![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Receptor Types |
IGED: ion channel (ms) G-protein (s) Enzyme linked (min) DNA linked (hrs) |
|
|
|
Ion channel linked receptor |
Very fast (ms) synaptic neurotransmission, ex. Nicotine |
|
|
|
G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) |
Fast (s), sits on cell membrane, easy target. Most drugs use this |
|
|
|
Enzyme linked receptors |
Slow (min). Growth, differentiation, metabolism. Amplification of signals. Targets: insulin receptor, epidermal growth factor receptor. |
|
|
|
DNA linked receptors |
Very slow (hrs or days). Intracellular. Reproduction, growth. Ex. Vitamin D. |
|
|
|
Drug targets |
Receptors, enzymes, carriers, channels ( or no target ex. Antacid) |
|
|
|
Drug target: enzymes |
Drugs can act as false substrate binding to enzyme. Ex Aspirin |
|
|
|
Drug target: carriers |
ATP powered ion channels, active, direct ion transfer, Na+, Ca2+, H+ pumps. Ex. Digoxin (Na pump inhibitor), Omeprazole (proton pump inhibitor) |
|
|
|
Drug targets: voltage gated ion channels |
Na channel blockers: local anesthetics block sodi channel Ca channel antagonist: dihydropyridine |
|
|
|
Drug target (new): g protein associated ion channels |
GABA receptor Glutamate receptor 5 HT receptor Prodrug: an inactive compound that can be converted to an active drug by enzymatic modifications |
|
|
|
Agonists |
Drug binds and activates receotor |
|
|
|
Inverse agonist |
Higher affinity for inactive state of receptor. Disables receptor, blocks and REVERSES effect |
|
|
|
Partial agonist |
Binds receptor, leads to PARTIAL biological response |
|
|
|
Antagonist |
Binds receptors, PREVENTS ACTIVATION Many drugs in this category |
|
|
|
Efficacy |
Ability of drug to elicit. Biological response |
|
|
|
Dose response curve |
Biological response vs drug conc |
|
|
|
EC50 |
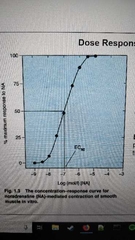
Concentration producing a response 50% of max |
50 perCent of max response |
|
|
ED50 |
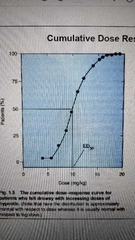
Dose producing a response in 50% of patients |
|
|
|
Full vs partial agonist |
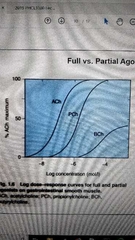
Full agonist: elicits 100% response (pch in graph) Partial agonist: elicits partial response (bch) |
|
|
|
Reversible Competitive Antagonist |

|
|
|
|
Irreversible competitive antagonist |
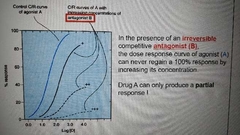
|
|
|
|
Pharmacokinetics |
QUANTITATIVE description of drug disposition and body's response. Determined by: Absorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion |
|
|
|
Pharmacodynamics |
QUALITATIVE. Effects of drugs on body mechanisms of action |
|
|
|
Drug administration |
Topical Enteral: via gut (oral, sublinqual, rectal) Parenteral (avoids guts, IV, other injections) Pros cons of enteral: Oral: common, predictable; first pass metabolism is liver Sublinqual: No first pass metabolism; not applicable for most drugs. Rectal: less first pass metabolism; inconsistent |
|
|
|
Volume of distribution |
Drug's penetration into various body compartments |
|
|
|
Toxic metabolites |
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) becomes toxic metabolite |
|
|
|
Zero order kintetics |
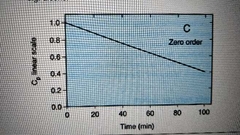
Decrease in drug level independent on concentration in plasma, constant rate of decrease. Ex alcohol |
|
|
|
1st order kinetics |
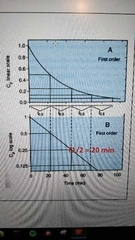
Decrease in drug level depends on plasma concentration. Rate of decrease exponential. Most drugs. T1/2: Time to reduce 50% of administered drug. |
|
|
|
Repeated drug adminstration |
Time to reach steady state (95%). When rate of administration equals rate of loss. ABOUT 4-5X HALF LIFE |
|
|
|
Therapeutic Index (TI) |
TI = TD50/ED50 TD50: Dose to produce toxicity in 50% of patients. ED50: dose to produce therapeutic effect in 50% of patients. LARGER TI = SAFER DRUG |
|
|
|
Most useful genetic polymorphism in puarmacogenomics |
Single nucleotide polymorphism |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters: Ions |
Ca, Na excite K, Cl inhibit |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters: Glutamate |
Attention, memory (CNS), sensation (PNS) |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters: GABA |
Sedation |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters: Dopamine |
Intensity, reward |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters: Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) |
Brain alarm Organ alarm |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters: Epinephrine (Adrenaline) |
Bloodstream PNS organ alarm |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine |
Memory (CNS) Sensation, movement, secretion (PNS) |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters: Anandamide |
(cannabinoid) Cosmic oneness, appetite |
Anands always high |
|
|
Neurotransmitter: Adenosine |
Sleep-repair |
Sineusoidal sleep repair cycle |
|
|
Neurotransmitter: Histamine |
Emergency alert - vomit |
History makes me sick |
|
|
NM: Substance P |
Pain |
P for pain |
|
|
NM: Endorphins |
Pain? Meh |
I Endurephin pain |
|
|
NM: Neuropeptide Y |
Appetite |
|
|
|
NM: Cortistatin |
Sleep |
Under the satins and sleep |
|
|
NM: Hypocretin/ Orexin |
Wakefulness |
Oryx that never sleeps |
|
|
NM: Leptin |
Apetite |
Shai Lipton after a nice meal |
|
|
NM: Oxytocin |
Trust, love, social neediness |
|
|
|
NM: vasopressin |
Emergency, blood pressure |
Presses veins |
|
|
CNS |
Brain, spinal cord. Mediated involuntary but trainable activities: Sensory perception Emotional perception Memory Cognition |
|
|
|
PNS |
Cranial nerves III - XII, spinal nerves, ganglia and peripheral nerves Mediates multiple involuntary: Sensory input to CNS Organ function Gland secretion Cardiac rythm |
|
|
|
PNS Circuit: Autonomic NS (ANS): SNS vs PSNS |
Involuntary. Sympathetic NS (SNS): FIGHT OR FLIGHT Parasympathetic: rest and digest |
|
|
|
PNS Enteric NS (ENS) |
Involuntary. Can mediated by itself all aspects of digestion |
|
|
|
PNS Somatic NS (SoNS) |
Voluntary. Mediates voluntary & reflex muscle contractio |
SoNS out Guns out |
|
|
Reversible ACh Inhibitors |
Calabar bean extract (0physostigmine), AD drugs |
|
|
|
Irreversible ACh inhibitors |
Organophosphate pesticides, nerve gas: Sarin, VX, Novichok |
|
|
|
Physostigmine |
Rhymes with Calabar bean Past therapeutic for Myasthenia Gravis DUMBBELSS Counteracts atropine |
Phys = natural = Calabar bean PhySOStigmine |
|
|
*Pilocarpine |
Isolated from tropical South American Pilocarpus (Jaborandi) plant Used to treat dry mouth |
Pilot was South American Jaborandi |
|
|
*Atropine |
Named after atropine Active ingredient in Belladonna Used for pupil dilation (mydriasis) |
Atropine Belladonna |
|
|
Mecamylamine |
Ganglionic blocker Used to treat hypertension |
|
|
|
*Tubocurarine |

CURARE ( dart poison) Paralyzing all muscles Death by suffacation Still awake and feel pain |
|
|
|
*Botox |
Botulinum Toxin Isolated from bacterium (C. Botulinum) Paralyzes diaphragm muscle Blocks muscle spasticity disorders |
|
|
|
Phenylephrine |
Vasoconstrictor, alleviates permanent erection Blood pressure elevator
|
Fen El efreet? |
|
|
Prazosin |
Vasodilator Treats hypertension |
|
|
|
Isoproterenol |
Cardiac stimulant Bronchodilator |
|
|
|
Dobutamine |
Cardiac sttimulant |
|
|
|
Albuterol |
Bronchodilator |
|
|
|
Propranolol |
Reduces cardiac output Worsens asthma |
|
|
|
Metoprolol |
Cardiodepressant |
|
|
|
Amphetamine |
Increases NE and DA resealse |
AMPhetamine AMPs it up |
|
|
Cocaine |
Decreases reuptake and removal of NE and DA |
|
|
|
Resperpine |
Indian snakeroot |
Serpentine serpent |
|
|
AD: Prophylaxis anti inflammatory (aspirin, naproxen) |
NSAID Anti inflammatory |
|
|
|
AD: prophylaxis Anti degeneration |
Statins (lovastatin) Reduces hypercholesterolemia |
|
|
|
AD: Donepezil |
Long half life 70hr Not for use with other drugs |
D(Onepill (this one only) |
|
|
AD: Rivastigmine |
Short half life, more sustained action (10hr) twice daily Drug if choice for ppl on multi drug regiments |
Rivitalize every 10hrs |
|
|
AD: Memantine |
Moderate affinity for NMDA Glutamate receptor Additive benefit |
|
|
|
PD: Sinemet |
Replacement therapy for parkinsonism L-dopa + carbidopa Side effects: Dyskinesia Psychosis |
Cinement replacement for the parkingson |
|
|
PD: Entacapone (comtan) |
COMT inhibitor Extends Sinemet duration of action |
|
|
|
PD: scopolamine |
1st of drug (>100 years), now only used for vertigo |
|
|
|
PD: Bromocriptine |
Dopamine receptor agonist Monotherapy early PD Fibrosis side effect |
|
|
|
PD: Amantidine |
Antiviral |
|
|
|
PD: Selegiline |
Early PD, expensive, mild benefit. Increases BP |
|
|
|
PD: Apomorphine |
Rescues PD patients from "off" state. Administered SC IV sublingual, rectal, intranasal |
|
|
|
AD: Aspirin + Naproxen |
Anti inflammatory. |
|
|
|
AD: lovastatin |
Statin, anti degeneration, reduces hypercholesterolemia |
|
|
|
Psychosis: Thioridazine |
High sedative, Low motor side effects High anticholinergic Cardiac arrhythmia rism |
|
|
|
Psychosis: Haloperidol |
Low sedative, Hight motor side effects Low anticholinergic |
HaLOW sedative |
|
|
Psychosis: Risperidone |
Less motor side effects May increase anxiety/depression |
ResperImDone With Life |
|
|
Psychosis: Clozapine and Olanzapine |
No motor side effects Weight gain |
My clozapine don't fit me anymore |
|
|
Psychosis: Quetiapine |
Also Used off label to alleviate psychosis caused by PD therapy |
Queit I'm used off label |
|
|
Psychosis: Pimavanserin |
5-HT2a Inverse agonist |
PimavanserInverse agonist |
|
|
Psychosis: Lurasidone |
Also FDA approved for bipolar depressive episodes |
LauraIsDone being bipolar |
|
|
Psychosis: Aripiprazole (Abilify) |
Mild nigral d2 agonist No weight gain, no motor side effects |
Abilify no side effects |
|
|
Psychosis: treating TD: Valbenazine |
Alleviates tardive dyskinesia. |
|
|
|
Psychosis: treating nausea. Domperidone |
Treating nausea caused by anti psychotic drugs |
|
|
|
Epilepsy: phenobarbital |
Low dose barbiturate |
|
|
|
Epilepsy: Clonazepam and Lorazepam |
Clonazepam: tonic CLONic seizures Lorazepam: status epilepticus |
|
|
|
Epilepsy: carbamazepine* |
Blocks sodium channel also treats bipolar depression |
carbAMAZEpine (miracle 2 in 1) |
|
|
Epilepsy: Ethosuximide |
Blocks calsium channels Side effects: GI distress |
Side effect SUX |
|
|
Epilepsy: Charlotte's Web |
Oil from strain of marijuana with no THC Only CBD |
Pass the Charlotte's Web |
|
|
Depressed painter |
William blake |
|
|
|
Antidepressants: Clomipramine |
Blocks Norepinephrine reuptake Uses: unipolar depression, OCD, hair plucking |
|
|
|
Antidepressants: Phenelzine |
Must NOT consume red wine, beer, chocolate |
Fen El zine? No zine for u |
|
|
Antidepressants: Prozac or Zoloft |
SSRI, no OD, no major side effects, safe |
Everyones on Prozac because it works |
|
|
Antidepressants: Venlafaxine (Effexor) |
SNRI Side effex: hypertension |
Some side effex |
|
|
Antidepressants: Bupropion (Wellbutrin) |
NE + DA reuptake Inhibitor Also for nicotine addiction Side effects: nervousness, insomnia |
Umm well but (nervous) |
|
|
Antidepressants: Lithium |
Unsure mechanism Bipolar disorder and mania Side effects: fatigue, muscle weakness, thirst, OD = coma |
|
|
|
Antidepressants: Carbamazepine* |
Blocks sodium channels Low doses used to stabilize mood Side effects: ataxia, vertigo |
carbAMAZEpine (2 in 1 amazing) |
|
|
Antidepressants: Ketamine |
Immediately alleviates suicidal desire Side effects: hallucinations |
|

