![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
147 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When a child complaining of knee pain, what parts of the body should be assessed? Why?
|
Must assess the hip and the ankle (joints above and below the complaint) because the child has referred pain.
|
|
|
What are the general assessment features of gait?
|
-observe walking and running
-arm movement with respect to legs -look at each part of the child separately: head, trunk, arms, hips, knees, feet/ankles -limp? |
|
|
What is the minimum number of times that an xray should be taken on a child?
|
twice
|
|
|
Describe how hip films should be taken.
|
Should always be bilateral hips and pelvis (never do a film of only one hip)
|
|
|
During the 2 minute exam, what should the nurse inspect for when the child is standing facing you?
|
Symmetry
|
|
|
Describe how the nurse would check range of motion of the cervical spine during the 2 minute exam.
|
Forward flexion, extension, rotation, and lateral flexion of the neck
|
|
|
How does the nurse check for proper function of cranial nerve 11?
|
Have the child resist should shrug and look for strength of the trapezius
|
|
|
When the nurse asks the child to resist shoulder abduction, what muscle are they testing?
|
The strength of the deltoid
|
|
|
How should the nurse check for range of motion of the shoulder joint during the 2 minute exam?
|
Internal and external rotation of the shoulder
|
|
|
After the nurse assess the shoulder in the 2 minute exam, what should the nurse check next?
|
extension and flexion of the elbow
|
|
|
Following the extension and flexion of the elbow, what is the next step in the 2 min exam?
|
pronation and supination of the elbow
|
|
|
How can the nurse check ROM of the hands in a child's 2 min exm?
|
-Clench fist
-Spread fingers -thumbs up -cross fingers -then spread them |
|
|
What is the name of the "walk" the nurse asks the child to do in the 2 min exam and how many steps?
|
Duck walk, 4 steps
|
|
|
During the time the child is doing the duck walk away from the nurse, what is the nurse assessing?
|
Inspecting the trunk and upper extremities for symmetry
|
|
|
What is the nurse looking for when the child extends their back with straight knees?
|
Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis
|
|
|
What is spondylolysis?
|
It is typically caused by stress fracture of the bone, and is especially common in adolescents who overtrain in activities. It has been proposed that the pars interarticularis is especially vulnerable when the spine is in an extended position, and a force suddenly presses the vertebrae together, such as when landing on one's feet after a hop.
|
|
|
Describe spondylolisthesis.
|
is the anterior or posterior displacement of a vertebra or the vertebral column in relation to the vertebrae below.
|
|
|
After the patient extends their back, what should the nurse have them do next?
|
Flex it forward
|
|
|
What should the HCP look for when inspecting the lower extremities during the 2 min exam?
|
Contraction of the quadriceps muscles
|
|
|
How should the HCP provider go about assessing symmetry, strength and balance of the calf and the lower extremities?
|
Have the patient standing and walking on their heels and then their toes.
|
|
|
List the potential causes of toeing in and toeing out.
|
-Femoral Neck Anteversion
-Tibial Torsion -Metatarsus Adductus -or a combination of any of the 3 |
|
|
What are the 4 assessment pieces when examining a child with in toeing or out toeing?
|
-Foot Progression angle (while walking)
-Heel bissector Line (laying down) -thigh foot angle (laying down) -hip rotation (easiest on the stomach) |
|
|
Describe the foot progression angle of a child with in toeing.
|
As the child is walking, the knees are pointing forward but the toes are pointed inward. Means that the torsion is coming from below the knee
|
|

What is the name of this assessment and what does the child have?
|
Heel bissector Line
-Child has Metatarsus adductus and thus in toeing |
|
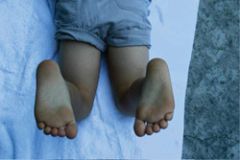
What is the HCP assessing in this picture? What is the likely diagnosis?
|
Assessing the foot thigh angle
-Child has internal tibial torsion and in toeing |
|
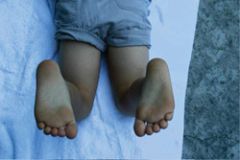
What is the HCP assessing in this picture? What is the likely diagnosis?
|
Assessing the foot thigh angle
-Child has internal tibial torsion and in toeing |
|
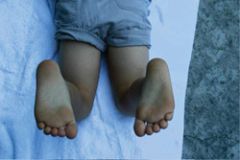
What is the HCP assessing in this picture? What is the likely diagnosis?
|
Assessing the foot thigh angle
-Child has internal tibial torsion and in toeing |
|
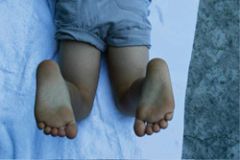
What is the HCP assessing in this picture? What is the likely diagnosis?
|
Assessing the foot thigh angle
-Child has internal tibial torsion and in toeing |
|

What is this called? Children with which gait dysfunction often have this?
|
W-sitting
Seen in children with femoral anteversion (in toeing) |
|
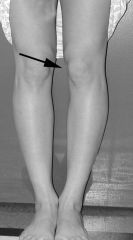
What is the name of this and what is it the hallmark sign of?
|
Patellar squint
-Hallmark sign of Femoral Neck Anteversion |
|
|
What is the medical term for bow leg?
|
Genu Varum
|
|
|
WHat is genu valgum?
|
Knock knees
|
|
|
What are the possible causes of genu varum and valgum?
|
-physiologic
-familial -blount's disease -metabolic |
|
|
Why are children under age 3 rarely given treatment for genu valum?
|
Because it corrects itself.
|
|
|
What are the appropriate circumstances to get an x-ray in children with bow legs?
|
-inappropriate alignment compared to the age of the child
-Sharp curve is present -Has a lateral thrust -Asymmetry -intercondylar distance > 15 cm |
|
|
Describe the Blount's disease and when can it be diagnosed?
|
-Metaphyseal Diaphyseal Angle
-Widening of the Physis -Beaking -Cannot be diagnose until age 2 at minimum |
|
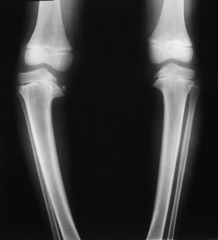
What is the name of the disease associated with this xray?
|
Blount's disease
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of pathological rickets?
|
-Frontal bossing
-Severe bowing -Low phosphate -short stature |
|
|
What are the treatment options for genu varum/valgum?
|
-Based on the cause of the deformity
-Physiologic: just observe -Blount's; Correct if progressive -Rickets: address metabolism before/ instead of surgery. If surgery then use an asphyxiator that slowly changes the angel of the tibia |
|
|
What deficiency can lead to rickets?
|
Vitamin D
|
|
|
What is a steppage gait? When is it seen?
|
Child cannot lift their toe, so they walk lifting their entire knee.
Seen in CP and Charcot Marie Tooth (CMT) disease |
|
|
What is equinus gait? Is it pathologic
|
Toe walker. Not always pathologic. Ask if it is a new finding.
|
|
|
If a child has diskitis or severe pain, what type of gait may they have?
|
Cautious gait: walking very slowly as if something will break or hurt if they move too quickly
|
|
|
What is a trendelenburg gait? When is it seen?
|
-Hip check!
-When there is a leg length discrepancy, gluteus weakness and hemiplegia |
|
|
What is the top differential diagnosis to catch if a child presents with single joint pain with fever? Why?
|
Septic arthritis, because without treatment it can destroy the joint
|
|
|
what are the differential diagnoses for joint pain WITH fever?
|
-septic arthritis
-reactive arthritis -osteomyelitis -post infectious arthritis -rheumatic disease -hemoglobinopathy -malignancy |
|
|
List the differential diagnoses for joint pain presented WITHOUT fever and no trauma?
|
-lyme disease
-rheumatic disease -avascular necrosis AVN -psychogenic pain -infection -diskitis |
|
|
What is the mean age for children who suffer from diskitis?
|
3
|
|
|
What is a technique that can be used to see if a child has diskitis?
|
if you tap on the lower back the child will scream because there is inflammation of the disk
|
|
|
What are the possible differential diagnoses for a child presenting with multiple joint pain and FEVER?
|
-infection: sepsis
-Rheumatic disease -immune deficiency -post immunization (mmr) -malignancy -inflammatory bowel disease -familial mediterranei fever |
|
|
What is an asymmetrical aberration of normal gait?
|
a limp
|
|
|
What is the most critical assessment of a child with a limp?
|
the HISTORY!
|
|
|
WHat are the 3 primary types of limp?
|
-antalgic: pain
-trendelenburg: weak abductors -short leg/circumduction: leg length discrepancy |
|
|
What are the possible causes of an acute limp?
|
-trauma
-infection -inflammatory -tumor -congenital |
|
|
If a child has a chronic limp, what may be the possible causes?
|
-CP
-DDH -Slip capital femoral epiphysis SCFE -legg/calve perthes LCP -AVN -tumor |
|
|
List the 3 most common causes of hip pain in a 0-3 year old?
|
-DDH
-septic arthritis -transient synovitis |
|
|
WHat are the physical examination test to do to check for DDH?
|
-Ortolani/Barlow
-asymmetry abduction -Galeazzi -Gait: assess for trendelenburg |
|
|
What is the age range in which ortolani and barlow can be used as a test for DDH?
|
3-4 months only
|
|
|
What should the HCP be feeling for when conducting barlow and ortolani?
|
a CLUNK, not a click
|
|
|
WHat are the 4 risk factors for DDH?
|
4 F"s
-Female -first born -feet 1st -family history |
|
|
What is the #1 cause of lawsuits against HCP in terms of pediatric orthopedics?
|
missed diagnosis of DDH
|
|
|
When assessing the asymmetric abduction of the legs of a baby, how far should the infant be able to abduct the legs?
|
all the way to the table in a frog like position
|
|
|
When conducting the Galeazzi test, the knee that is (higher/lower) is thought to have the dislocated hip.
|
lower!
|
|
|
What test can be used on infants younger than 4 months old and not overweight to assess for DDH?
|
Ultrasound
|
|
|
A ____ is the preferred radiological evaluation tool for children older than 4 months or pudgy to check for DDH
|
xray
|
|
|
What are the common characteristics of a septic hip?
|
-Young age
-posture in flexion in the ER (will cry when you try and swaddle them -Refusal to walk -ESR > 40 CRP > 2 -Temp > 101.5 -WBC > 11.5 |
|
|
How should a septic hip be ruled out?
|
If suspicion --> aspirate hip
--white cell count ouver 50,000 --open I and D If unclear --> -ultrasound defects effusion -bone scan |
|
|
___ ___ presents with fever, lethargy, and signs of joint pain/swelling/reddness.
|
Septic Joint
|
|
|
T or False: Transient Synovitis presents with pain, fever, and no lethargy.
|
False: no fever!
|
|
|
Transient synovitis is diagnosed by ____.
|
exclusion
|
|
|
T or F: transient synovitis is a one time event?
|
False: it can be recurrent
|
|
|
What are the consequences of an untreated septic joint?
|
complete destruction of the -articular cartilage and the underlying epiphysis
-loss of the adjacent growth plate -dislocation of the joint |
|
|
What are the common causes of hip pain in 3-10 year olds?
|
-Leg Calve Perthes
-Transient Synovitis -Septic Arthritis/osteomyelitis -Bilateral DDH |
|
|
Septic joint will eventually destroy the ___ ___ if not treated?
|
growth plate
|
|
|
T or F: a child with transient synovitis will still be completing normal daily activities?
|
True
|
|
|
A child with (septic joint/transient synovitis) will not be acting like themselves.
|
septic joint
|
|
|
What is the common clinical age for children who get LCP?
|
4-10 years old
|
|
|
Boys (>/<) girls in terms of Leg/calve perthes?
|
>
|
|
|
WHat are the symptoms of LCP?
|
painless limp; mild pain may affect knee
|
|
|
What will the HCP see on examination for a child with LCP?
|
-LImited internal rotation
-dysfunction gait -apparent shortening Bilateral affected 20% |
|
|
What disease are children told not to run or jump for many years?
|
Perthes
|
|
|
Transient synovitis is seen in children up to age __.
|
6
|
|
|
What disease does the head of the femur become flattened over time and dies?
|
Perthes
|
|
|
What activity are children with perthes encouraged TO DO.
|
swim
|
|
|
What is the treatment plan for transient synovitis?
|
NSAIDS and observation
|
|
|
WHat is the number one most common cause of hip pain in kids 10-16?
|
SCFE
|
|
|
List the most common causes of hip pain in children 10-16.
|
-SCFE
-AVN femoral head -osteomyelitis -chondrolysis -residual DDH -Bone Tumor |
|
|
What disorder of the hip is often seen in kids with sickle cell?
|
AVN femoral head
|
|
|
What is the M:F ratio for Slipped Captial Femoral Epiphysis?
|
2:1
|
|
|
Boys with SCFE often range from ___ to __ years old; while girls who have it are usually __ to __ years old.
|
10-16; 10-14
|
|
|
How often does SCFE occur bilaterally?
|
25-50% of the time
|
|
|
What are the risk factors for SCFE?
|
-obesity
-african american |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of SCFE.
|
-obligate external rotation
-loss of internal rotation -trendelenburg gait -acute if symptoms < 3 weeks |
|
|
What does SCFE look like on an xray
|
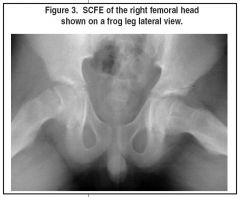
slips in the growth plate
|
|
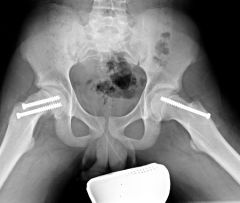
What is this image?
|
In-situ fixation for SCFE
|
|
|
WHat are the key test to conduct in a hip exam?
|
-Range of motion all directions bilaterally
-log roll test -Prone internal rotation -Faber test |
|
|
What does the log roll test show?
|
forced internal rotation of the hip
|
|
|
Why is the prone internal rotation test done on the hip exam?
|
it is indicative of intra-articular hip pathology
|
|
|
What is the faber test used for?
|
To detect SI pathologies
|
|
|
What are some miscellaneous causes of a limp?
|
-CP
-Abscess/Osteomyelitis -Back pain -knee injury -stress fractures -JRA -tarsal coalition |
|
|
What should the HCP ask for in assessing a child with a limp and possible CP?
|
-Birth Hx
-Ambidextrous until 24 months -milestones -posturing -asymmetric |
|
|
What is the number 1 place to examine when a child presents with knee pain?
|
the HIP!!
|
|
|
What are the knee specific injuries/diseases that can cause a limp
|
-meniscal or ligament injury
-osgood schlatter disease (bump on the front of the knee) -patellar-femoral -juvenile rheumatoid arthritis -septic joint -osteochondritis dissecans |
|
|
what is the name of the disorder that has an area of destruction usually on the femoral condyl?
|
osteochondritis dissecans
|
|
|
Patellar-femoral (anterior knee pain) is most often seen in ___ (boys or girls).
|
Girls
|
|
|
What are the differential diagnoses that are associated with limps and back pain?
|
-discitis
-spine or spinal cord tumor -spondylolysis/spondylolisthesis -spinal deformity -tethered cord |
|
|
True or false: scoliosis is painful?
|
False
|
|
|
surgical treatment for spondylolisthesis is only acceptable when...
|
the patient has continuing pain and a drop in activities
|
|
|
What are the foot associated problems that can cause limp?
|
-tarsal coalition
-cavus foot deformity -stress fractures -foreign body |
|
|
What is the common complaint of children with osteomyelitis?
|
"it hurts deep inside."
|
|
|
Which children are more likely to get osteomyelitis?
|
Sickle cell and immunosuppressed
|
|
|
What are the presenting symptoms of osteomyelitis?
|
-bone pain
-possible limp -swelling -fever |
|
|
Why is sepsis a concern for neonates with osteomyelitis?
|
They have a thinner cortex
|
|
|
List the labs to be ordered for a work-up or oteomyelitis.
|
WBC: will show increased bands and neutrophils
-CRP: higher -ESR: higher later in the process |
|
|
What are the 3 imaging tests used to dx osteomyelitis
|
-Bone scan
-CT -MRI CT and MRI used to determine the extent of the damage |
|
|
What is the most common cause of osteomyelitis in neonates?
|
Group B strep
|
|
|
Staph aureus is the common pathogen leading to osteomyelitis in children in the ___ period.
|
post-neonate
|
|
|
What are the common causes of osteomyelitis in infants/children?
|
-Staph
-Strep -Salmonella in SCD children |
|
|
Describe growing pains.
|
-no known etiology
-occurs almost exclusively at night -bilateral -subsides with massage and maternal/paternal attention -ibuprofen ok to give |
|
|
What is the Adams's forward bend test used for and what is it assessing?
|
Used for scoliosis and assess the presence of prominences on the back
|
|
|
What areas on a child are assessed for a scoliosis work-up?
|
Their should and pelvis heights to make sure they are even
|
|
|
After using a scoliometer a child with > __ to __ degrees should be sent for xrays
|
5-7
|
|
|
WHat should the HCP check in terms of kyphosis and scoliosis?
|
IF it is present and whether it is flexible or rigid
|
|
|
What can the HCP who is sitting see when assess the child bent forward.
|
leg length discrepancy
|
|
|
What directions should the HCP give to the child in order to conduct the Adam's test correctly?
|
Arms and head down and dangling with feet together and relaxed
|
|
|
What are the key questions to answer in a scoliosis exam?
|
-shoulder heights?
-flank creases? -hairy patches? -abnormal skin markings? -DTRs normal? -Babinski? -abdominal reflexes? (present or symmetric?) |
|
|
What are the motor exam tests for scoliosis?
|
-heel and toe walk
-one foot hop -squat like a frog and jump |
|
|
What can occur with physeal injuries?
|
-potential growth arrest
-potential remodeling |
|
|
Dislocation and ligament injuries are often actually __ __?
|
physeal fractures
|
|
|
true or false: child abuse is a clinical diagnosis?
|
true
|
|
|
Child abuse affect 1/3 of children < __ year old and ___ % of cases occur in children < 2 years?
|
1; 50
|
|
|
describe some suspicious fracture patterns.
|
-metaphyseal corner fractures
-posterior rib fractures -bilateral fractures -multiple fractures in various stages of healing |
|
|
What is a nurse maid's fracture?
|
radial head of the elbow subluxation.
supracondylar fracture |
|
|
It is worriesome to have a ___ fat pad on the arm because it can indicate fracture.
|
posterior
|
|
|
how would you describe a subtle buckle fracture?
|
squish down fracture
|
|
|
A sprain happens at the ___
|
ligament
|
|
|
What is the most common ankle sprain?
|
an inversion ankle sprain
|
|
|
___ ___ injuries take longer to heal than fractures.
|
soft tissue
|
|
|
Why are Salter 1's hard to be seen?
|
Because it is through the growth plate
|
|
|
What are the symptoms that would cause a HCP to suspect an ACL injury?
|
patient plant and twisted the knee, with immediate swelling and heard or felt a pop
|
|
|
What is a possible diagnosis if the symptoms include clicking and catching feeling with pain in the knee with flexion?
|
Meniscal injury
|
|
|
Describe the symptoms that correlate to a possible MCL injury.
|
Pain on the medial portion follow following a hit on the lateral side
|
|
|
What is the first line imaging test to use in orthopedics?
|
Xray
|
|
|
What are ultrasounds most often used for?
|
-Hip effusions
-Osteomyelitis on thinner/smaller child |
|
|
What imaging technique is good for seeing the cortical bone?
|
CT scan
|
|
|
What imaging test is used to see soft tissue injuries?
|
MRI
|
|
|
What are bone scans good for seeing?
|
suspected stress fracture
-osteomyelitis |

