![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
All cells composed of which 4 atoms |
C, H, N, O |
|
|
|
What makes up the plasma membrane |
Phospholipid bilayer, mostly unsaturated Glycolipid, sugar groups Cholesterol, keeps membrane fluid consistent Lipid rafts, platforms for cell signaling Glycocalyx, cell surface area |
|
|
|
Transmembrane Protein |
Integral protein that goes from extracellular enviro to intracellular enviro |
|
|
|
Integral proteins |
Involved in transport Deeply imbedded membrane |
|
|
|
Peripheral protein involved in: |
Support, enzymatic reactions, and mechanical functions |
|
|
|
Microvilli |
Increases surface area |
|
|
|
Name the membrane junctions: |
Tight junction, Desmosomes, and Gap junction |
|
|
|
Tight Junction |
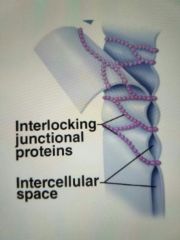
Fusion of integral protein, impermeable Found in skin and small intestines |
|
|
|
Desmosomes |
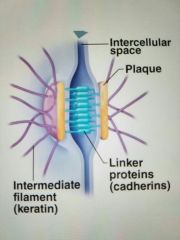
Anchoring junctions, attached by protein plaques linked with linker proteins
Found in tissues subjected to mechanical stress, skin |
|
|
|
Gap Junction |
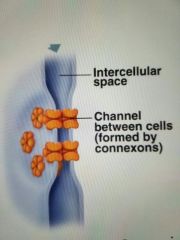
Communication of ions and small molecules |
|
|
|
Membrane Transport |
Selectively permeable membrane Can be active of passive |
|
|
|
Passive Transport, list some examples: |
No E needed Diffusion--Simple Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion; Osmosis |
|
|
|
Diffusion |
Movement if solute from high to low concentration |
|
|
|
Simple Diffusion: definition, which substances, examples |
Diffusion directly through the lipid bilayer Only nonpolar and lipid soluble substances Example. Oxygen, carbon dioxide, fat-soluble vitamins, alcohol |
|
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion - Carrier Mediated: how, which substances, which carriers |
Specific proteins attaches/bind to carrier substance and is transported into the cell Larger and polar molecules Transmembrane proteins |
|
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion - Channel Mediated: definition and which substances thru which channels |
Specific molecules based on size and charge that goes thru the leakage channel (always open) or gated channel (controlled by signals) Mostly ions |
|
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of water from hight to low concentration |
|
|
|
Where does water move? |
Water moves to where the "stuff" are |
|
|
|
Tonicity |
Ability of a solution to change shape of the cell by changing water volume |
|
|
|
Hypotonic |
More concentrate inside the cell Lysis, cell bursts |
Hippo likes? |
|
|
Hypertonic |
More concentration outside of cell so water leaves the cell Crenation - shriveled |
|
|
|
Isotonic |
Equal numbers of the concentration in and outside of the cell |
|
|
|
Active Transport, name some examples |
Requires E input, ATP Primary, Secondary, and Vesicular |
|
|
|
Primary Active Transport |
Solute travels against gradient Direct use of ATP Sodium Potassium Pump |
|
|
|
Sodium Potassium Pump |
3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in More K inside, More Na outside ATP used |
|
|
|
Secondary Active Transport |
Displays specificity Indirect use of ATP As one substance travels down its gradient, it "pulls" another substance along |
|
|
|
Vesicular Transport |
No proteins, moved by vesicles Larger particles Powered by ATP |
|
|
|
Endocytosis, examples? |
Substances moved into cell Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, Receptor mediated Endocytosis |
|
|
|
Exocytosis, how? Example? |
Substances move out of cell Fusion with plasma membrane by vesicles and released to the outside Example. Neurotransmitter |
|
|
|
Phagocytosis : specificity? Definition? Example? |
Maybe specific, large particles "engulfs/eats" material to form phagosome Combines lysosome to digest material Example. Macrophages |
|
|
|
Pinocytosis : specificity? Definition? Example? |
Nonspecific, small particles "dirt", sampling of extracellular fluid Example. Intestinal cell absorbing nutrients |
|
|
|
Receptor mediated Endocytosis : specificity? Definition? Example? |
Specific Receptors outside of membrane Example. Insulin, LDL |
|
|
|
What are the charges of the plasma membrane? |
Inside (-), outside (+) Due to chemical and electrical gradient Proteins line the inside of the membrane unable to leave |
Inside? Outside? Where do proteins line? |
|
|
K is the chemical formula for? |
Potassium |
|
|
|
P is the chemical formula for? |
Phosphorus |
|
|
|
What is the chemical and electrical gradient? |
Electrical: More K+ inside of cell so it attracts (-) charge Chemical: pulls it out |
Potassium pull... |
|
|
What is RMP? |
When concentration and electrical gradient equalizes |
Resting membrane potential |
|
|
G-Link Receptors (steps) |
1. First chemical messenger binds to membrane receptor 2. In turn sets off the second messenger G protein acts as a relay messenger |
|
|
|
Cillia |
Cellular extensions found on the apical side of a tissue |
|
|
|
Flagella |
Cellular extention involved in movement |
Only found in sperm |
|
|
Nucleus: overall function, contains what, what happens here |
Control center Contains genetic material Site of DNA Synthesis |
|
|
|
Cell that has more than one cell |
Mulinucleate |
Liver cells, osteoclasts |
|
|
Cell with no nucleus |
Anucleate |
Red blood cells |
|
|
Nucleoli |
Site of ribosomal Synthesis and assembly |
|
|
|
Chromatin |
DNA and histones |
|
|
|
Histones |
Type of DNA ; protein that organizes the DNA and regulates gene expression |
|
|
|
Chromosomes |
Condensed chromatin formed during cell division |
|
|
|
Name the steps in Cell Life Cycle |
Interphase : G1, S, G2 Mitotic Phase : Pro, Meta, Ana, Telo, Cytokinesis |
|
|
|
Describe Interphase |
First phase in the cell's life cycle 1. G1, growth 2. S, DNA Synthesis occurs 3. G2, growth and checkpoint for cell division |
3 steps |
|
|
Describe Mitotic Phase |
Division of the nucleus 1. Pro: chromatin condenses, Mitotic spindles form and attach to chromosomes, nucleolus disappears, nuclear envelope fragments 2. Meta: chromosomes line up at the center 3. Ana: sister chromatin pulled apart to opposite ends, cell lengthens 4. Telo and Cytokenesis: chromosomes uncoil, nuclear envelope and nucleoli reappear, spindles disappear, cleavage furrow forms for division of cytoplasm |
P. M. A. T. |
|
|
Semiconservative DNA replication |
Each parent strand serves as a template for the new DNA molecule |
|
|
|
What is the term that describes DNA replication? Parent-daughter strand |
Semiconservative |
|
|
|
What is G0 (zero) phase? |
When a cell reaches maturity and doesn't divide anymore |
|
|
|
Introns |
Contained in genes, they are the noncoding DNA sequences |
In genes |
|
|
Exons |
Code for Protein Synthesis in genes |
In genes |
|
|
tRNA |
RNA that brings the correct AA to the growing polypeptide chain |
|
|
|
rRNA |
Site of protein Synthesis |
|
|
|
mRNA |
Serves as a transcript, makes copies |
|
|
|
Describe Protein Synthesis |
Replication, Transcription, Translation Replication : DNA copies itself Transcription : information in DNA copied to mRNA Translation : mRNA sequence is made into protein |
3 steps |
|
|
Transcribe this DNA sequence : cat, gag, tag, tac |
GUA, CUC, AUC, AUG |
|
|
|
What are the steps of Translation of Protein Synthesis? |
1. Initiation : tRNA goes to P site, AUG starts the process 2. Elongation : codon recognized, tRNA goes to A site; peptide bond formed from protein in P site to AA in A site 3. Termination : special base sequence signals end of process; ribosome disassemble, mRNA released |
|
|
|
Transcription, what are the sites? |
P site, initiation starts with AUG, methionine
A site, new tRNA sits with AA and bonds with the polypeptide
E site, tRNA exits the ribosome |
|
|
|
What are the stop colons? |
UAA, UAG, UGA |
|

