![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
304 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
At which intercostal space can the base of the heart be heard best?
|
The 2nd on either side of the angle of Luis
|
|
|
Tracheal vascular ring?
|
An abnormality where the aorta is not located in front of the ring but wrapped around it
|
|
|
Where are murmurs usually heard best and when do they become a big problem?
|
Heard best in the back of the patient and become a problem if they radiate
|
|
|
What are the hallmark signs of a cardiac problem?
|
Diaphoresis, congested cough and respirations
|
|
|
Why must a HCP find if a mother used NSAIDs or ASA for a proper cardiac workup history>
|
-There is increased risk of pulmonary HTN in newborns
-Can cause increase risk of premature closure of the ductus |
|
|
What can lithium use in during pregnancy cause?
|
increased risk for Ebstein's anomoly of the tricuspid valve
|
|
|
If a mother were to have SLE, what cardiac problem might the child have?
|
neonatal Heart block
|
|
|
True or false: insulin dependent diabetic pregnant women have greater chance of cardiac problems with the baby than non-insulin dependent diabetics>?
|
TRUE
|
|
|
How many weeks do all expecting mothers have cardiac ultrasounds?
|
18 weeks
|
|
|
What % of babies born to women with SLE have heart block?
|
50%
|
|
|
What are the common cardiac complications to the infant born to a women with diabetes?
|
-Cardiomyopathy
-Transposition of the great veins -Ventricular septal defect -PDA -D-TGA/VAD |
|
|
What type of genetic trait is a hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
|
Autosomal Dominant
|
|
|
List the most pertinent general information that should be found in the history for a cardiac exam.
|
-Exercise tolerance, chest pain, syncope or family history
-feeding difficulty -history of dizziness or syncope -diaphoresis, congested cough, respirations |
|
|
Children who have a 20-30% chance of having and ASD, VDS or PDA probably have a mother who used ____.
|
alcohol
|
|
|
Which teratogen has the highest frequency for CHD? What is the frequency
|
Amphetamines; 75-100%
|
|
|
What are the common malformations with amphetamine use?
|
-ASD
-VDS -PDA -D-TGA |
|
|
What is the frequency of CHD with hydantoin use and what are the common malformations
|
2-3%
-PS, AS, Coarctation of aorta, patent ductus PDA |
|
|
10% of children born to mothers taking ___ will have Ebstein or ASD.
|
Lithium
|
|
|
What is Holt-Oram disease and what is it associated with?
|
Disorder that causes abnormalities in the upper extremities (bones in the arms) and can also cause congenital heart disease
|
|
|
What is often the cause of myocarditis?
|
inflammation of coxsackie B
|
|
|
What are the age appropriate history items that should be collected for an infant?
|
-growth
-feeding -color -congested cough -rapid deep breathing with SOB in a colicky baby suggest heart failure |
|
|
What is a common presentation of an ASD?
|
Fixed split S2 and the child will easily tire
|
|
|
List the history items that must be taken for a school aged child during a cardiac exam?
|
-Growth pattern
-Chest deformity -activity level -difficulty in keeping up iwth activity -history of dizziness or syncope -Tires after activity |
|
|
What are the important maternal medications to have in the prenatal history of a cardiac exam if they were taken.
|
-Dilantin
-Coumadin -psychotherapeutics -antiepileptics |
|
|
What are the 3 important infections of the mother to have documented in the family history for a cardiac workup?
|
-CMV
-Coxsackie -Herpes |
|
|
What is the most normal variation of heart rhythm and describe its pattern.
|
Sinus arrhythmias
-The heart rate speeds up and slows down in regular fashion and varies with respirations |
|
|
What is the most likely diagnosis if a child has a large drop in blood pressure in the legs compared to the upper extremities?
|
Coarctation of the aorta
|
|
|
True or False: Blood pressure should be lower in the legs than in the arms?
|
False! it should be higher
if lower think coarctation of the aorta |
|
|
What is the normal O2 sat for children with a right to left shunt?
|
75-85%
|
|
|
What are the 3 places to evaluate for cyanosis?
|
-Central: abdomen
-Peripheral: on extremities -acrocyanosis: common in newborns on the hands and feet |
|
|
Why might children with CHD have belly pain?
|
Because the blood is necessary for the heart and the brain, it is shunted away from the periphery and other organs causing hypoxia and thus pain
|
|
|
What type of lung sounds are heard in children with cardiac problems?
|
Clear wheezes
grunting rales |
|
|
True or false: All wheezes in children and associated with asthma?
|
False: CHD has wheezes
|
|
|
At what age range does the liver move under the costals?
|
preschool
|
|
|
What is normal size liver edge in children?
|
1-2cm soft edge
|
|
|
What is the name of the disorder where only the heart is inverted in the body?
|
dextracardia
|
|
|
Situs inverses is associated with which syndrome? What is the major symptom of that syndrome?
|
Kartegener's
results in the cilia not working resulting in recurrent pneumonia |
|
|
In reference to the nipple line, where is the PMI located in a normal patient?
|
To the right of the nipple line
|
|
|
If the heart is enlarged, where might the PMI be located?
|
To the left of the nipple line
|
|
|
List the 7 pertinent inspection items that should be done during a cardiac exam.
|
1. Close observation of growth and development
2. Cyanosis 3. Look for precordial bulging, sign of right sided enlargement 4. clubbing 5. VS 6. Jugular venous pulsation 7. Pallor, cyanosis, peripheral lymphedema |
|
|
The pulse rate increases by __ to ___ bpm for each centigrade of fever.
|
10-15
|
|
|
Why do premature babies often have bounding pulses?
|
lack of subcutaneous fat and higher incidence of PDA
|
|
|
What is waterhammer pulse?
|
bounding rapid pusle that is usually taken at the radial or ulnar arteries
|
|
|
What is Corrigan's pulse?
|
A bounding rapid pulse heard at the carotid artery
|
|
|
Describe the Quinke pulse and which CHDs it is associated with.
|
It is a visible pulsation at the end of the finger in the nail bed.
Associtated with: -PDA -AR -Peripheral AV fistula -Sinus arrhythmias |
|
|
What is the best position for the child to be in to feel basal thrills?
|
with the child sitting up
|
|
|
How should the child be positioned to palpate the apex?
|
on their left side
|
|
|
Are thrills present with ventricular septal defect? If so, where?
|
Yes: they are high pitched along the LBD
|
|
|
IF a patient has a low frequency thrill in the 2nd ICS what might be the diagnosis?
|
Aortic stenosis
|
|
|
What is the thrill of mitral stenosis?
|
Diastolic thrill at the apex
|
|
|
What can Eisenmenger Syndrome lead to?
|
precardial bulge
|
|
|
At what age does the apex of the heart remain at the 5th ICS midclavicular?
|
7
|
|
|
Before the age of 7, where is the apex of the heart located?
|
at the 4th ICS to the right of the midclavicular line
|
|
|
What is the most common area of the heart for hearing flow murmurs?
|
Erb's point
|
|
|
What are flow murmurs?
|
Think Pocahantis, Turbulence that occurs when there is a bend in the flow
|
|
|
When are flow murmurs heard commonly?
|
In the newborn period and from 3-7 years old
|
|
|
What are the extra areas to auscultate in the cardiac exam in children?
|
-Infraclavicular
-Carotid -Axillary -Posterior aspect -under the scapula |
|
|
What are you actually listening for when you are assessing a diastolic murmur.
|
Low pitched sounds and the absence of silence during diastole
|
|
|
When auscultating the axillary and the posterior aspect, what is the HCP checking for?
|
Radiation
|
|
|
when is the best time to listen to the heart in infants?
|
During feeding
|
|
|
How/When should the nurse listen to the 4 month old-1year old's heart sounds?
|
When the baby is being brought to sitting position: strain causes valsalva and can hear the murmur
|
|
|
How can a nurse best listen for heart sounds in a toddler?
|
Play with them and help them have confidence in you. Give them time to warm up.
|
|
|
True or false: innocent murmurs go away during the valsalva maneuver?
|
True
|
|
|
what causes S1
|
the closure of the tricuspid and mitral valves
|
|
|
What might a split S1 be in children?
|
-Can be normal
-Or if wide can be right bundle branch block or Ebstein anomaly |
|
|
What causes S2
|
The closure of the aortic and pulmonic
|
|
|
Which valve (aortic/pulmonic) closes first?
|
aortic
|
|
|
Describe physiological splitting.
|
Normal heart sounds on expiration, but the S2 is split on inspiration
|
|
|
What is fixed splitting?
|
The S2 has a split beat on both inspiration and expiration
|
|
|
What does a fixed split S2 almost always indicate?
|
ASD
|
|
|
What is the quality of a split S2?
|
each of the sounds are of equal intensity and quality
|
|
|
where are Split S2s heard best?
|
At the base
|
|
|
Describe physiological splitting.
|
Normal heart sounds on expiration, but the S2 is split on inspiration
|
|
|
What is fixed splitting?
|
The S2 has a split beat on both inspiration and expiration
|
|
|
What does a fixed split S2 almost always indicate?
|
ASD
|
|
|
What is the quality of a split S2?
|
each of the sounds are of equal intensity and quality
|
|
|
where are Split S2s heard best?
|
At the base
|
|
|
What are the things to look for when attempting to distinguish between splitting and S3?
|
LIst for the intensity, quality, position, and the distance between the sounds
|
|
|
How are murmurs produced?
|
Produced when the blood velocity becomes critically high in the presence of an irregularity or narrowing of the surface over which the blood flows.
|
|
|
The loss of ___ results in turbulence which in turn produces a sound.
|
Laminarity
|
|
|
True or false: the frequency of the sound from the turbulence varies directly with velocity of the blood flow.
|
True
|
|
|
What is an example of high sound frequencies murmurs?
|
Mitral regurgitation
|
|
|
High sound frequencies are associated with ___ ___ jets.
|
high velocity
|
|
|
What is the direction of flow in murmurs such as mitral regurg?
|
Flow from the high pressure left ventricle to the low pressure left atrium
|
|
|
What are the aids to auscultation?
|
-Quiet room
--quiet patient -no distractions -good stethoscope -good hearing -close your eyes |
|
|
What are the type of murmurs?
|
-Systolic
-Diastolic -continuous |
|
|
What are the types of systolic murmurs?
|
-Ejection
-holosystolic or regurgitant -Lub sh Dub, Lub sh Dub |
|
|
What type of murmurs are characteristic with heart disease?
|
Diastolic
|
|
|
WHat is mean by the quality of a murmur?
|
-Frequency: early, late, continuous
-Pitch |
|
|
List the factors related to the intensity of a murmur?
|
-The velocity of the blood
-The volume of blood causing the murmur -the distance from the site of the origin of the murmur to the stethoscope |
|
|
What is the grade of a murmur that is faint, and not easily heard?
|
1/6
|
|
|
A murmur that is faint but heard immediately would be graded ___?
|
2/6
|
|
|
If a murmur is loud with with no thrill, what is its grade?
|
3/6
|
|
|
If a murmur has a palpable thrill, what is the minimum grading?
|
4/6
|
|
|
What is 5/6 murmur?
|
Loud with a thrill and heard with the edge of the stethoscope on the chest
|
|
|
How would a HCP provider describe a 6/6 murmur?
|
Heard with the stethoscope 1cm off of the chest wall
|
|
|
Where is the 3rd heart sound heard the best?
|
Loudest in the non-compliant left ventricle
|
|
|
WHat filling is the 3rd heart sound associated with?
|
Left ventricular filling
|
|
|
True or false: an intermittent S3 may be a normal variant
|
true
|
|
|
What are the extra cardiac sounds?
|
-Friction rubs
-Bronchial sounds -Rales -Pleural rubs -Wheezes |
|
|
What is the likely diagnosis if a child has a friction rub heart sound?
|
pericarditis likely associated with lupus or viral infection
|
|
|
True or false: innocent murmurs can radiate, but with no thrill.
|
FALSE: they do not radiate!
|
|
|
What is the radiation of a murmur based on?
|
-Direction of blood flow
-Site of origin -Intensity of the murmur |
|
|
If a patient has a thrill, they most likely have ___ or ____
|
CHD or cardiomyopathy
|
|

What is this an example of?
|
Late systolic murmur
|
|
|
How do you characterize an innocent murmur?
|
-systolic
-less than grade 4/6 (no thrill) -Generally increased with fever, anemia, anxiety, excitement -sitting or standing decreases murmur due to venous pooling -several specific types |
|
|
T or F: all sickle cell kids will have murmurs?
|
True
|
|
|
Why does anemia cause murmurs?
|
less RBCs = more turbulence
|
|
|
Why can murmurs occur post-operatively?
|
Do to anemia from blood loss in surgery
|
|
|
List the names of the innocent murmurs.
|
-Still's murmur
-Pulmonary flow murmur -Peripheral pulmonic stenosis murmur -supraclavicular bruit -venous hum |
|
|
When does the Still's murmur usually appear and disappear?
|
Usually found in preschool and disappears at puberty
|
|
|
What is the most common innocent murmur?
|
Still's murmur
|
|
|
What causes Still's murmur?
|
Uniform periodic vibration of the left heart structure
|
|
|
What age group is most commonly seen with Still's and at what location on the chest can it be heard?
|
Age 3-7 and heard at Erb's point
|
|
|
Describe how Still's murmur sounds.
|
Buzzy sound short systolic.
Strong when laying down |
|
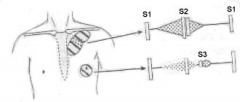
What is the top murmur?
|
Ejection systolic
|
|
|
___ % of murmurs are pulmonary ejection flow murmurs?
|
15
|
|
|
What is the probably cause of pulmonary ejection murmurs?
|
mildy turbulent flow in the right side of the heart
|
|
|
pulmonary ejections murmurs are usually (diastolic, systolic), (long/short) ejection murmurs.
|
systolic short
|
|
|
Where on the chest are pulmonary ejection murmurs heard best?
|
upper left sternal
|
|
|
What is the age group associated with pulmonary ejection flow murmurs?
|
All ages, (rare in infants) much more common in late childhood and early adolescents
-6th-8th grade |
|
|
Pulmonary ejection murmurs are heard louder on (inspiration/expiration/both).
|
expiration
|
|
|
True or false: pulmonary ejection murmurs are associated with a normal Split S2
|
True
|
|
|
What are the factors that can increase the intensity of pulmonary ejection murmurs?
|
-increased cardiac output
-supine position -fever/anemia -exercise |
|
|
What is the highest grading for a pulmonary ejeciton murmur?
|
3/6
|
|
|
What murmur is associated with straight back syndrome?
|
pulmonary ejection murmur
|
|
|
Thin back habitus is common with ___?
|
pulmonary ejection murmur
|
|
|
What is the best way to hear pulmonary ejection murmur?
|
in the supine position during exhalation
|
|
|
Describe where the pulmonary ejection murmur is heard on the body?
|
right and left sternal border and transmits to the back
|
|
|
What is the most common click?
|
mitral valve stenosis
|
|
|
What is the cause of peripheral pulmonic branch stenosis?
|
turbulence arising the acute angle at which the relatively small branch pulmonary arteries take off from the main pulmonary artery
|
|
|
Peripheral pulmonic branch stenosis is a (diastolic/systolic), (ejection/filling) murmur that disappears at ___ months?
|
systolic, ejection; 6
|
|
|
What might be the dx if a peripheral pulmonic branch stenosis murmur does not disappear by 6 months?
|
It is associated with Williams syndrome and congenital rubella
|
|
|
Where are peripheral pulmonic stenosis murmurs usually heard best?
|
in the axillary area best also on the chest
|
|
|
what murmur usually goes away as the pulmonary artery gets wider and less bent?
|
peripheral pulmonic stenosis murmur
|
|
|
What is the cause of a supraclavicular carotid bruit?
|
Turbulence at the take off area of the brachiocephalic and carotid arteries from the aortic arch
|
|
|
Does a supraclavicular carotid bruit mean that there is a narrowing of the carotid artery?
|
NO: just turbulence
|
|
|
What murmur is a systolic ejection murmur that is high pitched and harsh?
|
supraclavicular carotid bruit
|
|
|
Where is a supraclavicular carotid bruit heard best?
|
in the supraclavicular fossa on the right more than the left
|
|
|
T or F: a supraclavicular carotid bruit radiates far
|
False
|
|
|
Is the supraclavicular carotid bruit heard below the clavicle?
|
no
|
|
|
Does changing to sitting or lying position affect the supraclavicular carotid bruit?
|
no
|
|
|
What action decreases the supraclavicular carotid bruit?
|
hyperextension of the shoulder
|
|
|
What murmur is continuous and characterized as background noise?
|
Venous hum
|
|
|
when is a venous hum heard best?
|
when sitting or standing
|
|
|
what causes a venous hum to dissappear?
|
change in head position, digital pressure, lying supine
|
|
|
Is a venous hum heard at the supraclavicular location?
|
Yes
|
|
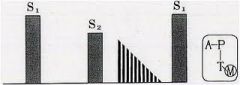
What kind of murmur is this?
|
mid diastolic murmur
|
|
|
T or F: murmurs are common in neonates?
|
TRUE
|
|
|
T or F: the absence of murmurs means no heart disease
|
FALSE
|
|
|
When should a HCP refer a neonate for a cardiac workup?
|
1. Loud or long murmur
2. Murmurs radiating to the back 3. appears ill 4. any diastolic murmur 5. Abnormal CXR or EKG 6. dysmorphic features 7. abnormal cardiac sounds (clicks, rubs, abnormal split S2 or single S2 |
|
|
What is a S4 also known as?
|
gallop
|
|
|
What are the clues to cardiac disease in neonates?
|
1. Cyanosis
2. Tachypnea and Tachycardia 3. diaphoresis 4. gallop 5. Abnormal splitting S2 6. abnormal precordial activity (thrill) 7. hepatomegaly 8. abnormal pulses: coarctation 9. BP lower in lower extremities: coarctation 10. Mottle extremities: coarctation |
|
|
What are the significant history items that would warrant a referral over 6 weekss old for cardiac exam?
|
1. Tachypnea
2. feeding intolerance, poor weight gain 3. exercise intolerance, exercise fatigue 4. frequent respiratory infections 5. syncope 6. persistent cough, wheezing (not asthma) 7. chest pain with exertion 8. cyanosis 9. palpitations |
|
|
What heart specific abnormalities would warrant a referral?
|
1. Abnormal pulse or BP
2. abnormal S1 or S2 3. displaced apical impulse 4. click, gallop, rumble 5. murmur ( diastolic, continuous, loud) |
|
|
What are the general characteristic of murmurs needing evaluation?
|
1. Murmurs in symptomatic kids
2. loud murmur 3. diastolic murmur 4. murmurs that don't fit into the categories of innocent murmurs |
|
|
What are the most common heart defects?
|
septal defects
|
|
|
What are the common septal defects?
|
ASD and VSD
|
|
|
Where are ASDs heard?
|
2nd intercostal
|
|
|
What ICSs are associated with VSDs?
|
3rd and 4th
|
|
|
What are the common murmurs that cause obstruction to ventricular outflow?
|
1. Valvar, subvalvar, supravalvar, aortic or pulmonic stenosis
2. Coarctation fo the aorta 3. PDA |
|
|
Describe turbulence in ventricular outflow associated with systolic murmurs.
|
1. narrowing of aortic or pulmonary valve, aorta or pulmonary artery
2. increased flow |
|
|
What are the causes of systolic murmurs?
|
1. turbulence in ventricular outlfow
2. AV valve regurg 3. abnormal ventricular or arterial communications |
|
|
Give 2 examples of abnormal ventricular or arterial communications.
|
1. VSD
2. PDA |
|
|
Aortic valve stenosis occurs in __% of chidlren with CHD.
|
5
|
|
|
What are the associated defects with aortic valve stenosis?
|
coarct, VSD, PDA
|
|
|
What is the MOST COMMON congenital heart defect and what % of the population has it?
|
non-obstructive isolated bicuspid aortic valve and occurs in 1% of the population
|
|
|
What occurs with children who have bicuspid aortic valve?
|
they get aortic stenosis at a younger age
|
|
|
What is the most common presentation of aortic stenosis?
|
murmur
|
|
|
What is required if a child with aortic stenosis has a very narrow valvular opening? How might that child initially present?
|
Need the right to left shunting available through a PDA. Child may present acutely with shock or CHF is ductus closes
|
|
|
What is needed to maintain life for a child with atresia?
|
a PDA and PFA
|
|
|
T or F: aortic stenosis may be valvular, subvalvular, or supravalvular?
|
TRUE
|
|
|
What sound helps to distinguish aortic stenosis from pulonary flow murmur?
|
the click that begins early in systole
|
|
|
can aortic stenosis radiate? Where?
|
Yes, to the neck
|
|
|
where might a thrill be felt in children with aortic stenosis?
|
suprasternal notch or carotid arteries area
|
|
|
___ Aortic stenosis usually causes a sytsolic ejection click at the __ of the heart.
|
Valvular; apex
|
|
|
T or F: a click is present in the most severe cases of aortic stenosis.
|
FALSE!!!!!
|
|
|
where is pulmonic stenosis heard best?
|
Uppoer left sternal border
|
|
|
where does pulmonic stenosis radiate?
|
to the back
|
|
|
if a thrill is present for pulmonic stenosis, where does it occur?
|
suprasternal notch
|
|
|
Describe where the click occurs for pulmonic stenosis?
|
systolic ejection click at the lower left sternal border which varies with respirations
|
|
|
when does a PDA normally close?
|
48 hours after birth
|
|
|
where does the blood flow in a PDA?
|
blood from right ventricle into descending aorta, bypasses the lungs
|
|
|
what does the direction of the shunt in a PDA depend on?
|
the differential resistance between the aorta and the pulmonary artery
|
|
|
What are the disorders associated with right to left ductal shunting? Is this severe?
|
severe coarctation and HLH. Yes they are severe cases
|
|
|
What is a child at risk for if a PDA is not found?
|
Pediatric STROKE!!
|
|
|
when does a child present with a PDA?
|
usually present with pulmonary overcirculation around 4-6 weeks when the pulmonary pressure falls
|
|
|
what does a single S2 mean?
|
pulmonary hypertension
|
|
|
what are the example of pulses related to PDAs?
|
wide bounding (waterhammer) pulses with quinke pulses
|
|
|
what is a coartation of the aorta?
|
narrowing of the aortic arch adjacent to the site of the ductus
|
|
|
What CHD is associate with a systolic ejection murmur below the left scapula?
|
coarctation of the aorta
|
|
|
What can occur is coarct is severe?
|
shock
|
|
|
what type of murmur occurs with a ventricular septal defect VSD?
|
holosystolic murmur: harsh, high pitched if VSD is small
|
|
|
A __ rumble is heart at the apex with VSD?
|
diastolic
|
|
|
Will a child with a VSD be cyanotic?
|
no
|
|
|
What occurs with large VSD?
|
1. Increase in LA pressure
2. pulmonary edema 3. increase work of breathing 4. poor growth |
|
|
What does VSD lead to if not found?
|
pulmonary hypertension
|
|
|
What causes the diastolic rumble of a VSD?
|
vibration of the mitral valve as the large volume of flow from the lungs goes into the left ventricle
|
|
|
True or false: the size of the VSD increase the size of the murmur?
|
FALSE
|
|
|
At birth, a child with a VSD will have shunting that occurs in which direction?
|
right to left because of increased pulmonary vascular resistance at birth.
|
|
|
Describe the S2 of of the VSD.
|
normal to wide split S2 that varies with respirations
|
|
|
when the pulmonary valve tend to close with a VSD?
|
later because of increase volume transfersing it
|
|
|
IS CHF seen with ASDs?
|
NO
|
|
|
Describe how children with ASD's exercise?
|
they have suble intolerance
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of an ASD.
|
1. Systolic ejection murmur
2. upper left sternal border 3. wide fixed split S2 4. right ventricular impulse 5. diastolic rumble at lower left sternal border |
|
|
What causes diastolic murmurs?
|
1. Turbulence in ventricular inflow: narrowing or increased flow
2. semilunar valve regurg |
|
|
What causes continous murmurs?
|
1. Abnormal systemic to pulmonary artery communications: PDA
2. Abnormal arteriovenous communications: AV fistula, coroanary artery fistula (really rare) |
|
|
What are the normal common murmurs in the first few days of life?
|
1. PPS
2. pulmonary flow murmurs 3.transitional murmurs a. closing PDA b. transient tricuspid regurg |
|
|
What are the common abnormal outflow obstructions in the first few days of life?
|
1. AS
2. PS 3. coarctation |
|
|
what are the abnormal communication problems that occurs in the first few days of life?
|
1. VSD
2. PDA |
|
|
What are the characteristics of transient tricuspid regurg murmurs?
|
they are trasitional
-LLSB -regurg, systolic -often seen with asphyxiated infants or infants with pulmonary HTN -takes several days to resolve |
|
|
List the complex congenital heart diseases?
|
1. Ebstein anomaly
2. common AV canal (truncus) 3. tetrology of fallot 4. HLH 5. trasposition of the great veins (d-TGA) |
|
|
are children with HLH cyanotic?
|
not initially but over the stage of repair
|
|
|
are transitional murmurs vibratory?
|
occasionally
|
|
|
transitional murmurs are often __ as the PDA gets smaller?
|
louder
|
|
|
what occurs in ebstein's anomaly?
|
Low insertion of the tricuspid valve which divide the right ventricle into proximal and distal chambers
|
|
|
which chamber of the right ventrical acts as the pumping chamber in ebstein's anomaly?
|
the distal chamber
|
|
|
What the proximal atrialized division of the right ventricle act as in ebstein's anomaly?
|
works as the receiving chamber
|
|
|
What is the problem with the tricuspid valve in ebstein's anomaly? What does it lead to?
|
it is deformed and leads to tricuspid regurg
|
|
|
In ebstein's anomaly, a __ to __ intra-atrial shunt is often present.
|
right to left
|
|
|
Which CHD increases in intensity/loudness as you have the child go from a squatting to a standing position>
|
hypertophic cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
T or F: most children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy have symptoms.
|
FALSE
|
|
|
What occurs with infants with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy>
|
may have biventricular outflow tract obstruction in infancy
|
|
|
What occurs when you raise the leg of a child with HCM?
|
the intensity actually decreases!! They have a small chamber and a thick wall@!
|
|
|
what are the maneuvers that increase the intensity of the murmur of HCM?
|
1. decreasing preload: valsalva
2. increasing contractility: exercise 3. decrease afterload: standing suddenly |
|
|
What maneuvers decrease the intensity of the murmur of HCM?
|
1. increase afterload: squat or hand grasp
2. increase preload: raise legs |
|
|
T or F: syncope is a symptom, not disease.
|
true
|
|
|
what is the underlying mechanism of syncope?
|
transient global cerebral hypoperfusion (ischemia)
|
|
|
Are seizures common with syncope?
|
no
|
|
|
what % of syncope is normal mediated?
|
40%
|
|
|
What are the prodromal symptoms of syncope?
|
1. nausea
2. palpitations 3. diahporesis, cold sweat 4. tinnitus, hearing loss 5. pallor 6. dizziness, light headedness 7. blurred vision 8. weakness |
|
|
What are the neurally mediated classes of syncope?
|
1. cardioinhibitory (bradycardia)
2. vasodepressor (hypotension) 3. combination |
|
|
What are the 3 cardiovascular conditions associated with syncope?
|
1. congenital heart disease
2. coronary heart disease 3. arrhythmia |
|
|
What are some causes of syncope that are not related to neural or cardiovascular issue?
|
1. epilepsy
2. psychogenic 3. metabolic |
|
|
What mediates vasovagal syncope?
|
neurocardiogenic
|
|
|
What is bezold-jarisch relfex?
|
paradoxical response of bradycardia, vasodilation and hypotension leading to vasovagal syncope
|
|
|
What 2 aspects of circulation decrease during vasovagal syncope?
|
1. decrease systemic venous return (standing)
2. decrease left ventricular end diastolic volume |
|
|
what function of the heart is increased in vasovagal syncope?
|
mechanical contractility of the Left ventricle
|
|
|
what is reflex syncope?
|
results from hypersentitive autonomic response fro various afferent inputs
|
|
|
what are the various afferent inputs that contribute to reflex syncope?
|
1. micturition
2. swallowing 3. coughing 4. sneezing 5. defecation 6. noxious stimuli: blood |
|
|
What are the predisposing factors to vasovagal syncope?
|
1. physical exhaustion
2. prolonged recumbency: quick stand 3. prolonged standing 4. peripheral vasodilation: exercise, hot shower, hot weather 5. pregnancy 6. noxious stimuli: blood, emotional stress |
|
|
Is syncope with exercise worrisome?
|
YES!!!!
|
|
|
is neural-mediated syncope often associated with sudden death?
|
no
|
|
|
When is syncope worrisome?
|
1. family hx of sudden death
2. family hx of seizure disorder (long QT) 3. myocardial disease 4. syncope with exercise |
|
|
What will the HCP be looking for during a syncope work-up with the EKG?
|
1. Long QT
2. Wolf-parkinsons wiffe syndrome WPW 3. complete heart block 4. mycoardial ischemia 5. myocarditis 6. ventricular hypertrophy |
|
|
why can surgery to repair complex CHD cause syncope?
|
arrhythmias may result from electrical rewiring
|
|
|
What testing techniques might cardiologist use to monitor for cardiac related syncope?
|
1. event monitoring
2. exercise stress testing 3. EKG 4. nuclear studies |
|
|
What are the therapy options for syncope?
|
1. Volume and solute replacement: salty snacks
2. beta-blockers 3. mineralcoritcoids: volume expansion with salt retention, reserved for problematic recurrent syncope |
|
|
what is the mean age of children who complain of chest pain?
|
12
|
|
|
how many visits to the ED are for chest pain?
|
6 in 1000
|
|
|
does chest pain occur equally in boys and girls?
|
yes
|
|
|
what is the likely cause of chest pain in young children?
|
cardiorespiratory
|
|
|
What is the likely cause of chest pain in adolescents?
|
psychogenic
|
|
|
What is the overall most common cause of chest pain in kids?
|
musckuloskeletal costalitis
|
|
|
how many children with chest pain are awaken from their sleep?
|
1 in 3
|
|
|
how many kids with chest pain will miss school because of symptoms>?
|
1 in 3
|
|
|
List the differential dx for chest pain.
|
1. Musculoskeletal pain
2 respiratory conditions 3. psychogenic disturbances 4. gastrointestinal disorders 5. cardiac disease 6. idiopathic: 20-45% in some studies |
|
|
What are thee common causes of musculoskeletal chest pain?
|
1. new exercise
2. wrestling 3. heavy books 4. chest wall trauma 5. costochondritis: tenderness on palpation, worse with breathing, persistent |
|
|
What are the causes of respiratory related chest pain?
|
1. persistent cough
2. asthma 3. pneumonia 4. new exercise 5. spontaneous pneumothorax 6. pulmonary embolism |
|
|
what are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
|
1. fever, dyspnea, pleuritic pain, cough, hemoptysis
2. more common in adolescent females because of OC use 3. males with hisotry of leg trauma |
|
|
what is the most common cause of psychogenic chest pain?
|
family member or friend with recent heart attack
|
|
|
What are the GI causes of chest pain?
|
1. reflux esophagitis
2. foreign body (quarters, batteries; must come out!) 3. hiatal hernia 4. sub-diaphragmatic abscess |
|
|
List the cardiac causes of chest pain.
|
1. myocardial ischemia
2. kawasaki disease 3. cocaine and other drugs 4. arrhythmias 5. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 6. marfan syndrome: wide aorta prone to tearing 7. pericarditis |
|
|
what are the symptoms of myocardial ischemia?
|
pressure sensation with or without burning
-radiation to the neck, shoulder or arm -occurs during or following exercise -improves with rest |
|
|
what are the 2 listed coronary disease types that should have a work-up for myocardial ischemia?
|
1. kawasaki disease
2. transposition of the great arteries |
|
|
Describe the pain of aortic dissection.
|
usually acute and sharp and may present in the anterior chest or the back depending on the area of the aorta affected
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of marfan syndrome?
|
1. autosomal dominant
2. disorder of fibrillin 3. chromosome 15, FBN1 gene |
|
|
other than marfan syndrome, what other disease is associated with aortic dissections?
|
Ehlers-Danlos
|
|
|
how is the pain of pericarditis described?
|
squeezing or tightening
|
|
|
is the pain of pericarditis worse or better with movement, including breathing?
|
worse
|
|
|
how might a patient with pericarditis be positioned>
|
leaning forward, refusing to lay down
|
|
|
when does a friction rub occur with pericarditis?
|
when it is small and has no effusion
|
|
|
what occurs with large effusion in pericarditis?
|
no rub, but have distant heart sounds
|
|
|
when is an echocardiogram indicated for chest pain?
|
Rub, family history of HCM, congenital heart disease
|
|
|
when should a HCP refer out for chest pain?
|
1. with or after exercise
2. with syncope or near syncope 3. in patient with previous cardiace disease or hisotry of cardiac surgery 4. acute, sudden onset in marfan syndrome |
|
|
what cardiac condition is very common with drug users?
|
endocarditis
|
|
|
what area of the heart is most commonly involved in endocarditis?
|
the valves
|
|
|
list the endocardial surfaces that may get endocarditis.
|
1. margins of the septal defects
2. chordae 3. grafts and other foreign materials 4. blood vessels (ductus arteriosus) |
|
|
What is the new recommended treatment for endocarditis?
|
early surgery over antibiotics
|
|
|
Is endocarditis life threatening?
|
Yes! It was fatal prior to antibiotics: now it has > 85% survival rate
|
|
|
Have studies found a high incidence of endocarditis with invasive procedures?
|
no
|
|
|
true or false: the majority of endocartitis cases are attrbuted to invasive procedures.
|
FALSE
|
|
|
what should be considered before beginning SBE prophylaxis?
|
1. the degree of risk for endocarditis of the patient's underlying CHD
2. the risk of bacteremia for the procedure 3. the potential adverse reaction of the antibiotic prophylaxis 4. the cost-benefit aspects of the recommended antibiotic prophylaxis |
|
|
What are the cardiac conditions that increase the risk for endocarditis?
|
CHD that is unrepaired, repaired within 6 months, valvular disease after transplant
|
|
|
If pre-schoolers have chest pain, what should be the first differential dx?
|
supraventricular tachycardia: palpitations
|
|
|
what are the cardiac causes of palpilations in children?
|
1. premature atrial contractions
2. PVCs 3. SVTs 4. Afib 5. Vtach |
|
|
what is one of the number 1 reasons for palpitations in children?
|
Caffeine, especially in those on ADHD drugs
|
|
|
does SVT usually cause syncope?
|
no, they are still perfused well. Vtach causes syncope
|
|
|
What findings on the EKG can show palpitation?
|
1. P wave mophology, axis
2. pre-excitation: wolfe-parkinson-white syndrome 3. long QT 4. premature beats |
|
|
what is the name of the abulatory ECG that can capture 24 readings?
|
holter monitor
|
|
|
true or false: premature atrial and single, monomorphic ventricular beats when asymptomatic generally should be referred?
|
FALSE
|
|
|
T or F: ADHD meds have been found to increase the risk for cardiac conditions?
|
FALSE
|
|
|
What does a sports physical address?
|
1. exercise induced asthma
2. mild traumatic brain injury 3. female atheletic triad 4. scoliosis |
|
|
what is the rate of HCM?
|
1 in 500
|
|
|
which gender has higher rates of sudden death due to HCM?
|
males
|
|
|
True or false: the intensity of exercise is related to the incidence of sudden death related to HCM?
|
TRUE
|
|
|
what are the sports associated with high intensity?
|
football, basketball, track and soccer
|
|
|
What is the common demoninator for why athletes die on the field?
|
they develop fatal arrhythmias
|
|
|
What are the congenital disorders associate with sudden death?
|
1. HCM
2. coronary anomalies 3. aortic stenosis 4. arrhythmias (WPW, Long QT syndrome) |
|
|
what are the acquired heart disorders that can lead to sudden death?
|
1. myocarditis
2. dilated cardiomyopathy 3. coronary artery disease |
|
|
what is commotio cardis?
|
cardiac concussion due to trauma: a punch in the chest that can cause sudden death
|
|
|
Other than cardiac anomalies, what other conditions have been found to cause sudden death?
|
1. cerebral aneurysm
2. sickle cell trait 3. bronchial asthma 4. durg use: cocaine, meth etc 5. commotio cardis |
|
|
What are the heart defects that are cyanotic?
|
-Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF)
-Transposition of the great arteries (d-TGA) -Truncus arteriosus (Persistent) -Tricuspid atresia -Pulmonary atresia (PA) -Eisenmenger syndrome(Reversal of Shunt due to Pulmonary Hypertension) . -Ebstein's Anomaly |
|
|
What are the non-cyanotic heart defects?
|
-Atrial septal defect
-Ventricular septal defect -Coarctation of aorta (may cause cyanosis in some cases) -HLH -PDA -Tracheal Rings -pulmonic stenosis -aortic stenosis |

