![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
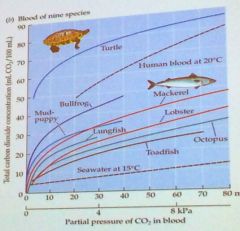
Using the graph, which statement regarding the CO2 physiology of turtles and mackerel is most accurate?
A: Turtles can tolerate a higher CO2 partial pressure B: Mackerels' blood saturates at a lower partial pressure of CO2 C: Turtles hold more bicarbonate in their blood at a given CO2 partial pressure than mackerel. |
C: Turtles hold more bicarbonate in their blood at a given CO2 partial pressure than mackerel.
|
|
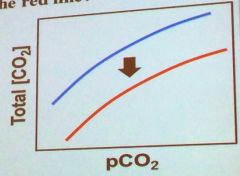
Which of the following would most likely cause the change in the CO2 equilibrium graph seen below from the blue line to the red line?
A: Removal of protons B: Removal of O2 C: Addition of CO2 D: Removal of O2 E: Addition of protons |
E: Addition of protons
|
|
|
How is O2 transported across the respiratory epithelium from the lung into the blood stream?
A: Bound to a hemoglobin transporter B: Simple diffusion C: O2 ATPase D: Vesicle fusion E: Cardiac pumping |
B: Simple diffusion
|
|
|
Thinking all the way back to the Fick equation, which of the following would increase the rate of O2 transport across?
A: Decreasing the area of the respiratory epithelium B: Increasing the amount of O2 transporters C: Decreasing the thickness of the respiratory epithelium D: Increasing the blood O2 level |
C: Decreasing the thickness of the respiratory epithelium
|
|
|
How is O2 transported from the lungs to the tissues?
A: Simple diffusion B: Facilitated diffusion C: O2 ATPase D: Vesicle fusion E: Cardiac pumping |
E: Cardiac pumping
|
|
|
How is O2 carried during cardiovascular transport?
A: Bound to hemoglobin B: Dissolved O2 gas in plasma C: Dissociated in plasma as H30- D: Bound to carbonic anhydrase |
A: Bound to hemoglobin
|
|
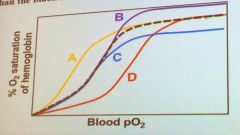
Which of the following colored hemoglobin binding curves represents a higher affinity hemoglobin than the black dashed curve?
|
A
|
|
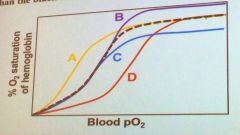
Which of the following colored hemoglobin binding curves represents a higher carrying capacity than the black dashed curve?
|
B
|
|
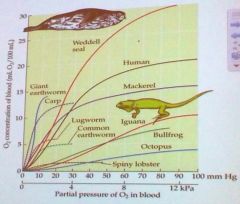
What makes Weddell seal blood able to carry so much O2?
A: It has more hemoglobin molecules B: It has stronger binding in the hemoglobin active sites C: It has a higher cardiac output D: It has a higher pO2 |
A: It has more hemoglobin molecules
|
|
|
Where in the cardiovascular system is pH lowest?
A: The lung capillaries B: The arteries that go to the brain C: The veins that come from the lungs D: The tissue capillaries |
D: The tissue capillaries
|
|
|
Where in the cardiovascular system would it beneficial for hemoglobin to suddenly lose affinity?
A: The lung capillaries B: The arteries that go to the brain C: The veins that come from the lungs D: The tissue capillaries |
D: The tissue capillaries
|
|
|
What is the adaptive value of the Bohr effect?
A: It makes hemoglobin more likely to release O2 at the systemic tissues B: It allows buffering of the blood at systemic tissues C: It allows low pH venous blood to carry more O2 D: It keeps O2 bound to hemoglobin at the systemic tissues E: It keeps myoglobin from taking the O2 from the hemoglobin |
A: It makes hemoglobin more likely to release O2 at the systemic tissues
|
|
|
Where are O2 levels lowest?
A: Systemic veins B: Systemic arteries |
A: Systemic veins
|

