![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Drop Zone References |
AFI 13-217 Drop Zone and Landing Zone Operations. AFI 11-231 Computed Air Release Point Procedures. FM 3-21.38 Pathfinder Operations. TC 3-21.220 Static Line Parachuting Techniques and Training. USASOC REG. 350-2 Training Airborne Operations. AFI 11-2C-130v3 C130 Operations Procedures. AFI 11-2C-17v3 C-17 Operations Procedures. |
|
|
Reference for the Ground Element for Drop Zone Operations |
AFI 13-217. |
|
|
Reference for GMRS Operations. |
USASOC REG. 350-2 |
|
|
Definition of a Drop Zone |
designated area where personnel and/or equipment are delivered by means of a parachute or free drop. |
|
|
Drop Zone requirements for Peace-Time |
- government owned or government leased. - current survey or tactical assessment. |
|
|
Drop Zone Selection Factors |
(A SODA MAT) - Airdrop Airspeed. - Size of Drop Zone. - Obstacles. - Drop Altitude. - Access. - Method of Airdrop. - Adequate Approach and Departure Routes. - Type of Airdrop. |
|
|
DZSTL = |
Drop Zone Support Team Leader |
|
|
DZSTL role in drop zone selection |
advise the Ground Unit Commander on suitability. |
|
|
Ground Unit Commander role in drop zone selection |
Ground Unit Commander selects the DZ. |
|
|
Weighing Drop Zone Selection Factors' importance |
- equal importance. |
|
|
STOL = |
Short Take-Off and Landing |
|
|
Selection of Airspeed for combination drops. |
Use higher airspeed. |
|
|
Difference between Knots and KIAS |
Knots (nautical mile per hour) - speed relative to ground. KIAS (knots indicated airspeed) - speed through medium (A/C flying at 150 KIAS with 30-knot headwind is traveling 120 KIAS with respect to ground). |
|
|
Measure airspeed in knots or KIAS? |
KIAS |
|
|
Drop Altitude is measured from _______. |
Above Ground Level (AGL). |
|
|
Some drop aircraft may request drop altitude in _____________. |
Mean Sea Level (MSL). |
|
|
Rounding Field Elevation |
Up to nearest 50 feet. |
|
|
If rotary-wing / STOL aircraft is flying 90 KIAS or faster, the aircraft can drop personnel at _______. |
1250 feet AGL, except UH-series aircraft. |
|
|
Definition of a combination drop |
- Different aircraft in a formation are dropping different loads during the same pass over the DZ. - Different types of loads are exiting the same aircraft during the same pass over the DZ. |
|
|
Selection of altitude for combination drop |
Highest airdrop altitude |
|
|
Minimum airdrop altitude for equipment using the 5,000 lb, 10,000 lb, or 15,000 lb parachute release system. |
1000 Feet AGL or by parachute type (whichever is higher). |
|
|
When to use parachute release system (PRS) |
High wind conditions |
|
|
Types of delivery for airdrop items |
- Low velocity: sensitive equipment and personnel; prevent damage or injury. - High velocity: stabilize the load; acceptable landing shock. - Free drop: non-sensitive items; no parachute. |
|
|
Caution should be taken when using high velocity or free drop around ______ or _______. |
- Built up areas. - Airfields. |
|
|
Methods of Airdrop |
- Personnel and Door Bundles: self-exits, is pushed, or is skidded from door or ramp. - Gravity: nose-high attitude, rolls out. - Extraction: extraction parachute pulls load. |
|
|
Personnel Airdrop exit interval |
One second for each jumper, starting after first jumper exits. |
|
|
On _____ and _____ drop zones, allow ______ seconds for each door bundle to exit. |
- GMRS. - VIRS. - three. |
|
|
On _____ drop zones, ________ are treated the same as ______. |
- CARP. - door bundles. - personnel. |
|
|
Obstacles to personnel |
Any feature, natural or man-made, that would pose a hazard to the jumper or prevent jumper from accomplishing mission. |
|
|
Obstacles to equipment. |
Any feature, natural or man-made, that may hinder recovery or cause damage to load. |
|
|
Primary Obstacles |
- Trees: 35 feet or higher. - Water: 4 feat or deeper and 40 feet wide at widest point; within 1000 meters of any edge of the DZ; the DZSTL can declare any body of water a water obstacle. - Power lines: 50 volts or greater, within 1000 meters of any edge of the DZ. |
|
|
Action if power lines are located within 1000 meters of any boundary of the DZ. |
Coordinate with Power Company to shut off power NLT 15 minutes prior to TOT. |
|
|
Guidance for Drop Zone Access |
- Avoid major obstacles to personnel and equipment between the DZ and the objective. - Ensure that adequate routes are available for equipment recovery. |
|
|
Evaluating Adequate Approach and Departure Routes |
- No-Fly Areas (Impact Areas are NOT). - Obstacles to the aircraft (man-made). - Terrain higher than the DZ (natural). - Enemy situation and location. |
|
|
Size of a VIRS drop zone is dictated by: |
FM 3-21.38. |
|
|
Size of a ____ drop zone is dictated by FM 3-21.38. |
VIRS. |
|
|
Size of a GMRS drop zone is dictated by: |
USASOC Reg. 350-2. |
|
|
Size of a ____ drop zone is dictated by USASOC Reg. 350-2. |
GMRS. |
|
|
Size of a CARP drop zone is dictated by: |
AFI 13-217. |
|
|
Size of a _____ drop zone is dictated by AFI 13-217. |
CARP. |
|
|
Primary reference for CARP Drop Zones. |
AFI 13-217. |
|
|
Secondary reference for CARP Drop Zones. |
AFI 11-231. |
|
|
DZST = |
Drop Zone Support Team |
|
|
PI = |
Point of Impact |
|
|
Actions of DZST Party on DZ |
locate and mark PI. |
|
|
CARP = |
Computer Air Release Point |
|
|
Who determines the Release Point? |
Aircraft Navigator. |
|
|
Placement of PI for HAARS (CARP)
|
Center of the DZ
|
|
|
Placement of PI for HV-CDS (CARP)
|
Center of the DZ for the first item released (center of required length for the first item: factors are initial "1NA" of "1NANAS").
|
|
|
Conditions under which Random Points of Impact may be used |
Visual Meteorological Conditions (VMC) only. |
|
|
RPI = |
Random Points of Impact |
|
|
RPI Options - planning requirements |
- notify 24 hours in advance. - minimum DZ size requirements are met. - entire DZ falls within surveyed boundaries. - preferred DZ for contingency resupply. - Option One: DZSTL randomly selects PI. - Option Two: Mission Commander or Supported Force Commander requests specific PI. |
|
|
Random Approach / Circular DZs have ______ |
no set drop heading. |
|
|
Definition of Random Approach DZ |
Variation of previously surveyed DZ, of sufficient size to permit multiple run-in headings. |
|
|
The _______ option is the Air-Force preferred option for Circular / Random Approach. |
Surveyed (option 1) |
|
|
The Surveyed Option is the ______ preferred option for Circular / Random Approach.
|
Air Force. |
|
|
The ________ option is the Army-preferred option for Circular / Random Approach. |
Mission Specific (option 2). |
|
|
The Mission Specific option is the ______ - preferred option for Circular / Random Approach. |
Army. |
|
|
Placement of PI in a Surveyed DZ |
- center of circular DZ. |
|
|
Placement of PI in a Mission Specific DZ |
- offset from center of circular DZ. |
|
|
Radius of Surveyed DZ |
From PI (center of circle) to corner. |
|
|
Radius of Mission Specific DZ. |
From Center of Mass of DZ (and center of circle) to circle. |
|
|
Air Force and Army Fixed Wing Aircraft instruments work in units of _____ |
feet from MSL (Mean Sea Level) |
|
|
How to measure MSL |
round up to nearest increment of 50 feet. |
|
|
All drop altitudes are expressed in: |
feet AGL (Above Ground Level) |
|
|
Alll ______ altitudes are expressed in feet AGL. |
Drop. |
|
|
PI can be offset to both sides of the surveyed PI _____ for _____ and ____ for _______. |
- 125 yards for 2 x C-17s. - 250 yards for 3 x C-17s. |
|
|
PI can be delayed for __________. |
Placement of equipment. |
|
|
New PIs must be relayed to the aircraft by the DZSTL NLT _______ prior to ______ for ____________. |
- 15 minutes. - TOT. - C-17 and C-130J. |
|
|
______ is the minimum required and primary marking for __________, per __________. |
- RAM. - day drops. - FM 3-21.38. |
|
|
RAM is the ________ and _________ marking for day drops, per FM 3-21.38 |
- minimum required. - primary. |
|
|
Block letters authorized for RAM on rectangular DZs |
- J - C - A - R - S |
|
|
Block letters authorized for RAM on circular DZs. |
- H - O |
|
|
Minimum size of RAM Code Letter |
35 ft x 35 ft |
|
|
Lighting requirement for RAM Code Letter |
9 white omni-directional lights. |
|
|
RAM markings during day |
VS-17 |
|
|
Location of the control center is determined by |
type of mission |
|
|
Location of control center: personnel drops / door bundles. |
At PI. |
|
|
Location of control center: DRAS and CDS drops |
200 yards to 6 o'clock of PI. |
|
|
Location of control center: heavy equipment drops |
300 yards to 6 o'clock of PI |
|
|
Location of Control center: HV-CDS, actual IMC (ceiling of 600 feet or less), HAARS, free drops, AWADS: |
off the drop zone. |
|
|
Location of Amber Rotating Beacon |
1000 meters or tail edge of DZ, on drop heading (from RAM). |
|
|
Location of left & right flanker lights |
90 degrees off of PI (from drop heading), 250 meters (500 meters between the two lights). |
|
|
Number of lights on a DZ, with RAM, both flanker lights, and amber rotating beacon. |
11. |
|
|
Striker Report form |
AF 4304 |
|
|
Measurement of landing of first jumper ______ from PI de-certifies aircrews. |
300 yards. |
|
|
Drop Zone / Landing Zone Control Log: form |
AF 4304 |
|
|
AF 4304 is forwarded to _____, then to ____. |
- S3 Air. - AMLO. |
|
|
DZSTL establishes control center, accounting for pertinent factors like: |
- Winds. - Positive control of the DZ. - Unobstructed view of the DZ. - Surrounding airspace. - Security requirements. Must always consider safety. |
|
|
Strike report: if #1 parachutist lands _______ of PI, score using ______. |
- within 25 yards. - "PI". |
|
|
If #1 jumper can be observed, measure distance using methods: |
- Estimated. - Paced. - Measured. |
|
|
If #1 jumper can't be observed: |
- Less than 90% land on DZ, score "U". - At least 90% land on DZ, score "S". |
|
|
Reference: Drop Zone and Landing Zone Operations |
AFI 13-217 |
|
|
Reference: AFI 13-217 |
Drop Zone and Landing Zone Operations (Ground Element) |
|
|
Reference: Computed Air Release Point Procedures |
AFI 11-231 |
|
|
Reference: AFI 11-231 |
Computed Air Release Point Procedures |
|
|
Reference: FM 3-21.38 |
Pathfinder Operations
|
|
|
Reference: Pathfinder Operations
|
FM 3-21.38 |
|
|
Reference: Static Line Parachuting Techniques and Training |
TC 3-21.220 |
|
|
Reference: TC 3-21.220 |
Static Line Parachuting Techniques and Training |
|
|
Reference: Training Airborne Operations |
USASOC REG 350-2 |
|
|
Reference: USASOC REG 350-2 |
Training Airborne Operations (GMRS ops) |
|
|
Reference: C-130 Operations Procedures |
AFI 11-2C-130v3 |
|
|
Reference: AFI 11-2C-130v3 |
C-130 Operations Procedures |
|
|
Reference: C-17 Operations Procedures |
AFI 11-2C-17v3 |
|
|
Reference: AFI 11-2C-17v3 |
C-17 Operations Procedures |
|
|
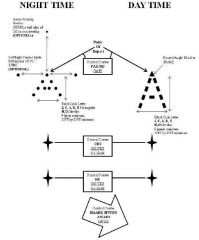
CARP Markings diagram |
|

