![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fxn:
-responsible for integrating, processing, and coordinating sensory data and more commands Location: -brain and spinal cord |
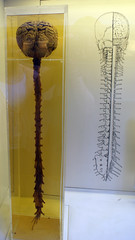
Central Nervous System
|
|
|
Fxn:
-delivers sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands Location: -neural tissue outside the CNS |
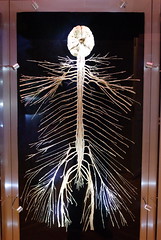
Peripheral Nervous System
|
|
|
Fxn:
-"automatic" -provides automatic regulation of smooth and cardiac muscle, and glandular secretions -sympathetic (fight or flight) -parasympathetic (rest and digest) Location: -PNS |
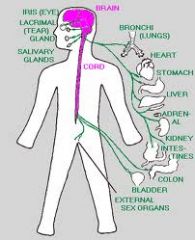
Autonomic Nervous System
|
|
|
Fxn:
-"body" -controls skeletal muscle contractions -afferent (sensory; towards CNS) -efferent (motor; away CNS) Location: -PNS |
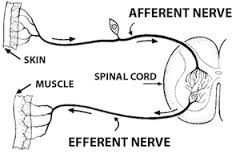
Somatic Nervous System
|
|
|
Fxn:
-basic functional unit of the nervous system Location: -apart of the nervous system |
Neuron
|
|
|
Fxn:
-receives information from other neurons primarily at the dendritic spines Location: -neuron |
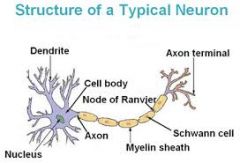
Dendrite
|
|
|
Fxn:
-long cytoplasmic process capable of propagating an electrical impulse known as an action potential Location: -neuron |
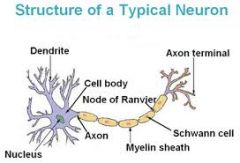
Axon
|
|
|
Fxn:
-where messages can be sent out -where the neuron communicates with another cell Location: -neuron |
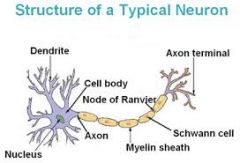
Synaptic Terminal
|
|
|
Fxn:
-membranous wrapping of electrical insulation -speeds up impulse transmission Location: -neuron -covers axon |
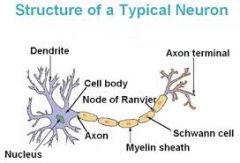
Myelin
|
|
|
Fxn:
-separate myelin Location: -between myelin |
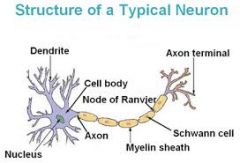
Nodes of Ranvier
|
|
|
Fxn:
-coat the axon with myelin Location: -on top of myelin |
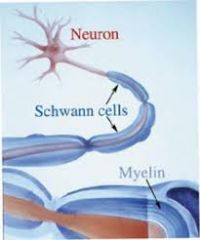
Schwann Cells
|
|
|
Fxn:
-supporting cells -"glue" -supports nerve cells Location: -surround neurons |
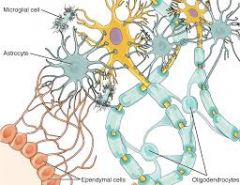
Glial Cells
|
|
|
Fxn:
-membranous coverings of the brain Location: -cranium |
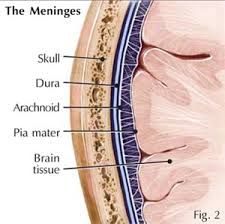
Meninges
|
|
|
Fxn:
-out layer membrane -tough and fibrous Location: -cranium |
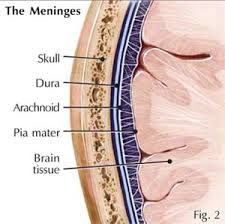
Dura Mater
|
|
|
Fxn:
-middle membrane - think, weblike membrane without blood vessels Location: -cranium |
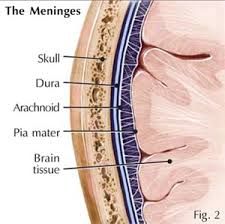
Arachnoid
|
|
|
Fxn:
-inner membrane -very thin -tightly envelopes the brain and spinal cord -penetrates into each groove and depression Location: -cranium |
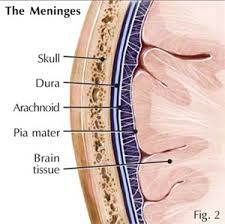
Pia Mater
|
|
|
Fxn:
-cell bodies -"butterfly" -interneurons -where things happen Location: -brain |
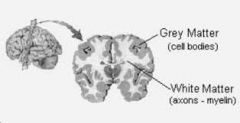
Grey Matter
|
|
|
Fxn:
-myelinated axons -where information travels quickly -motor and sensory neurons Location: -brain |
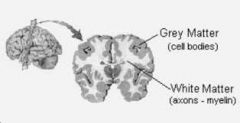
White Matter
|
|
|
Fxn:
- movement, thinking, emotion Location: -cranium |
Cerebrum
|
|
|
Fxn:
-ridges -what goes wiggling wobbly Location: -cerebrum |
Gyrus (gyri)
|
|
|
Fxn:
-grooves -the ditches Location: -cerebrum |
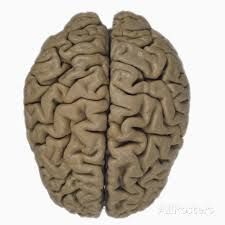
Sulcus (sulci)
|
|
|
Fxn:
-outer covering of grey matter over the hemispheres Location: -brain |
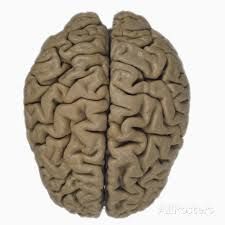
Cerebral Cortex
|
|
|
Fxn:
-"cauliflower" -coordination -arbor vitae Location: -below the occipital and temporal lobes |
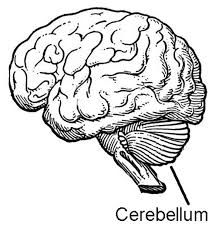
Cerebellum
|
|
|
Fxn:
-stalklike portion of the brain that joins higher brain centers to the spinal cord Location: -joins spinal cord to brain |
Brain Stem
|
|
|
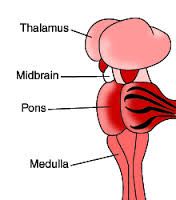
Fxn:
-contains reflex centers for head, eye, and body movements in response to visual and auditory stimuli Location: -small part of the brain stem located between the hypothalamus above and pons below |
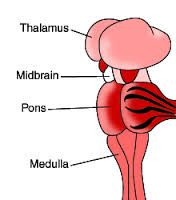
Midbrain
|
|
|
Fxn:
-consists of nerve fibers -works with medulla oblongata to control the rate and depth of breathing Location: -between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata |
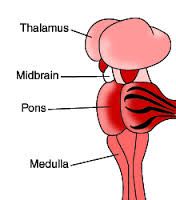
Pons
|
|
|
Fxn:
-connecting link with the spinal cord -control homeostasis Location: -lowest portion of the brain |
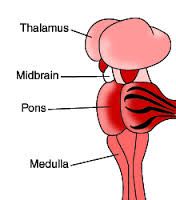
Medulla Oblongata
|
|
|
Fxn:
-sensory integration Location: -brain |
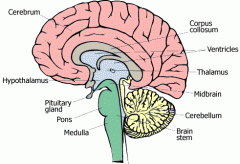
Thalamus
|
|
|
Fxn:
-hormones and homeostasis -major control center of the autonomic nervous system Location: -inferior to the thalamus |
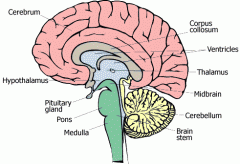
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
Fxn:
-nutrients, cushion -"circulation" Location: -brain |
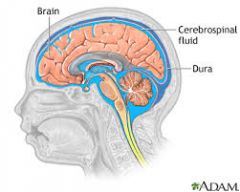
Cerebrospinal Fluid
|
|
|
Fxn:
-holds CSF -four interconnections Location: -brain |
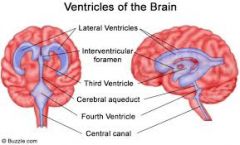
Ventricles
|
|
|
Fxn:
-mass of special capillaries that secrete the cerebrospinal fluid Location: -each ventricle |
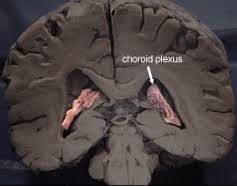
Choroid Plexus
|
|
|
Fxn:
-motor -efferent Location: -white matter |

Ventral Horn (White Matter Divisions) |
|
|
Fxn:
-sensory -afferent Location: -white matter |

Dorsal Horn
(White Matter Divisions) |
|
|
Fxn:
-sensory -transmits sensory impulses from olfactory receptors in nasal mucosa to the brain Location: - |
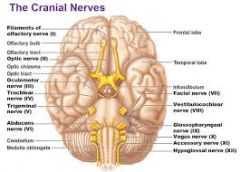
I. Olfactory
|
|
|
Fxn:
-sensory -transmits sensory impulses for vision from the retina of the eye to the brain Location: - |
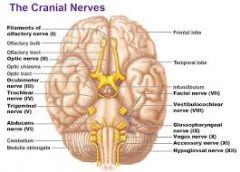
II. Optic
|
|
|
Fxn:
-motor -transmits motor impulses to muscles the move the eyes upward, downward, and medially -adjusts pupil size -control the shape of the lens Location: - |
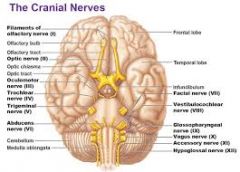
III. Oculomotor
|
|
|
Fxn:
-motor -transmits motor impulses to muscles that rotate the eyes Location: - |
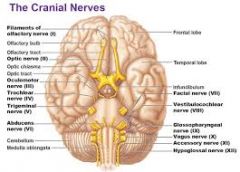
IV. Trochlear
|
|
|
Fxn:
-motor and sensory -transmits sensory impulses from scalp, forehead, face, teeth, and gums to the brain -Transmits motor impulses to chewing muscles and muscles in floor of mouth Location: - |
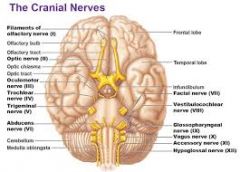
V. Trigeminal
|
|
|
Fxn:
-motor -transmits motor impulses to muscles that move the eyes laterally |
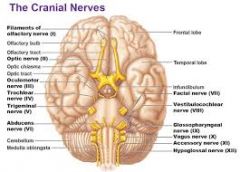
VI. Adnucens
|
|
|
Fxn:
-motor and sensory -transmits sensory impulses from the anterior part of the tongue to the brain Location: - |
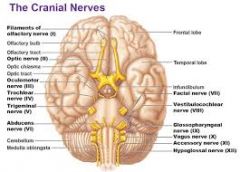
VII. Facial
|
|
|
Fxn:
-sensory -transmits sensory impulses form the inner ear associated with hearing and equilibrium Location: - |
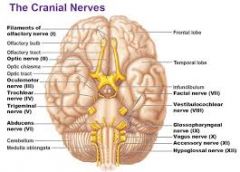
VIII. Vestibulocochlear
|
|
|
Fxn:
-motor and sensory -Transmits sensory impulses form posterior portion of the tongue, tonsils, pharynx, and carotid arteries to the brain Location: - |
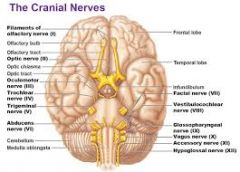
IX. Glossopharyngeal
|
|
|
Fxn:
-motor and sensory -Transmits sensory impulsed from thoracic and abdominal organs, esophagus, larynx, and pharynx to the brain -transmits motor impulses to these organs and to muscles of speech and swallowing Location: - |
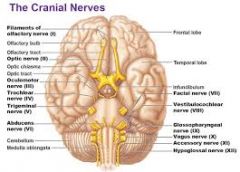
X. Vagus
|
|
|
Fxn:
-motor -transmits motor impulses to muscles of the palate, pharynx, and larynx, and to the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Location: - |
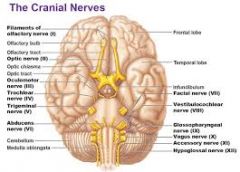
XI. Accessory
|
|
|
Fxn:
-motor -transmits motor impulses to the muscles of the tongue Location: - |
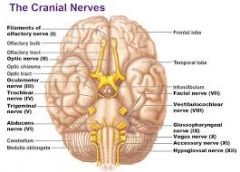
XII. Hypoglossal
|
|
|
Fxn:
-reasoning and making decisions -higher order thinking skills -speaking, muscle movement, making plans Location: -anterior to the central sulcus and superior to the lateral sulcus |
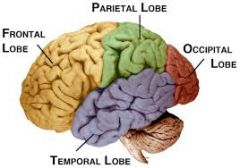
Frontal Lobe
|
|
|
Fxn:
-sensing of the body -perception and recognition Location: -posterior to the central sulcus, superior to the temporal lobe, and anterior to the occipital lobe |
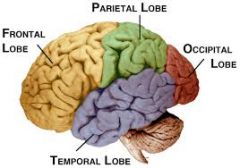
Parietal Lobe
|
|
|
Fxn:
-auditory cortex -auditory functions Location: -inferior to the frontal and parietal lobes and anterior to the occipital lobe |
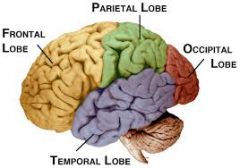
Temporal Lobe
|
|
|
Fxn:-vision cortex
Location:-posterior to the parietal and temporal lobes |
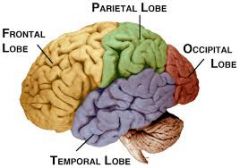
Occipital Lobe
|

