![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Contraries |
Iff cannot both be true |
|
|
Subcontraries |
Iff cannot both be false |
|
|
Subalternations |
Immediate inference between universal sentence and particular sentence of the same quality |
|
|
Contradictories |
Iff cannot both be true |
|
|
Sentence properties |
Logical truth, logical falicy, logical contingency |
|
|
Theory properties |
Consistency and inconsistency |
|
|
Argument properties |
Validity and invalidity |
|
|
Logical truth |
A sentence that is true and cannot be false |
|
|
Logical falicy |
False and cannot be true |
|
|
Logical contingency |
Neither logically true nor false |
|
|
Quality |
Affirmative or negative |
|
|
Quantity |
Universal or particular |
|
|
Traditional interpretation |
A and E type sentences have existential import |
|
|
Existential import |
Iff entails that something exists |
|
|
Consistent |
Iff it is possible for all the sentences in the set to be true |
|
|
Inconsistent |
It is not possible for all the sentences in a set to be true |
|
|
Valid |
Iff it cannot have two true premises and a false conclusion |
|
|
Invalid |
It's possible to have two true premises and a false conclusion |
|
|
Syllogism |
An argument that has two premises |
|
|
Middle term |
Appears in both premises |
|
|
Minor term |
Subject of the conclusion |
|
|
Major term |
Predicate term of the conclusion |
|
|
Mood |
Three letters representing the categorical sentences |
|
|
Figure |
Determined by the position of the middle term |
|
|
Traditional square of opposition |
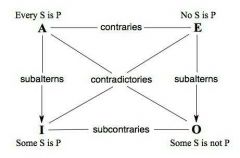
|
|
|
If an A-type sentence is true then... |
E is false, O is false, I is true |
|
|
If an A-type sentence is false then... |
O is true and E and I are indeterminate |
|
|
If an E-type sentence is true then... |
A and I are false, and O is true |
|
|
If an E-type sentence is false then... |
I is true, and A and O are indeterminate |
|
|
If an I-type sentence is true then... |
E is false, and A and O are indeterminate |
|
|
If an I-type sentence is false then... |
A is false, and E and O are true |
|
|
If an O-type sentence is true then... |
A is false, and E and I are indeterminate |
|
|
If an O-type sentence is false then... |
E is false, and A and I are true |
|
|
If a sentence is true then it's subcontrary is... |
Indeterminate |
|
|
If a sentence is false then its subcontrary is... |
True |
|
|
Any theory with all false sentences is... |
Not necessarily inconsistent because it's not necessarily impossible for the sentences to be true |
|
|
If an argument has true premises and a true conclusion then... |
It could still be invalid if it's not impossible to have two true premises and a false conclusion |
|
|
Every sound argument has a... |
True conclusion |
|
|
All logically true sentences are... |
Logically equivalent to each other |
|
|
If a sentence is logically false then... |
It is false |
|
|
Any theory with all true sentences is... |
Consistent |
|
|
If a sentence is true then its contrary must be... |
False |
|
|
If a sentence is false then its contrary must be... |
Indeterminate |
|
|
All true sentences are... |
Not necessarily logically true |
|
|
If an argument has true premises and a false conclusion then it is... |
Invalid |
|
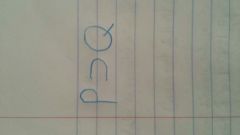
|
False iff P is true and Q is false; if, then, only if, unless |
|
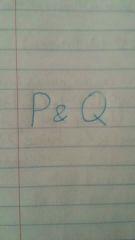
|
True iff both are true; and, but, both, although |
|
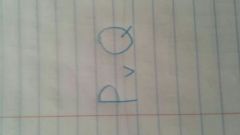
|
False iff both are false; or, either, unless |
|
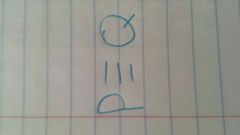
|
True iff both have the same value; iff |

