![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
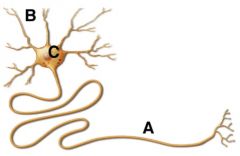
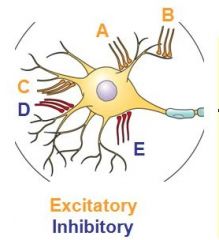
The neuron structure labelled B is a ___________ and performs the function of _________________.
A: axon, accepting neurotransmitters B: soma, integrating information C: axon terminal, transmiting information to muscle D: dendrite, recieving information from receptors or neurons |
D: dendrite, recieving information from receptors or neurons
|
|
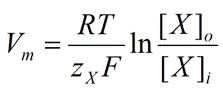
The Nernst Equation tells us that if a positive ion is ten times more concentrated inside the cell, its Nernst equilibrium potential is ____________ and ______________ with temperature.
A: negative, increases B: positive, decreases C: negative, decreases D: zero, increases E: None of the above |
A: negative, increases
|
|
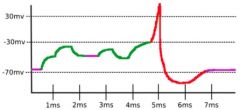
A neuron is stimulated at several voltages to explore its membrane potential. From our recording above we know that the action potential threshold is ________ and we were least likely to expect an action potential initiation at ______.
A: 0 mV, 2 ms B: -30 mV, 6 ms C: -10 mV, 7 ms D: -60 mV, 1.5 ms E: -30 mV, 2 ms |
B: -30 mV, 6 ms
|
|
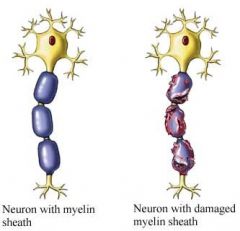
MS is a desease which damages the myelin sheath of neurons. What problem would this cause with signal propagation?
A: signal conducted too fast B: impulse triggered too often C: neuron threshold lower D: lower resistance to leakage |
D: lower resistance to leakage
|
|
|
Which of the following most ensures a one way movement of signal along a neuron?
A: inhibition of ion channels B: gap junctions C: neurotransmitters D: synapses E: connexons |
A: inhibition of ion channels
|
|
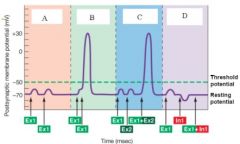
Ex 1 and Ex 2 are EPSPs located at different locations on an axon, and In1 is an IPSP.
In the above diagram, ____ would represent ____________. A , two action potentials B, temporal summation C, facilitation B, spatial summation D, habituation |
B, temporal summation
|
|
You are researching the neural response above of a poisoned neuron. You know that the above 3 EPSPs and 2 IPSPs are all active at the same time. A and B involve calcium channels, C involves Acetylcholine, and both D and E are glutamate initiated. If the local synapse strength of the five synapses can be described as A + B = D + E = C and we observe a net negatively charged membrane in the axon hillock, which poison was most likely applied?
A: Argiotoxin (glutamate antagonist) B: Alpha-Bungarotoxin (blocks Acetylcholine receptors) C: Apamin (blocks calcium activated potassium channels) D: Conotoxin (blocks calcium channels and Acetylcholine receptors) |
D: Conotoxin (blocks calcium channels and Acetylcholine receptors)
|
|
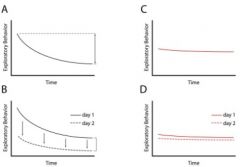
You place a mouse in a new cage and are examining a mouse's tendency to explore that same cage over time on two consecutive days. Which mouse likely has had a valuable habituation gene knocked out on accident?
A B or D B C D C or D B or D |
C or D
|
|
|
At which site are action potentials formed?
A: Dendrite B: Soma C: Axon hillock D: Schwann cell |
C: Axon hillock
|
|
|
As you move your finger to touch your nose, specialized neurons called Purkinje cells in the cerebellum are receiving weak motor function signals from hundreds of thousands of other neurons. What aspect of Purkinje cells would you expect to be more extensively developed than other neurons?
A: Smaller soma B: More dendrites C: Increased axon length D: Less myelination E: More axon terminals |
B: More dendrites
|
|
|
A cell at resting membrane potential is triggered by a neurotransmitter to open up Na+ ion channels. Which of the following is then least accurate?
A: Na+ equilibrium potential will not change B: Na+ resistance is lowered C: The membrane will depolarize D: Resulting Na+ concentration will be much larger inside the cell E: Resulting Na+ concentration will be much larger inside the cell |
E: Resulting Na+ concentration will be much larger inside the cell
|
|
|
You observe a cell with a membrane potential of approximately -20 Mv. Which phase(s) of an action potential are potentially happening?
A: Depolarization (rising) B: Repolarization (falling) C: Hyperpolarization (refractory period) D: overshoot (peak) E: A or B F: None of the above |
E: A or B
|
|
|
Which is true as the membrane potential moves farther away from the equilibrium potential?
A electromotive force rises B resistance for ion increases C: ionic current is reduced D: A or B E: B or C |
A electromotive force rises
|
|
|
Of chemical and electrical synapses, which statement is best?
A: Both can be either excitatory or inhibitory B: Chemical synapses influence learning C: Both carry electrical signals between axons D: Electrical synapses use synaptic vesicles |
B: Chemical synapses influence learning
|
|
|
If the equilibrium potential for K+ is -58 mV and +58 mV for Na+, which is true the ions at a membrane potential of -58mV? (assume that the membrane is permeable to both ions)
A: K+ should diffuse into the cell B: K+ should diffuse out of the cell C: Na+ should diffuse out of the cell D: Na+ should diffuse into the cell |
D: Na+ should diffuse into the cell
|
|
|
The ____________ enable an action potential to be regenerated in vertebrate neurons, while _____________ minimizes leak of the signal.
A: Nodes of Ranvier, Myelination B: Propagation, Myelination C: Inactivation of Na+ channels, leak channels D: Nodes of Ranvier, leak channels |
A: Nodes of Ranvier, Myelination
|
|
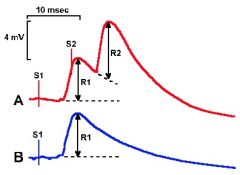
You record motor neuron response after two identical presynaptic impulses S1 and S2 are delivered 6 milliseconds apart (A). The response (R1) to a single stimuli is given in B. Why is postsynaptic impulse R2 more than twice as large as response R1?
A: Facilitation B: Temporal summation C: Habituation D: Sensitization |
A: Facilitation
|
|
|
A single EPSP is not sufficient to bring about an action potential. You also notice an IPSP relatively equivalent in strength to the EPSP is happening at the same time. How might we get closer to an action potential?
A: If we trigger another EPSP quickly after the first B: If the IPSP synapsed farther from the axon hillock C: facilitation of EPSP by more neurotransmitter D: All of the above |
D: All of the above
|
|
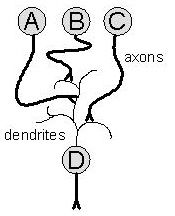
The simple circuit diagram above shows three sensory nerves A, B and C forming synapses on the dendrites of motor nerve D. Sensory nerves B and C are inhibitory, and sensory nerve A is excitatory. Assuming local synapse strength is equivalent, which of the following would be most likely to generate action potentials in motor nerve D?
A: action potentials in nerve B B: action potentials in nerve C C: simultaneous action potentials in nerves A and B D: simultaneous action potentials in nerves A and C E: simultaneous action potentials in nerves B and C |
C: simultaneous action potentials in nerves A and B
|
|
|
A presynaptic nerve terminal releases a neurotransmitter that activates K+ conductance in the postsynaptic membrane. If the postsynaptic cell body had an initial voltage of –65 mV and ENa = +70 mV, ECl = -70 mV and EK = -90 mV, the new postsynaptic voltage will be:
A: between 0 mV and +70 mV B: between 0 mV and -70mV C: between -70 mV and -90 mV D: more negative than -90 mV E: -70 mV |
C: between -70 mV and -90 mV
|
|
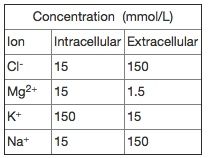
Consider a cell with intracellular and extracellular concentrations of the four ions listed below. Which of the ions are in electrochemical equilibrium when the membrane potential is -58 mV at 18° C?
A: Cl- B: Mg2+ and K+ C: Cl- and K+ D: Cl- and Na+ E: K+ and Na+ |
C: Cl- and K+
|
|
|
Which of the following would most likely increase the likelihood of generating an action potential in a cell?
A: increase in K+ permeability B: increasing the refraction period in voltage gated Na+ channels C: inhibition of voltage gated Na+ channels D: inhibition of K+ leak channels E: inhibition of voltage gated Cl- channels |
D: inhibition of K+ leak channels
|
|
|
A __________ is a form of external force to which a sensory receptor cell can respond.
A: Stimulus B: Wavelength C: Impulse D: Sensilum |
A: Stimulus
|
|
|
A snail initially only tucks into its shell when dropped. Physiologists repeatedly applied the dropping sensation neurotransmitter simultaneous with an unrelated neurotransmitter that normally is present during high temperature. Now the snail tucks in whenever its too warm even if it's not dropping. What happened?
A: facilitation B: long term potentiation C: sensitization D: habituation |
B: long term potentiation
|
|
|
These are swellings containing discrete agregations of nerve cell bodies and processes.
A: Ganglia B: Interneurons C: Effectors D: Axons |
A: Ganglia
|
|
|
To conduct a signal at relatively comparable speeds, a smaller diameter axon needs more ____________, to compensate for the _____________ as axon size decreases.
A: Current, Lower conductance B: Hyperpolarization, Lack of myelination C: Myelination, Increased resistance D: Refraction, Loss of propagation |
C: Myelination, Increased resistance
|
|
|
An action potential:
A: is the main function of glial cells B: is initiated by a localized increase in membrane permeability C: is a graded potential, but bigger D: degrades as temperature increases |
B: is initiated by a localized increase in membrane permeability
|
|
|
Absolute and relative refractory periods are caused, respectively, by:
A: K+ channels still open, Na+ channels inactivated B: Na+ channels still open, K+ channels inactivated C: K+ channels inactivated, Na+ channels still open D: Na+ channels inactivated, K+ channels still open |
D: Na+ channels inactivated, K+ channels still open
|
|
|
When is a neuron membrane potential closest to its Nernst equilibrium for Na+?
A: at the peak of the action potential B: during hyperpolarization C: during absolute refractory period D: at resting membrane potential |
A: at the peak of the action potential
|
|
|
Action potential propagation rate is not influenced by:
A: temperature B: stimulus strength C: axon diameter D: myelination |
B: stimulus strength
|

