![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
is a process of food production that happens in plant or autotrophs- organisms that can produce their own food. |
PHOTOSYNTHESIS |
|
|
-organisms that can produce their own food. |
AUTOTROPHS |
|
|
AUTOTROPHS |
(plants) |
|
|
- organisms that don't have the capabilities to produce their own food. |
HETEROTROPHS |
|
|
HETEROTROPHS |
(Animals /who eats plants) |
|
|
- main organ of photosynthesis in plants. |
LEAVES |
|
|
- tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for gas exchange. |
STOMATA |
|
|
- it contains the green pigment called chlorophyll, which gives the plants it distinct color. - organelle in cell where photosynthesis takes place. |
CHLOROPLAST |
|
|
- green pigment, which gives the plants it distinct color. |
CHLOROPHYLL |
|
|
kapag orange yung color ng plants |
CAROTENOID |
|
|
- Carbondioxide that appears as GASES |
STOMATA |
|
|
- Carbondioxide that appears in SOLID ways |
- PHLOEM - CO2 - XYLEM - H2O |
|
|
roots have two passive ways to the leaves |
- PHLOEM - CO2 - XYLEM - H2O |
|
|
- Sun gives off visible (white) light.
- White light is a mixture of ROY G BIV.
- Colors are either reflected or absorbed by objects.
- Green leaves - reflect green light. |
LIGHT ABSORPTION |
|
|
Is a mixture of ROY G BIV. |
WHITE LIGHT |
|
|
Green leaves reflect |
GREEN LIGHT |
|
|
are either reflected or absorbed by objects. |
COLORS |
|
|
Sun gives off |
VISIBLE (WHITE) LIGHT |
|
|
CHLOROPLAST HAVE TWO MEMBRANES: |
- STROMA - GRANUM |
|
|
refers to the colorless fluid surrounding the granum within the chloroplast. |
STROMA |
|
|
which is the series of flattened interconnected dise/sacs. |
GRANUM |
|
|
Reduction |
PINAGHIWAHIWALAY |
|
|
Oxidation |
PAGSAMA-SAMA |
|
|
CELLULAR RESPIRATION OF CHEMICAL EQUATION |

C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY |
|
|
2 STAGES OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS |
- LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS - THE CALVIN CYCLE |
|
|
PHOTOSYNTHESIS CHEMICAL EQUATION |
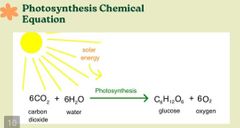
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C6H12O6 + 60₂ |
|
|
- also known as photochemical stage. |
LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION |
|
|
- it is the stage where the chlorophyll absorbs the energy from the sun (photons). |
LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION |
|
|
2 GROUPS OF LIGHT ABSORBING MOLECULES: |
1. Photosystem I 2. Photosystem II |
|
|
- Chlorophyll in Photosystem II absorbs light energy which will excites the electrons. |
STEP 1 |
|
|
- it is the chain of events set in motion by the electrons. |
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN |
|
|
- Breaking down of water molecules. - release of oxygen as a waste. |
STEP 2 |
|
|
- Electrons help bond - NADP+ and H+ to create NADPH. |
STEP 4 |
|
|
NADP meaning |
NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATE. |
|
|
- H+ diffuses into the stroma |
STEP 5 |
|
|
SUMMARY OF LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION |
1.It occurs on the granum (Thylakoid Membrane)
2. It has 2 light absorbing molecules: Photosystem I and Photosystem II.
3. Expected products: Oxygen gas (O2), NADPH, and ATP. |
|
|
- The light independent cycle |
THE CALVIN CYCLE |
|
|
CHEMICAL EQUATION OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION |

C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY |
|
|
DESCRIBE CELLULAR RESPIRATION |
• The breakdown of glucose molecules to release energy • Turns glucose into ATP • Takes place in all living things • Is a step by step process |
|
|
- is the process by which the energy of glucose is released in the cell to be used for life processes (movement, breathing, blood circulation, etc...) |
CELLULAR RESPIRATION |
|
|
- means "sugar-splitting" that occurs in the cytosol of the cell. It does not require oxygen to breakdown glucose into pyruvate. |
GLYCOLYSIS |
|
|
- completes the metabolic breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and produces 2 ATP. |
KREBS CYCLE |
|
|
- a process occurring in mitochondria and accounts for majority of the ATP production. |
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION |
|
|
- contains the chain members (carrier and protein complexes, ATP synthase complex and ATP channel protein. These membrane |
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN |
|
|
2 TYPES OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION |
- AEROBIC PROCESS - ANAEROBIC PROCESS |
|
|
WITHOUT OXYGEN |
- ANAEROBIC PROCESS |
|
|
MOST ESSENTIAL PROCESSES |
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS - CELLULAR RESPIRATION |
|
|
BUILD UP OF GLOCUSE |
ANABOLIC PROCESS |
|
|
BREAK DOWN OF GLOCUSE |
CATABOLIC REACTION |
|
|
What is the overall function of Calvin Cycle in photosynthesis? |
- to produce glucose from carbon dioxide |
|
|
What is the primary molecules that enters the Calvin Cycle to start the process? |
- CO2 |
|
|
What is the primary product of the Calvin Cycle? |
- Glucose |
|
|
What is the overall function of the light dependent reaction in photosynthesis? |
- To capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy. - To release oxygen into the atmosphere. |
|
|
What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain of Photosystem I? |
- NADP+ |
|
|
What is the role of electron transport chain in the light dependent reactions? |
- To produce ATP |
|
|
What molecule is produced as a byproduct of the light dependent reaction? |
- Oxygen |
|
|
What is the source of electrons for photosystem II? |
- Water |
|
|
What is the role of water in photosynthesis? |
- to release oxygen |
|
|
What is the function of stomata in photosynthesis? |
- To regulate gas exchange |
|
|
Which part of the chloroplast is responsible for capturing sunlight? |
Thylakoid |
|
|
Which part of the chloroplast is responsible for capturing sunlight? |
Thylakoid |
|
|
- captures lights |
Thylakoid |
|
|
What is the role of chloroplasts in photosynthesis? |
- To absorb sunlight |
|
|
What is the main purpose of photosynthesis? |
- To convert sunlight into chemical energy |
|
|
What is the primary pigment responsible for capturing sunlight in photosynthesis? |
- Chlorophyll |
|
|
WITH OXYGEN |
- AEROBIC PROCESS |
|
|
What is the main purpose of Calvin Cycle in photosynthesis? |
- To produce glucose |
|
|
Where does photosynthesis primarily occur in plants? |
- Leaves |

