![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
268 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Definitive host |
Defined as the host that harbours the Adult parasite or the Sexual stage |
|
|
Intermediate Host |
Defined as the host that harbours the larval stage or the Asexual stage |
|
|
Nematodes - Roundworms Trematodes - Flukes Cestodes - Tapeworms |
Other common names for the helminthes? |
|
|
E. histolytica |
What is the only pathogenic amoeba? |
|
|
Balantidium coli |
The only important parasite under ciliates? |
|
|
A.lumbricoides |
Giant intestinal roundworm/eelworm? |
|
|
A.lumbricoides |
Largest nematode? |
|
|
S.stercoralis |
Smallest nematode? |
|
|
D.latum |
Longest tapeworm? |
|
|
E.granulosus |
Shortest tapeworm according to length? |
|
|
Trichuris trichiura |
Whipworm? |
|
|
E.vermicularis |
Pinworm/Seatworm? |
|
|
Capillara philippinensis |
Pudoc worm? |
|
|
Trichina worm or pork muscle round worm |
T.spiralis is also known as? |
|
|
Strongyloides stercoralis |
Threadworm? |
|
|
N.americanus |
New world hookworm? |
|
|
A.duodenale |
Old world hookworm? |
|
|
A.caninum |
Dog hookworm? |
|
|
A.braziliense |
Cat hookworm? |
|
|
T.canis |
Ascaris in dogs? |
|
|
T.cati |
Ascaris in cats? |
|
|
W.bancrofti |
Bancroft's filaria? |
|
|
B.malayi |
Malayan filaria? |
|
|
Eyeworm |
Loaloa? other name? |
|
|
O.volvulus |
Convuluted filarial? |
|
|
M.ozzardi |
Ozzard's filarial? |
|
|
M.perstans |
Persistent filarial? |
|
|
Dragon worm, Guinea worm, serpent worm |
other name for D.medinensis? |
|
|
Rat lung worm |
common name for A.cantonensis |
|
|
Dog heart worm |
other name for D.immitis? |
|
|
S.japonicum |
Oriental blood fluke? |
|
|
S.mansoni |
Manson's Blood fluke |
|
|
Vesical Blood fluke |
Other name for S.haematobium? |
|
|
P.westermani |
Oriental lung fluke? |
|
|
Sheep Liver fluke |
Other name for F.hepatica? |
|
|
Chinese liver fluke/ Oriental liver fluke |
Other name for C.sinensis? |
|
|
O.felineus |
Cat liver fluke? |
|
|
Garrison's fluke |
other name for E.illocanum? |
|
|
Busk Fluke Giant Intestinal Fluke |
other name for F.buski? |
|
|
Von siebold fluke Dwarf fluke |
Other name for H.heterophyes? |
|
|
Yokogawai fluke |
Common name for M.yokogawai? |
|
|
Fish broad tapeworm Russian broad tapeworm |
Common name of D. latum? |
|
|
Pork Tapeworm or Armed tapeworm |
common name of T.solium? |
|
|
Beef tapeworm or unarmed tapeworm |
common name of T.saginata? |
|
|
H.diminuta |
Rat tapeworm? |
|
|
H.nana |
Dwarf tapeworm? |
|
|
Dog tapeworm or Double pired tapeworm |
Common name of D.caninum? |
|
|
Hydatid worm |
Common name of E.granulosus? |
|
|
-Non Motile -Usually the infective form -Found in formed feces -Smaller than trophozoite -Multi-nucleated -Resistant to damage -Use Iodine for better visualization |
Describe cyst |
|
|
If the protozoa has cyst then it is the infective form if it only has trophozoite then the infective form is trophozoite |
Rule for protozoans in terms of infectivity |
|
|
Metacyst |
Transitory stage prior to excystation |
|
|
Precyst |
Transitory stage prior to encystation? |
|

|
Explain transitory stages for amoebas? |
|
|
Naegleria Acantamoeba |
2 Exampkes of facultative amoebas (could live outside body) |
|
|
Entamoeba gingivalis Habitat: Buccal Cavity |
All amoebas lives in the colon except_______ w/c lives in ______ |
|
|
Entamoeba histolytica |
The only pathogenic amobe? |
|
|
-Entamoeba gingivalis -Dientamoeba fragilis They only have trophozoite forms |
All amoebas have cyst and troph forms except?________ |
|
|
-E. gingivalis & D.fragilis Since they only have the trophozoite form, it is their sole infective stage |
All amoebas have cyst as infective form except? |
|
|
E. gingivalis Since its the only one w/ mouth as its habitat it is transmitted through Oral Contact |
All Amoebas have Fecal-Oral Route as MOT except? |
|
|
Dientamoeba fragilis Stained by trichrome stain |
No longer an amoeba but now classified as a flagellate? Eggs of E.vermicularis might carry this causing double infection? Also could be stained by what? |
|
|
-Motile -Usually the Non-infective form -Found in Liquid or Watery stool -Larger than cyst -Usually uni-nucleated -Susceptible to damage -Not suited for: Concentration Techniques |
Describe a trophozoite |
|
|
Permanent stain E.g: Gomori's Trichrome, Iron Hematoxylin |
Trophozoites are better visualized using? Examples of which? |
|
|
FALSE Iodine makes trophozoites disappear |
Iodine could not cause disappearance of Trophozoite true or false? |
|
|
4 E.histolytica has 1-4 nuclei but only those w/ 4 nuclei are considered infective |
At what number of nuclei of E.histolytica is it considered infective? |
|
|
Entamoeba nana |
Smallest intestinal protozoa? |
|
|
E.nana |
Amoeba with 1-8 nuclei? |
|
|
E.nana |
Amoeba with 4 nuclei but with Karyosome on the end causing it to be called "CROSS-EYED CYST" |
|
|
Iodamoeba butschlii |
Amoeba with only 1 nuclei? |
|
|
Stained by IRON HEMATOXYLIN Color: Black |
Chromatoidal bodies of protozoan cysts are stained with _____ causing ______ color |
|
|
E.histolytica |
Cigar shaped or Sausage shaped chromatoidal bodies? |
|
|
Entamoeba coli |
Broomstick or Splintered glass like chromatoidal bodies in cyst? |
|
|
E.nana |
Small and spherical chromatoidal bodies in cysts belong to? |
|
|
Iodamoeba butschlii |
No chromatoidal bodies but has a big glycogen mass instead that could be stained w/ iodine causing this to be called "IODINE CYST" |
|
|
Pseudopodia |
Organ of trophozoites that makes movement possible? |
|
|
-E.histolytica - long & finger like pseudopia -D.fragilis - hyaline, multiple, leaf like pseudopodia |
All trophozoite have blunt & rounded pseudopodia except? |
|
|
E. histolytica D.fragilis |
Progressive & Directed motility of trophozoite? |
|
|
E.coli |
Sluggish & Non-directed movement of trophozoite |
|
|
E.nana & I.butschlii |
Sluggish but progressive movement of trophozoite |
|
|
E.gingivalis It has multiple pseudopodia that is why it is quite active |
Moderately active movement of trophozoite |
|
|
E.histolytica |
Bull's eye karyosome is found in what trophozoite? |
|
|
D.fragilis |
Tetrakaryosome trophozoite is found on what? |
|
|
E.histolytica |
Amoeba with ingested rbcs on their cytoplasm? |
|
|
E.gingivalis |
Amoeba with ingested WBCs and food vacuoles in their cytoplasm? |
|
|
E.dispar -Currently closest morphology w/E. histolytica -To differentiate do PCR or Immunoassay E.hartmanni -"SMALL RACE HISTOLYTICA" -Previously closest to E.histolytica but does not ingest RBC E.polecki -Parasitize monkeys & pigs -Has only one nuclei |
3 amoebas that closely resembles E.histolytica? |
|
|
Entamoeba nana (smallest) Balantidium coli (largest) |
Smallest intestinal protozoa? Largest intestinal protozoa? |
|
|
Balantidium coli |
Directional & tumbling motility of trophozoite? |
|
|
Balantidium coli |
Causes intraintestinal lesions? |
|
|
Large intestine |
Habitat of B.coli? |
|
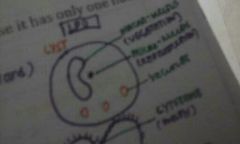
Macro-nucleus : for vegetation
Micro-nucleus: for reproduction |
Balantidium coli cyst has distinguishing feature that is only unique to it. What is it? |
|
|
Stool exam
Entero test -
|
2 Tests used to diagnose G.lamblia |
|
|
Trichomonas specie |
What are the only flagellates that consist of only the trophozoite form? |
|
|
Trichomonas tenax Trichomonas Vaginalis |
What are the species considered as atrial flagellates? |
|
|
G.lamblia C.mesnilii T.hominis |
Luminal flagellates? |
|
|
Giardia lamblia |
The only small intestine inhabiting protozoa? |
|
|
Trichomonas tenax -Also called "Flagellate of the mouth" |
All flagellates are transmitted through fecal-oral route except? |
|
|
Steatoherric / Contains fats -Because of sucking discs of G.lamblia that causes malabsorption |
Distinguishing feature of stool infected with G.lamblia? |
|
|
Giardia lamblia |
Bilaterally symmetrical, "KITE-LIKE MOTILITY" "FALLING-LEAF LIKE MOTILITY" "OLD MAN WITH GLASSES" Is used to describe what? |
|
|
Gardia lamblia |
Causes GAY-BOWEL DISEASE? |
|
|
Chilomastix mesnilii |
cyst is commonly referred to as "NIPPLE-LEMON LIKE" |
|
|
Chilomastix mesnilii |
Trophozoite showing a "SHEPHERD-CROOK'S APPEARANCE" "CORK-SCREW" "SPIRAL-JERKY" |
|
|
Trichomonas vaginalis |
Only pathogenic trichomonas |
|
|
LONGEST - T.hominis SHORTEST - T.vaginalis AS LONG AS COSTA - T.tenax |
Umdulating membrane of trichomonas species? |
|
|
T.vaginalis |
"FAST-JERKY MOVEMENT" |
|
|
Urine Vaginal discharge |
Specimen for diagnosis of T.vaginalis? |
|
|
Enteromonas hominis -Binucleate, Rapid-Jerky Movement Retortomonas intestinalis -"BIRD'S BEAK FIBRILLAR APPEARANCE" |
2 rare intestinal flagellates and their distinguishing characteristic? |
|
|
L.donovani- mucosal organs L.tropica- Lymphoid tissue L.braziliense- Nose, mouth pharynx |
Location of Leishmania species? |
|
|
Amastigote -Diagnostic and seen in man intracellularly
Promastigote- Develop in vectors |
2 Developmental stages of Leishmania species? |
|
|
Sandflies (Phlebotomus papatazi) |
Vector for Leishmania? |
|
|
Skin Inoculation |
MODE OF TRANSMISSION FOR LEISHMANIA? |
|
|
Leishmania donovani |
What causes Kala-azar fever?/Dum-Dum fever/Black disease/ Visceral Leishmaniasis |
|
|
Leishmania donovani |
Causes worst Leishmaniasis? |
|
|
Leishmania tropica |
Causes cutaneous leishmaniasis/oriental sore/Aleppo/Baghdad boil/Delhi ulcer |
|
|
Leishmania braziliense |
Causes muco-cutaneous leishmaniasis/espundia/Chiclero ulcer/UTA |
|
|
Leishmania braziliense |
Causes leprosy like lesions, "TAPIR NOSE" |
|
|
EXTRACELLULAR -Trypanosoma gambiense -Trypanosoma rhodesiense INTRACELLULAR -Trypanosoma cruzi |
Species of trypanosomes |
|
|
Tse-tse fly |
Vector of EXTRACELLULAR Trypanosomes? (T.rhodisiense, T.gambiense) |
|
|
Epimastigote -> Metacyclic Trypanosome -> Trypomastigote
Metacylcic Trypanosome = Infective to man
Trypomastigote = Diagnostic & develop in man |
Life cycle of trypanosomes |
|
|
Trypanosome chancre -Develops in bite site Winterbottom sign - enlargement lymphnodes Kerandell sign- All signs related to CNS |
African Sleeping sickness? |
|
|
Assasin, Cone-Nose, Kissing, Triatoma, Redavid, Panstrongylus,Rhonius Bug |
Vector of INTRACELLULAR Trypanosomes? (T.cruzi) |
|
|
T.gambiense T.rhodisiense |
What are considered mmembers of the Brucei complex? |
|
|
West African Sleeping Disease / Old world trypanosomiasis/ Gambian Trypanosomiasis |
T.gambiense causes what disease? |
|
|
East african trypanosomiasis/ Rhodesian trypanosomiasis |
T.rhodesiense causes what disease? |
|
|
Chaga's disease/ South American trypanosomiasis/ New World trypanosomiasis |
Trypanosoma cruzi causes what disease? |
|
|
Diagnostic stage: Trypomastigote & Amastigote Infective stage: Metacyclic Trypanosome |
Diagnostic stage in T.cruzi and Infective stage |
|
|
Chagoma (Lesions at bite size) Romana's Sign (Swelling of eyelids) |
Symptoms of T.cruzi? |
|
|
C, S, U shape |
Trypomastigote of T.cruzi assumes what shape? |
|
|
Female anopheles species |
Vector for the plasmodium species? |
|
|
Plasmodium knowlesi |
Pllasmodium specie that infects old world monkeys/ machques |
|
|
Plasmodium falciparum |
Causes the most severe form of malaria? |
|
|
Plasmodium falciparum |
Infects all ages of RBCs |
|
|
Plasmodium ovale , Plasmodium vivax |
Infects young, juvenile forms of RBCs? |
|
|
Plasmodium malaria |
Affects mature RBCs? |
|
|
P.falciparum - No effect P.malariae - Reduced RBCs P.vivax - Enlarge smooth RBCs P.ovale- Enlarge fimbriated RBCs |
Effects to RBCs of Plasmodium species? |
|
|
Plasmodium falciparum - maurer's dots Plasmodium malaria- Ziemann's dots Plasmodium vivax - Schauffner's dots Plasmodium ovale- James dots or Schauffner's (If no james is available) |
Cytoplasmic inclusions or malarial stipplings of Plasmodium? |
|
|
T.rhodisiense -Patient dies before CNS signs starts appearing |
Trypanosome causing rapid and fast death? |
|
|
SCHIZOGONY (Asexual stage) - Happens in Man SPOROGONY (Sexual Stage) - Happens in Vectors |
2 life cycles of plasmodium species and their location |
|
|
P.falciparum - 36 Hours P.malaria - 72 Hours P.ovale & P.vivax - 48 Hours |
Time of paroxysm or the moment where RBCs burst? For the plasmodium species? |
|
|
Sporozoites |
infective to man form of the plasmodium? |
|
|
EXO-ERYTHTOCYTIC CYLCE Sporozoites -> Liver -> Cryptozoic Schizonts -> Merozoites -> Infected cell ruptures merozoites liberated
ERYTHROCYTIC CYCLE Merozoites infect RBC -> Ring form trophozoites -> Schizont -> Merozoite -> infected cell bursts liberating merozoites Merozoites not becoming schizonts will eventually become Gametocytes which will infect female anopheles |
2 cycle of a Plasmodium specie |
|
|
Gametocytes |
Infective form of Plasmodium to vector |
|
|
Gametocytes -> Mature gametes -> Zygote egg -> Ookinete -> Oocyst -> sporozoites within sporocyst -> rupture of sporocyst liberating sporozoites -> migration of sporozoites on the salivary glands of anopheles |
explain the sporogony cycle in female anopheles |
|
|
Thick smear Thin smear |
Gold standard in detection of malaria? |
|
|
Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium ovale -This two species causes reoccurring malaria because of hidden hypnozoites in liver cells |
Hypnozoites are part of tge lifecycle of what plasmodium species? |
|
|
P.falciparum - Malignant tertian malaria P.vivax- Benign tertian malaria P.ovale- Ovale malaria P.malaria - Quartan malaria |
Plasmodium species and the malaria they cause? |
|
|
P.falciparum -Blackwater syndrome is where there is massive hemoglobinuria |
Black water fever is also caused by? |
|
|
P.vivax |
Duffy negative individuals shows resistance to? |
|
|
P.falciparum |
people having Sickle cell trait anemia are resistant to? |
|
|
Relapse of fever due to P.falciparum being increase in too many stages of rbcs |
What is Recrudesence? |
|
|
Before height of fever |
When is the best time to collect blood for the diagnosis of malaria? |
|
|
Thin smear is for identification Thick smear is for rapid diagnosis |
Thin smear is for ____ while thick smear is for ____ |
|
|
Giemsa: (Thick) - Dehemohlobinize by Distilled H2O (Thin) - Fixed by Alcohol |
In giemsa method thick smear is DEHEMOGLOBINIZE by ______ while thin smear is fixed by ____ |
|
|
Fixation |
In wright's stain _____ is no longer needed |
|
|
2% Formalin with 1% Acetic acid |
In Delafield Hematoxylin to dehemoglobinize use? |
|
|
Ringed form & Gametocytes |
What stages are seen in blood in P.falciparum infection? |
|
|
Plasmodium malariae |
Rosette/ daisy formation of merozoites are found in? |
|
|
Plasmodium falciparum |
Aplique/ Accole/ Headset form of ring form trophozoite is found where? |
|
|
Plasmodium malariae |
Band form trophozoite is found where? |
|
|
Plasmodium falciparum |
Crescent form/Sausage form/ Banana shaped gametocytes is found where? |
|
|
Babesia microti |
same cycle as plasmodium specie but no hepatic cycle? |
|
|
Babesia microti |
Maltese cross merozoite? |
|
|
It is transmitted through tick bites by Tick genus: Exodes |
How is B.microti transmitted? Vector of Babesia microti? |
|
|
Cyst: "OUTER WRINKLED WALL" Culture: Non nutrient agar with E.coli Disease: Causes infection among soft contact lense wearers |
Characteristic of Acantamoeba ? |
|
|
Naegleria |
An amoebo-flagellate that has two trophozoite form the 1.) Amoeboid form 2.) The Flagellated form |
|
|
T.gondii DH: Cats IH:Man Infective stage: Oocyst Mode of transmission: Ingestion of oocyst from cat litter Other MOT: Inhalation, Transplacental, Organ transplant,Ingestion of oocyst from infected animals |
Toxoplasma gondii hosts? DH?IH? Infective stage?Most common mode of MOT? |
|
|
Sabin Feldman Dye test -Sero test - (+) result : Lost affinity for methylene blue |
Lab diagnosis of T.gondii?Name of test? |
|
|
Cryptosporidium parvum |
What is diagnosed through DFS, Conc. technique like Sheeters Concentration , modified AF staining? |
|
|
Vacuolated |
Most common form of Blastocystis Hominis? |
|
|
Male : Curved Tail Female : Straight tail |
In Males & Females of nematodes what are the distinguishing characteristics? |
|
|
Cytosome -mouth Cytopyge- Anus |
What do you call the mouth and anus of B.coli? |
|
|
Cytosome -mouth Cytopyge- Anus |
What do you call the mouth and anus of B.coli? |
|
|
Cephalic receptor - Amphids Caudal receptor - Phasmids |
Cephalic (Head) chemoreceptor is called? Caudal (Tail) Chemoreceptor is called? |
|
|
All have Amphids (Head receptor) but not all have Phasmids (Tail receptors) |
In nematodes all have _____ but not all have _____ |
|
|
PHASMIDS (S.H.A.E) S - S.stercoralis H - All Hookworms A - Ascaris lumbricoides E - Enterobius vermicularis APHASMIDS (T.T.C) T - Trichuris trichiura T - Trichinella spiralis C - Capillara philippinensis |
What are examples of Phasmids and Aphasmids? |
|
|
SMALL INTESTINE (C.A.S.H) C - C.philippinensis A - A.lumbricoides S - S.stercoralis H - Necator & A.duodonale LARGE INTESTINE (T.E) T - Trichuris trichiura E - Enterobius vermicularis EXTRAINTESTINAL -All Filariae -Trichinella spiralis is both intestinal & extraintestinal |
Location of Nematodes summarize? |
|
|
OVIPAROUS(H.A.T)- eggs w/ no larvae H - Hookworms A - A.lumbricoides T - Trichuris trichiura OVOVIPAROUS/OVIVIPAROUS (S.E) - Eggs w/Larva .vermicularis VIVIPAROUS/LARVIPAROUS -no egg just larva S - S.stercoralis E- E.vermicularisVIVIPAROUS/LARVIPAROUS -no egg just larva -Trichinella spiralis-All filarial worms-D.medinensis -Trichinella spiralis -All filarial worms -D.medinensis |
Classification of female nematodes & their samples? |
|
|
Embryonated egg |
Infective stage of A.lumbricoides, Hookworms, E.vermicularis? |
|
|
Egg -> Larva -> Man & woman -> Egg |
life cycle of Nematodes? |
|
|
A.lumbricoides |
Only nematode with trilobate lips? |
|
|
Fertilized (Corticated) : ovoid, thick shell, has mamilliary coat outside *Only fertilized eggs continue on the life cycle Unfertilized (Uncorticated) : Irregular ovoid, thin shell , unorganize germ cell 240,000 Eggs / day |
Eggs of ascaris lumbricoides? differentiate? How many? |
|
|
Male: Dies after mating Females: At night lays all her eggs causing anus pruritus then dies 4,000-6,000 EGGS / Day |
Distinguishing characteristics of male and female E.vermicularis? |
|
|
A.lumbricoides T.trichiura E.vermicularis T.canis T.cati |
Acquired through ingestion of embryonated egg? |
|
|
T.spiralis |
Acquired through ingestion of encysted larva? |
|
|
C.philippinensis D.medinensis A.cantonensis |
Acquired thru ingestion of ingested larva |
|
|
S.stercoralis Hookworms |
Acquired through filariform larval skin penetration? |
|
|
W.bancrofti B.malayi L.loa O.volvulus M.ozzardi M.perstans |
Acquired thru inoculation by vectors? |
|
|
Undergoes : Embryonation No : No lung migration |
T.trichiura infection undergoes?_____ but no _____ |
|
|
Autoinfection: Hand to Mouth contamination Retroinfection: Re-entry if parasites through anus Pruritus ani: When itching at your anus during scratching Are all present in? E.vermicularis |
Autoinfection: Retroinfection: Pruritus ani: Are all present in? |
|
|
Tichuris trichiura |
Has Japanese lantern ova? |
|
|
Trichuris trichiura |
Most difficult to expel using anti-helminthic drug? |
|
|
Larva: Migrates to lungs Embryonation: (+) Dse cause: Ascariasis & Pneumonitis Spx: Stool (Fertilized&Unfertilized) & Sputum (Larva) |
Life cycle of A.lumbricoides? |
|
|
No |
does E.vermicularis have embryonation & lung migration? |
|
|
Diagnostic: Eggs in stool Has lung migration |
C.philippinensis? Dx: Is lung migration present? |
|
|
Borborygmi = Gurgling of the stomach |
Capillaria philippinensis causes capillariasis a mystery diseasr in which the characteristic symptoms is? |
|
|
TYPICAL -Peanut - shaped -Flattened polar plugs -Striated shell -With single non-segmented cell ATYPICAL -not peanut shaped -no flattened polar plugs -contains multi-segmented cell or even larva -Shell not striated |
2 Types of OVA of C.philippinensis? |
|
|
Typical female: Female whose uterus contains 1 row of eggs Atypical female: Female with uterus containing 2-3 rows of eggs |
2 types of females of C.philippinensis? |
|
|
Egg -> Rhabditiform -> Filariform -> Adult |
Life cycle of strongyloides & hookworm? |
|
|
RHABDITIFORM -Is considered as Feeding stage -It has open mouth -Shorter & robust -Not infective -Considered as diagnostic in S.stercoralis FILARIFORM -Nonfeeding form -Closed mouth -Longer & slender than rhabditiform -Usually infective -Could penetrate skin |
Differentiate Rhabditiform & Filariform? |
|
|
D.immitis |
"COIN LESIONS" is characteristic of what? |
|
|
A.cantonensis |
"BARBED POLE APPEARANCE" characteristic of? |
|
|
A.castillani |
Amoebic KERATITIS Is caused by what? |
|
|
Unsheated; nuclei extend to tip of hooked tail |
What is the characteristic tail morphology of Mansonella streptocerca? |
|
|
Leishmania spp: Sandfly (Phlebotomus) T.brucei complex: TseTse Fly T.cruzi: Bug Plasmodium spp: Female Anopheles B.microti: Exodes (tick) W.bancrofti: Aedes, Culex, Anopheles (A.C.A) B.malayi: Mansonia (Fresh water plant) Loaloa: Mango/Deer/Chrysops Fly O.volvulus: Black/Simullium Fly M.ozzardi: Cullicoides Fly M.perstans: Cullicoides Fly |
Provide the vectors of each Leishmania spp: T.brucei complex: T.cruzi: Plasmodium spp: B.microti: W.bancrofti: B.malayi Loaloa O.volvulus: M.ozzardi: M.perstans: |
|
|
Of Skin penetrstion of Hookworms |
Koolie itch / Dew itch happens because? |
|
|
N.americanus - 10,000 eggs/day A.duodenale - 20,000 eggs / day |
Number of eggs for each? N.americanus? A.duodenale? |
|
|
Direct cycle: (Parasitic Cycle) -Pathenogenic female -no male -Lung migration (+) -No embryonation -Eggs hatch in small intestine Indirect Cycle: -if soil is moist Rhabditiform will grow to Adult already Autoinfection: -Rhabditiform becomes filariform in small intestine |
Life cycles of Srrongyloides stercoralis? |
|
|
Eggs -> Rhabditiform -> Goes to soil -> Feeds -> Shreds -> Filariform -> Lungs -> S.I -> Adult (+)for lung migration & embryonation |
Lifecycle hookworms |
|

|
Differentiate the hookworm species according to teeth |
|
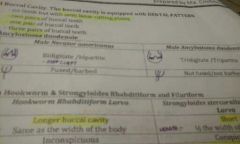
|
Differentiate Necator americanus from A.duodenale according to dorsal rays & copulatory spicules |
|

|
Differentiate rhabditiform of hookworm and strongyloides stercoralis |
|

|
Differentiate Filariform of S.stercoralis & hookworm |
|
|
Ascaris, Hookworm, Trichuris |
Unholy three? |
|
|
Ascaris, strongyloides, hookworm |
What parasite does lung migration? |
|
|
Adult parasite : S.I Larva: Found in Striated muscle |
2 locations of Trichinella spiralis? |
|
|
Infective form: Larva Female: Larviparous MOT: Ingestion of larva from uncooked pork Gravid female lays:1500 larvas / day d female lays:1500 larvas / day |
Infective stage of trichinella? what type o female? MOT?How many larvas delivered per day? |
|
|
4 weeks |
How many weeks does the eaten larva of T.spiralis mature in the small intestine? |
|
|
Trichenella spiralis |
What parasite infectipn wherein man is considered as tje Terminal Host?' |
|
|
Periorbital edema |
What do you call the encysment of larva of trichina worm in the eyes? |
|
|
Muscle Biopsy- Most accurate Bentonite flocculation test- BACHMAN |
2 ways to diagnose trichinosis? |
|
|
Adult -> Rhabditiform/L3 -> Microfilaria -> Adult L3- Infective form Microfilaria- Diagnostic to man |
Lifecycle of Filariforms? Infective form? Diagnostic form? |
|
|
W.bancrofti: Lower lymphatics B.malayi: Upper lymphatics Loaloa: Subcutaneous tse O.volvulus: Subcutaneous tse M.ozzardi: Body cavities M.perstans:Body cavities |
Summarize the areas that the filarial worms affects |
|
|
W.bancrofti-Aedes, Culex, Anopheles B.malayi- Mansonia Loaloa- Mangofly/Deerfly/Chrysops fly O.volvulus- Simullium fly/ Black fly M.ozzardi-Cullicoides M.perstans-Cullicoides |
Give the vectors for each microfilariae |
|
|
W.bancrofti- SHEATED; nuclei NOT extending to tip B.malayi- SHEATED; TWO nuclei at terminal Loaloa- SHEATED; nuclei EXTENDS to tip O.volvolus- UNSHEATED; nuclei NOT Extending to tip M.ozzardi- UNSHEATED; nuclei NOT extending to tip M.perstans- UNSHEATED; nuclei EXTENDS To tip
|
Note the Sheath & Presence of nuclei for each filaria |
|
|
*W.bancrofti- NOCTURNAL (8:00PM-2:00AM or 10:00pm-4:00am) *B.malayi- NOCTURNAL-SUBPERIODIC (Day or night much at night) *Loaloa- DiURNAL (Day time 11:00am-1:00pm) *O.volvulus- DOES NOT TRAVEL TO BLOOD *M.ozzardi- NO PERIODICITY (Any time) *M.perstans- NO PERIODICITY |
Periodicity of each microfilaria? |
|
|
KNOTT'S CONC. TECHNIQUE Rgt: 2 ml formalin 8-10ml blood Gold standard:ELISA |
Concentration technique used to detect filariasis?reagents? Gold standard to dx filariasis? |
|
|
Visceral larva migrans: T.catis & T.canis Cutaneous larva migrans (Creeping eruption): A.duodenale & A.caninum |
What causes these? Visceral larva migrans? Cutaneous larva migrans? |
|
|
BLOOD FLUKES OTHER FLUKE -Cercaria has -Cercaria has Forked tail straight tail -No Redia -Has redia -1 IH -2 IH -Cercaria is -Metacercaria Infective form is infective form -Non operculated- operculated Egg egg -non-hermaph -hermaphroditic roditic |
Differentiate blood flukes and other flukes |
|
|
S.japonicum(rbc may attach to shell) : minute/indistinct lateral knob S.mansoni: lateral spine S.haematobium: terminal spine |
Differentiate the blood flukes |
|
|
S.intercalatum- like S.haematobium, terminal spine with equitorial bulge (like shoulder) and shed in feces S.mekongi- like S.japonicum |
The schistosoma look alike? |
|
|
S.japonicum - Oncomelania S.mansoni- Biomphalaria, Planorbis, Tropicorbis S.mansoni- Bulinus, Physopsis |
Intermediate hosts of the blood flukes? |
|
|
Eggs-> miracidium develops in eggs -> contact w/ H20 miracidium (with cilia) swims in water -> infects IH(Appropriate Snail) -> in snail miracidium becomes sporocyst -> becomes cercaria -> penetrates man skin causing swimmer's itch -> cercaria looses tail -> becomes schistosomule -> infects site whilr travelling causes Katayama fever |
Life cycle of schistosoma? |
|
|
LEAF SHAPED |
Shape of Other flukes? (ALL except schistosoma) |
|
|
Gynecophoric canal- "SCHIST" |
Male schostosoma has this to hold the females duting copulation? |
|
|
E.ilocanum |
Fluke that has oral sucker with spine? |
|
|
P.westermani |
Fluke with coffee bean shape? And paralobule testes? |
|
|
F.hepatica F.buski -Cephalic cone -No cephalic (Shoulder) cone -intestinal ceca, -intestinal Testes & ovaries ceca is Branched/Dendritic unbranched |
Differentiate F.hepatic & F. Buski since they are so alike |
|
|
H.heterophyes |
With 3rd sucker so called as "genital sucker" |
|
|
C.sinensis O.felineus Testes: Dendritic Lobed Vitilaria: Granular Transverse |
Differentiate C.sinensis & O.felineus? |
|
|
E.ilocanum |
Require two snails as a host? |
|
|
P.westermani: (1st)Brotia asperata (2nd) Fresh Crabs E.ilocanum: (1st) Gyrolus (2nd) another snail F.hepatica: (1st)Lymnea philippinensis (2nd) Fresh H20 vegetation F.buski: (1st) segmentia hyputis (2nd) Fresh H2O vegetation C.sinensi,O.felineus,M.yokogawai, H.heterophyes : (1st) Snail (2nd) Fishes
Generally: (1st IH) Snail (2nd IH) others |
Intermediate host of other flukes |
|
|
Eggs-> Miracidium-> contact w/H2O-> miracidium penetrates snail (1st IH) -> becomes sporocyst -> REDIA -> Cercaria (straight tail) -> leaves snail-> infects (2nd IH) -> becomes Metacercaria -> ingested by man (DH) |
Life cycle of other flukes |
|
|
C.sinensis |
Resembles "OLD FASHIONED ELECTRIC BULB" ova |
|
|
Halzoun |
An arabic term for suffocation may happen due to lodgement of worms in the pharynx |
|
|
F.hepatica |
Causes liver rot? |
|
|
Purely hermaphroditic Can live up to 25 yrs Flat segmented ribbon like bodies |
Characteristic of Cestodes? |
|
|
Longest: D.latum Shortest: E.granulosus |
Longest & shortes cestode by length? |
|
|
H.nana |
Only tapeworm that could live and exist in one host? |
|
|
Head/Scolex -For attachment Neck- Region of growth it is where segments originate Segment/proglottid |
Parts of a tapeworm?(Cestodes) and their purpose or content |
|
|
With W/out -T.solium -T.saginata -H.nana -H.diminuta -D.caninum -E. granulosus |
Tapeworm scolex with and without hooklets? |
|
|
Diphyllobotrium latum |
Only tapeworm that is psedocyclophillidea & spatulste/spoon/diamond head? |
|
|
Immature - undeveloped F & M reproductive organs Mature- well developed reproductive organs (1 testes 2 ovaries 1 genital pore) with excemptions Gravid/Ripe- contains egg filled uterus Excemptions: T.solium- 3rd ovary , Accessory Ovarian lobe D.caninum- Double pore tapeworm/ Dog tapeworm |
Types of segments / proglottids? |
|
|
D.latum |
Rosette uterus is found where? |
|
|
T.solium: 8-12, 8-15 T.saginata: 15-30 |
Differentiate uterine branches of T.solium & T.saginata? |
|
|
H.nana & H.diminuta |
Sac like uterus? |
|
|
E.granulosus |
Loosely twisted or coiled uterus? |
|
|
D.caninum |
Vase shaped or pumpkin seed segment? |
|
|
E.granulosus |
Only tapeworm that doesn't cause intestinal infection? |
|
|
Egg pocket |
In gravid females uterus id divided each fragment is called? |
|
|
D.latum - non operculated egg |
All tapeworms have non operculated eggs except? |
|
|
P.westermani |
D.latum produces eggs similar to? |
|
|
H.nana: Has polar thickenings & polar filaments extending from it
H.diminuta: Has polar thickenings & no polar filaments extension, "FRIED EGG APPEARANCE" |
Differentiate H.nana & H.diminuta egg |
|
|
Loaloa |
Causes calibar swelling/ fugative swelling abd hard too catch? But doesn't cause blindness? |
|
|
Schistosoma |
Causes Katayama fever? |
|
|
E.granulosus |
Eggs that are NEVER SEEN in human feces |
|
|
Adult-> Egg (Oncosphere) -> Cysticercus Cysticercus solium = T.solium Cysticercus saginata = T.bovis Ingestion of OVA = CYSTICERCOSIS Ingestion of CYSTICERCOID = TAENIASIS |
Life cycle of Taenia? Disease they cause? |
|
|
Egg -> Procercoid -> Plerocercoid Ingestion of Procercoid : Sparganosis Ingestion of Plerocercoid: Diphylobotriasis |
Life cycle of D.latum? Disease they cause? |
|
|
Coenurus |
Larval form of multiceps multiceps? |
|
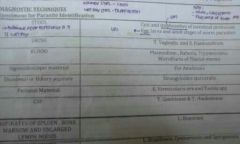
|
What are the probable parasites found on urin, stool, blood etc? |
|

|
Parasite located in different places |

