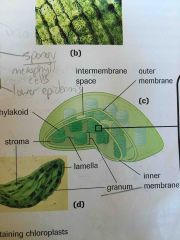
Membrane bound organelle Carries out photosynthesis Captures solar energy Obtains CO2 and water |
|
|
Stroma |
Protein rich liquid that fills the interior of the chloroplast |
|
|
Thylakoid |
Flattened membrane sacs forming a separate compartment within STROMA of CHLOROPLAST Are stacked on top of each other A group = grana |
|
|
Grana |
Stacks of thylakoids |
|
|
Lamellae |
Groups of in stacked THYLAKOIDS that connect GRANA to one another |
|
|
Thylakoid membrane |
Membrane within CHLOROPLAST Contains light gathering pigment molecules and ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAINS |
|
|
Thylakoid lumen |
Fluid filled space inside THYLAKOID |
|
|
How are the wave length and energy of a photon related? |
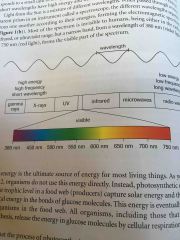
Short wave length = high energy Long wave length = Low energy |
|
|
What pigments are present in green leaves? |
Chlorophyll a, b, carotenoids, xanthophylls, anthocyanins |
|
|
ATP |
Adenosine Tri Phosphate Contains 3 high energy phosphate bonds Primary energy source for cellular functions |
|
|
ADP |
Adenosine Di Phosphate Contains 2 high energy phosphates |
|
|
NADP+
|
Electron acceptor Accepts 1 hydrogen atom and 2 electrons |
|
|
NADPH |
Electron donor Donates 1 hydrogen atom and 2 electrons |
|
|
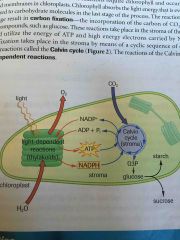
Stage 1 Light dependant reactions |
1st set of reactions in photosynthesis Light excited electrons in chlorophyll Powers ATP synthesis Results in reduction of NADP+ and NADPH |
|
|
Stage 2 Light independent reactions (Calvin cycle) |
2nd set of reactions Do NOT require solar energy |
|
|
Calvin cycle |
Set of reactions in STROMA of chloroplasts Fixes carbon in CO2 into carbohydrate molecules Recycles coenzymes |
|
|
Stage 3 Carbon fixation |
Incorporating CO2 molecules into carbohydrate molecules |
|
|
Photosystem |
Cluster of pigments embedded in the THYLAKOID MEMBRANE of a CHLOROPLAST Absorbs light energy |
|
|
Oxidation vs reduction reactions |
O- atom looses elections R- atom gains electrons OIL RIG oxidation is loss Reduction is gain |
|
|
ATP synthase complex |
Specialized protein complex Embedded in THYLAKOID MEMBRANE Allows H+ ions to escape from LUMEN Resulting energy generated ATP |
|
|
ATP synthase complex |
Specialized protein complex Embedded in THYLAKOID MEMBRANE Allows H+ ions to escape from LUMEN Resulting energy generated ATP |
|
|
Chemiosmosis |
Process of synthesizing ATP using energy of electrochemical gradient and ATP SYNTHASE ENZYME |
|
|
Electron transport chain |
Series of progressively stronger electron acceptors Energy is released each time an electron is transferred |
|
|
Photolysis |
Chemical reaction Compound is broken down by light Water molecules are split |
|
|
Where are photosystems I and II located? |
Thylakoid membrane of chloroplast |
|
|
What happens when chlorophyll absorbs a photon? |
Solar energy is captured Electrons are excited |
|
|
What happens when chlorophyll absorbs a photon? |
Solar energy is captured Electrons are excited |
|
|
How are the electrons passed on in the electron transport chain replaced? |
Replaced by electrons that came from water as a result of photolysis |
|
|
Where do light dependant reactions take place? |
Thylakoids |
|
|
Where does carbon fixation take place? |
Stroma |
|
|
Where does carbon fixation take place? |
Stroma |
|
|
What happens to electrons that are released during photolysis? |
They enter the electron transport chain |
|
|
Where does carbon fixation take place? |
Stroma |
|
|
What happens to electrons that are released during photolysis? |
They enter the electron transport chain |
|
|
What is the role of oxidation and reductions in the electron transport chain? |
To release energy in small amounts |
|
|
What are the H+ ions that are pulled inside the THYLAKOID MEMBRANES used for? |
Building a positive charge |
|
|
Where does carbon fixation take place? |
Stroma |
|
|
What happens to electrons that are released during photolysis? |
They enter the electron transport chain |
|
|
What is the role of oxidation and reductions in the electron transport chain? |
To release energy in small amounts |
|
|
What are the H+ ions that are pulled inside the THYLAKOID MEMBRANES used for? |
Building a positive charge |
|
|
Why is the production of NADPH important? |
To transfer high energy electrons to Calvin cycle |
|
|
What is Chemiosmosis? |
Making ATP from an H+ ion concentration gradient |
|
|
What is Chemiosmosis? |
Making ATP from an H+ ion concentration gradient |
|
|
Where in the chloroplast does the Calvin cycle occur? |
The stroma |
|
|
What is Chemiosmosis? |
Making ATP from an H+ ion concentration gradient |
|
|
Where in the chloroplast does the Calvin cycle occur? |
The stroma |
|
|
What is the final product of the Calvin cycle? |
G3P ➡️ glucose |
|
|
What is the primary function of photosynthesis? |
Convert electromagnetic radiation into chemical potential energy |
|
|
Active transport |
Movement of substance through membrane Against concentration gradient Uses membrane bound carrier proteins (pumps) and energy from ATP |
|
|
How do carrier proteins use ATP to transport molecules across the membrane? |
ATP converts to ADP This releases energy The energy changes he shape of the carrier to allow the molecule to pass through |
|
|
How is ATP used in muscle contraction? |
Muscle contraction involves 2 protein molecule sliding past each other Energy from ATP changes the shape of one molecule causing it to pull the other |
|
|
Aerobic cellular respiration |
Reactions that take place in the presence of oxygen Releases energy stored in glucose Step 1: glycolysis 2: pryuvate oxidation 3: Krebs cycle 4: electron transport chain and Chemiosmosis |
|
|
Anaerobic cellular respiration |
Reactions that take place without oxygen and releases energy stored in glucose Step 1: glycolysis 2: fermentation |
|
|
Glycolysis |
A glucose molecule is broken into two pryuvate molecules in the cytoplasm of a cell |
|
|
What is the first step in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration? |
Glycolysis |
|
|
What does glycolysis mean? |
Greek for "sugar splitting" |
|
|
What are the final products of glycolysis? |
NADH + 2 pyruvate molecules |
|
|
Where in the chloroplast do light dependant reactions occur? |
Thylakoid membrane |
|
|
What are the products of light dependant reactions? |
O2 ATP NADPH |
|
|
What gas is released as a byproduct of the light dependant reactions of photosynthesis? |
O2 (oxygen) |
|
|
What molecule is the source of oxygen? |
H2O |
|
|
What are NADH and FADH2? |
Electron carriers Donate electrons |
|
|
What are NAD+ and FAD+? |
Electron carriers Accept electrons |
|
|
Carbon fixation cycle |
Dark reactions Light independent Calvin cycle |
|
|
What is the primary function of cellular respiration? |
Convert glucose into ATP which is used by cells that need the energy for processes |
|
|
How do the oxidation and reduction reactions in electron transfer help form ATP? |
The energy released from these reactions attach a free phosphate to ADP to make ATP |
|
|
What stages of aerobic respiration take place in the mitochondria? |
Krebs cycle Electron transport chain Chemiosmosis |
|
|
What stages of aerobic respiration take place in the mitochondria? |
Krebs cycle Electron transport chain Chemiosmosis |
|
|
Krebs cycle |
Transfers energy from organic molecules to ATP, NADP, and FADH2 Removes carbon atoms as CO2 |
|
|
What stages of aerobic respiration take place in the mitochondria? |
Krebs cycle Electron transport chain Chemiosmosis |
|
|
Krebs cycle |
Transfers energy from organic molecules to ATP, NADP, and FADH2 Removes carbon atoms as CO2 |
|
|
Oxidative ATP synthesis |
Production of ATP from a series of oxidation reactions |
|
|
What stages of aerobic respiration take place in the mitochondria? |
Krebs cycle Electron transport chain Chemiosmosis |
|
|
Krebs cycle |
Transfers energy from organic molecules to ATP, NADP, and FADH2 Removes carbon atoms as CO2 |
|
|
Oxidative ATP synthesis |
Production of ATP from a series of oxidation reactions |
|
|
What are the final products of aerobic cellular respiration? |
6 CO2 6 H2O 36 ATP |
|
|
What stages of aerobic respiration take place in the mitochondria? |
Krebs cycle Electron transport chain Chemiosmosis |
|
|
Krebs cycle |
Transfers energy from organic molecules to ATP, NADP, and FADH2 Removes carbon atoms as CO2 |
|
|
Oxidative ATP synthesis |
Production of ATP from a series of oxidation reactions |
|
|
What are the final products of aerobic cellular respiration? |
6 CO2 6 H2O 36 ATP |
|
|
Only 36% of the energy of glucose is converted to ATP. What does the rest become? |
FADH2 NADH |
|
|
In eukaryotic cells, where does glycolysis occur? |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
In eukaryotic cells, where does glycolysis occur? |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
What 2 products of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria for further processing? |
NADH Pyruvate |
|
|
In eukaryotic cells, where does glycolysis occur? |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
What 2 products of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria for further processing? |
NADH Pyruvate |
|
|
What part of a glucose molecule provides electrons in cellular respiration? |
Hydrogen |
|
|
In eukaryotic cells, where does glycolysis occur? |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
What 2 products of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria for further processing? |
NADH Pyruvate |
|
|
What part of a glucose molecule provides electrons in cellular respiration? |
Hydrogen |
|
|
How is energy used to drive the synthesis of ATP? |
Chemiosmosis |
|
|
Fermentation |
Recycling products of glycolysis where either CO2 and ethanol, or lactic acid are the final products |
|
|
Fermentation |
Recycling products of glycolysis where either CO2 and ethanol, or lactic acid are the final products |
|
|
Alcohol fermentation |
Form of fermentation occurring in yeast NADH passes it's hydrogen atoms to acetaldehyde, generating CO2, ethanol and NAD+ |
|
|
Fermentation |
Recycling products of glycolysis where either CO2 and ethanol, or lactic acid are the final products |
|
|
Alcohol fermentation |
Form of fermentation occurring in yeast NADH passes it's hydrogen atoms to acetaldehyde, generating CO2, ethanol and NAD+ |
|
|
Lactic acid fermentation |
Fermentation occurring in animal cells NADH transfers its hydrogen atoms to pyruvate, regenerating NAD+ and lactic acid |
|
|
Other than ATP, what is a nonalcoholic product of alcohol fermentation? |
CO2 |
|
|
How many molecules of ethanol are produced by the fermentation of 1 molecule of glucose? |
2 |
|
|
How many molecules of ethanol are produced by the fermentation of 1 molecule of glucose? |
2 |
|
|
How much oxygen is used during the fermentation of 1 glucose molecule? |
None |
|
|
How many molecules of ethanol are produced by the fermentation of 1 molecule of glucose? |
2 |
|
|
How much oxygen is used during the fermentation of 1 glucose molecule? |
None |
|
|
Lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid from __________ |
Glucose |
|
|
How many molecules of ethanol are produced by the fermentation of 1 molecule of glucose? |
2 |
|
|
How much oxygen is used during the fermentation of 1 glucose molecule? |
None |
|
|
Lactic acid fermentation produces lactic acid from __________ |
Glucose |
|
|
How do humans feel the presence of lactic acid in the tissues of the body? |
Muscle fatigue, stiffness, sorenessa |
|
|
The main function of light dependant reactions is the production of: |
Hydrogen to form NADH and ATP |
|
|
The main function of light dependant reactions is the production of: |
Hydrogen to form NADH and ATP |
|
|
The product of glycolysis in animals when oxygen is not present is: |
Lactic acid |
|
|
The main function of light dependant reactions is the production of: |
Hydrogen to form NADH and ATP |
|
|
The product of glycolysis in animals when oxygen is not present is: |
Lactic acid |
|
|
The product in glycolysis in plants when oxygen isn't available is: |
Ethanol and carbon dioxide |
|
|
The molecule that is recycled in light independent reactions is: |
Ribulose biphosphate |

