![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
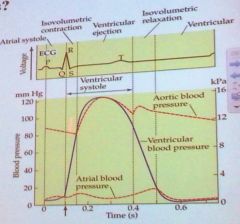
What happens when the ventricles contact, but do not eject its contents?
A: Ventricular pressure increases, but aortic pressure does not B: Blood flows back into the atria C: Ventricular and aortic pressure increase |
A: Ventricular pressure increases, but aortic pressure does not
|
|
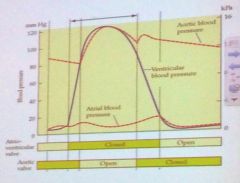
When do atrioventricular (AV) and aortic valves close?
A: When the autonomic nervous system excites them B: When the pressure in the post-valve chamber exceeds the pressure in the pre-valve chamber C: When the pre-valve chamber contracts |
B: When the pressure in the post-valve chamber exceeds the pressure in the pre-valve chamber
|
|
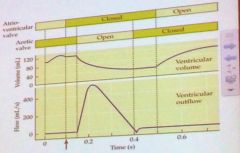
How is most of the blood transported into the ventricles and then the aorta?
A: Passive filling of the ventricles, and ventricular contraction to push blood into the aorta B: Atrial contraction to push blood into the ventricles, and passive filling of the aorta C: Atrial and ventricular contraction to push blood into the ventricles and aorta respectively D: Passive filling of both ventricles and aorta |
A: Passive filling of the ventricles, and ventricular contraction to push blood into the aorta
|
|
|
How is the heart muscle itself nourished with blood?
A: From arteries that branch off the aorta B: From the blood passing through the chambers C: Both |
A: From arteries that branch off the aorta
|
|
|
What are the common results when the coronary arteries become blocked?
A: Damage to heart muscle cells B: Heart attack C: Both |
C: Both
|
|
|
What results in the highest blood pressure?
A: High cardiac output, low resistance B: High cardiac output, high resistance C: Low cardiac output, low resistance D: Low cardiac output, high resistance |
B: High cardiac output, high resistance
|
|
|
What amount of blood is pumped out of the heart per minute if the heart beats 60 times per minute and the amount of blood ejected from the ventricle in each stroke is 50mL?
|
3,000mL
|
|
|
The autonomic nervous system can speed/slow the heart rate. Which pair below is most likely accurate regarding autonomic regulation?
A: Sympathetic - higher Cl- conductance. Parasympathetic - high K+ conductance B: Sympathetic - higher Ca2+ conductance. Parasympathetic - high K+ conductance C: Sympathetic - higher K+ conductance. Parasympathetic - high Na+ conductance D: Sympathetic - higher Na+ conductance. Parasympathetic - high Ca2+ conductance |
A: Sympathetic - higher Cl- conductance. Parasympathetic - high K+ conductance
|
|
|
What results in a decrease in vascular resistance?
A: Increase in length of vessels B: Increase in radius of vessels C: Increase in viscosity of blood D: All of the above |
B: Increase in radius of vessels
|
|
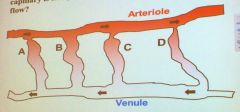
In the microcirculatory bed below, which capillary is likely to have the highest rate of blood flow?
|
B.
|
|
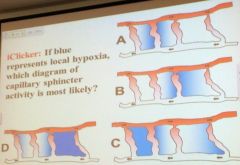
If blue represents local hypoxia, which diagram of capillary sphincter activity is most likely?
|
A.
|

