![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Type of bonds molecules can make ? |
Covalent - very strong - ie aspirin and alkylating agents
Electrostatic Hydrophobic or van dee waal |
|
|
|
What is an agonist?
Antagonist? |
Agonist - binds to and activates a receptor
Antagonist - binds and inhibits - ie prevents binding of agonists ie atropine to ACh |
|
|
|
Describe the terms full / partial and inverse agonists + antagonist |
Full - high binding for Ra (active receptor --> large activation/effect
Partial - intermediate binding for Ra + Ri (inactive) - small effect
Antagonist - maintains Ra+ Ri levels --> it sits at constitutive level --> ie baseline
Inverse agonist --> binds Ri mostly --> ie inhibition |

|
|
|
What is an inert binding site?
Effect? |
Binding with no function
Affects drug distribution |
|
|
|
Mechanisms of drug permeation? |
Diffusion via intercellular junctions Diffusion via cell membranes Transported by carrier proteins (ie ABC Family - ATP binding cassette - p-glycoprotein or MDR1) Endo/pino/exocytosis |
|
|
|
What is Ficks law ? |
Law of diffusion
Flux = concentration difference [area x permeability coefficient] / thickness Important for lipid diffusion |
|
|
|
Example of a weak acid? |
Aspirin |
|
|
|
Example of a weak base |
Lidocaine |
|
|
|
Acids / bases - which state are each more easily absorbed?
How can this be manipulated in renal excretion / toxicity? |
Acid absorbed better in acid environments, basic better in basic environments - ie non ionic state
Ie of trying to excrete weak acid --> make the urine more basic as this will increase the anion formation and prevent reabsorption - (opposite for base) |

|
|
|
What is an orthosteric site? What is an allosteric site? |
Orthosteric is where the natural / endogenous ligand binds - ie agonists and antagonists.
Allosteric - Ligands can bind and increase or decrease the effect of Ligands at the orthosteric site. Ie benzodiazepines bind the GABA receptor and potentiate effects |
|
|
|
Which Antagonist can an agonist overcome ? Competitive or noncompetitive ? |

Ie it over comes a competitive antagonist as this binds at the same site where as a non competitive - binds irreversibly |
|
|
|
What is potency? |
Concentration EC50 or dose ED50 that produces 50% of maximal effect |
|
|
|
What is efficacy? |
Reflects the maximal response when large amounts of drug are present
Ie a partial agonist will have a lower efficacy than a full agonist |
|
|
|
Explain the terms ED 50 TD 50 LD 50 ? |
ED 50 - dose at which 50% achieve a desired effect ie the median effective dose
TD50 - toxic dose for 50%
LD 50 - lethal dose for 50% of animals |
|
|
|
What is therapeutic index? |
Ratio of TD50 to ED50 Ie the range between efficacy and toxicity - therapeutic window |
|
|
|
What can be receptors? |
Generall are proteins channels, enzymes, transporters, structural proteins |
|
|
|
What does a low/high Kd mean? |
High Kd - Low affinity Low Kd - High affinity Ie inverse relationship |
|
|
|
Types of antagonism and examples? |
Competitive + Non-competitive Chemical antagonism - protamine - binds directly to heparin Physiological antagonism - antagonism by working via other mechanisms - ie using insulin to prevent hyperglycaemia secondary to glucocorticoids |
|
|
|
Ways in which receptors signal? |
1. Intracellular receptor (lipid soluble drugs) - steroids - transcription - slow 2. Enzyme bound to intracellular component 3. Tyrosine kinase linked - insulin , cytokines --> Jak /Stat 4. Ligand gated ion channel ie ACh Na channels 5. G protein coupled |
|
|
|
Types of G proteins |
Gs - stimulatory - Beta adrenergic, histamine --> Increase adenylyl cyclase --> increase cAMP Gi - Inhibitory - Alpha2 adrenergic, mACh --> inhibit adenylyl cyclase Gq --> Increase phospholipase C --> increase IP3; increase Ca2+ |
|
|
|
What do phosphodiesterases do? |
Break down cAMP to 5'AMP or cGMP Sildenafil blocks phosphodiesterases |
|
|
|
Name common intracellular messengers |
cAMP + cGMP Ca2+ DAG + IP3 PKC Tyrosine kinases such as JAK, STAT |
|
|
|
What type of receptor is nAChR and mAChR? |
nAChR - Ligand gated ion channel - Na mAChR - G protein coupled |
|
|
|
Describe the effects of propanolol. |
Beta selective adrenergic response Slow HR and bronchoconstriction No alpha effects like vasoconstriction |
|
|
|
Describe potency |
Comparing ED50 - amount of drug to have effect in 50% irrespective of their ceiling effect or efficacy (ie maximal response) |
|
|
|
Describe Efficacy |
Maximal response achieved Ie partial agonists will have a lower efficacy as they have a lower maximal response even with high concentrations |
|
|
|
Therapeutic Index Vs Therapeutic Window |
Therapeutic index - (Toxic dose) TD50 - ED50 (effective dose) Therapeutic Window - Window between minimum toxic dose and minimum therapeutic dose |
|
|
|
How does clonidine work?
What can happen with abrupt cessation? |
Alpha 2 adrenergic agonist in the brain --> binds presynaptic alpha2R --> reduced Ca --> reduced NA release in the vasomotor brainstem --> reduced SNS tone --> antihypertensive effects
Causes down regulation of receptors --> can precipitate a hypertensive crisis |
|
|
|
How do you work out clearance ? |
Elimination (first order) = clearance x concentration.
Can be estimated by finding the area under the curve - AUC
Only applicable to first order - not drugs with capacity limited excretion ie EtOH, phenytoin |
|
|
|
What factors affect first pass metabolism? |
Amount of absorption - Lipo/hydrophilic, transporters
Metabolism in the GIT or portal blood
Metabolism and or excretion in the liver |
|
|
|
What reactions occur in phase II bio transformation? |
Increasing polar - ie hydrophilic
Addition of glucuronic acid, sulfuric acid, acetic acid, amino acid - hepatic conjugation via transferase enzymes (UGTs, SULTs, GSTs, NATs)
Usually following phase 1 but can precede it |
|
|
|
What occurs in phase 1 reactions ? |
Convert to more polar via cytochrome P450 + P450 reductase + NADPH + O2
Addition or unmasking of OH, NH2, SH groups ie oxidation, reduction, hydrolyses, deamination and desulfuration
Nonspecific - mainly lipophilic drugs Slow reactions |
|
|
|
Which P450 enzyme is the most biologically important? |
CYP3A4 Metabolises 50% of prescription drugs
Represents 30% of all CYP |
|
|
|
What is the affect of cigarette smoking on P450 enzymes? |
Induction of CYP1A
May increase the metabolism of some drugs - reduced effect or increased if it is a prodrug
Via aromatic hydrocarbons and other toxins |
|
|
|
Which CYP does St. John's wort affect?
Which other drugs affect it also? |
CYP3A4 induction
Dexamethasone, rifampin, atorvastatin
Grapefruit juice is a strong inhibitor of this enzyme |
|
|
|
Do type 2 reactions always inactivate/ detoxify?
Why? |
No
Ie morphine-6-glucuronide is more active than morphine
Sulfation activates minoxidil (prodrug)
Or toxic products may be formed |
|
|
|
What does CYP 2D6 metabolise? |
Codeine
Can have poor metabolisers ... slower effects Ultra metabolisers - quick transformation to morphine ie increase adverse effects - ie abdominal pain
Also tamoxifen |
|
|
|
Example of phase 2 metabolism polymorphism ? |
Deficiency in pseudocholinesterase
Prolonged paralysis
Also isoniazid - slow metabolism - increased ADRs African American 50% |
|
|
|
GIT metabolism plays a major role in metabolism of which common drug? |
Digoxin
If given with erythromycin or a tetracycline -- 2 fold increase in serum levels - increased Risk of cardio toxicity |
|
|
|
What is the relationship between antipsychotics and warfarin ? |
May require +++ high warfarin doses
And on cessation of the antipsychotic may lead to increased INR and bleeding |
|
|
|
Common drugs that induce drug metabolism? |
Rifampin St johns wort Phenytoin Barbiturates Ritonavir |
|
|
|
Common drugs that inhibit drug metabolism? |
Grapefruit juice -azoles Cimetidine Isoniazid EtOH OCP |
|
|
|
Diazepam is mainly metabolised by ? |
The liver
In cirrhosis - normal doses may cause coma |
|
|
|
Which drugs have hepatic clearance limited by blood flow? Why? |
So efficiently metabolised even in liver disease that the rate limiting step in getting to the liver ie in heart failure
Verapamil Propanolol Morphine Isoniazid Imipramine Amitriptyline Lidocaine |
|
|
|
How do you calculate loading dose? |
Loading dose = Vd x TC
Volume of distribution Target concentration |
|
|
|
How do you calculate therapeutic index? |
TD50 / ED50 |
|
|
|
Describe agonists In a graph of response vs dose |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What are the phases of drug development |
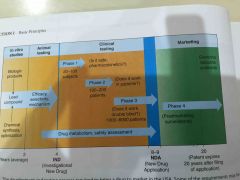
|
|
|
|
What is Kd? |
Concentration of drug for 50% of receptors to have drug bound |
|
|
|
What is EC50? |
Drug concentration for 50% effect |
|
|
|
What is a grade dose response curve ? |
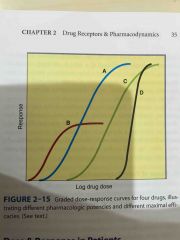
Can look at potency and maximal efficacy |
|
|
|
What do you calculate from a grade drug response curve? |
Potency Maximal efficacy |
|
|
|
What is a quantal dose effect curve ? |
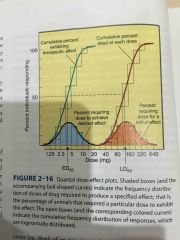
|
|
|
|
What do you calculate from a quantal dose effect curve? |
ED50 TD50 LD50 Therapeutic index Variability of response |
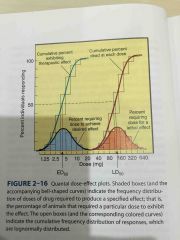
|
|
|
What is tachyphylaxis? |
RAPID diminishing of effect following drug administration
Similar to tolerance |
|
|
|
Difference between tolerance and tachyphylaxis? |
Tolerance - WEEKS! - receptor expression etc
Tachyphylaxis - FAST! Reduction in response - exhaustion of NT or substance i.e. Nitrates |
|

