![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What the structure of an atom?
|
Small positively charged nucleus surrounded by an equal number of negatively charged electrons
|
|
|
What causes electrostatic reactions?
|
Movement of electrons
|
|
|
Like charges ___
Different charges ____ |
Repel
Attract |
|
|
What happens when a polyethene rod is rubbed with a duster?
|
Electrons are transferred from the duster to the rod, making the rod negatively charged.
|
|
|
What happens when an acetate rod is rubbed against a duster?
|
Electrons transfer from the rod to the duster, leaving the rod positively charged.
|
|
|
What are charged atoms or molecules?
|
Ions
|
|
|
How can static electricity be a nuisance?
|
Dust and dirt attracted to TVs
Clothes made from synthetic materials often cling to each other. |
|
|
How can electric shocks be avoided?
|
-Earth wires to transport away excess charge
-Stand on a rubber mat so charge can't flow through you to the earth -Insulating soles on shoes do the same -Fuel tankers connected to an aircraft by a conducting cable during refuelling |
|
|
What do anti-static sprays do?
|
Carry away electric charge to prevent build up.
|
|
|
How do dust precipitators work?
|
Gasses containing particulates go through chimneys in factories where they meet a negatively charged grid and pick up said charge, they are then repelled (bc same charge) and continue up to positively charged plates. They stick to the plates because of opposite charge . The plates are routinely shaken to get the dust to fall down into dust collectors. The gas then continues out of the chimney without the particulates!
|
|
|
How is static electricity used in paint spraying?
|
-The gun and thus the paint is charged
-The paint particles repel each other so spread out - The object is given the opposite charge so it attracts the paint -Even coverage with minimal waste! |
|
|
What is defibrillation?
|
A procedure to restore regular rhythm to the heart by delivering a shock through the chest wall to the heart
|
|
|
Explain the process of defibrilleration.
|
1. Two paddles are charged w high voltage
2. Placed on patient's chest for good contact 3. Charge is passes through the patient 4. Heart contracts |
|
|
How can you make a wire more resistant?
|
Longer and thinner
Like this diccc |
|
|
What do you want?
|
These hands?
|
|
|
What does a variable resistor do?
|
Changes the resistance of a wire
|
|
|
What does a rheostat do?
|
Changes resistance of a wire
|
|
|
For a fixed resistor, what does current do as voltage increases?
|
Increases
|
|
|
For a fixed power, what does current do as resistance increases?
|
Decreases
|
|
|
What is resistance measured in?
|
Ohms (Ω)
|
|
|
What does a live wire do and what colour is it?
|
Carry high voltage
It's brown |
|
|
What does a neutral wire do and what colour is it?
|
Completes the circuit, a return path for a current
It's blue |
|
|
What does a earth wire do and what colour is it?
|
Prevents the appliance from becoming live
It's green with yellow stripes |
|
|
What is the fuse and what it do?
|
Contains wire which melts, breaking the circuit, if the current becomes to large. This prevents further overheating/damage to the appliance.
|
|
|
Fuse symbol?
|
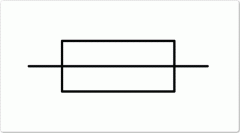
|
|
|
Variable resistor symbol?
|
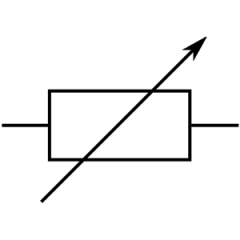
|
|
|
What is a power rating?
|
The rate at which an appliance transfers energy.
|
|
|
What is ultrasound?
|
A sound above 20k Hz that humans can't hear. Travels as a pressure wave containing compressions and rarefractions.
|
|
|
What are compressions?
|
Areas of higher pressure in a pressure wave
|
|
|
What are rarefractions?
|
Areas of lower pressure in a pressure wave
|
|
|
What are the features of longitudal sound waves?
|
-Can't travel through a vacuum
-Higher frequency means smaller wavelength -Louder sound means higher amplitude -Particles are parallel to wave direction |
|
|
In a transverse wave, particles are ____ to the wave direction.
|
At a right angle
|
|
|
What is ultrasound used for?
|
-Break down kidney stones
-Body scans -Xrays |
|
|
How is ultrasound used to treat kidney stones?
|
High pressure beam directed at the stone breaks it down and it's then excreted from the body in the normal way.
|
|
|
How is ultrasound used for body scans?
|
A pulse of it is sent into the body. At each boundary between tissues, some is reflected and some transmitted. The returning echoes are recorded to build up an image of the internal structure.
|
|
|
Why is ultrasound used for X-rays?
|
It is able to produce images of soft tissueDoesn't damage living cells
|
|
|
How does nuclear radiation cause ionisation?
|
Removing electrons from atoms or causing them to gain electrons.
|
|
|
git gud
|
no
|
|
|
What is the number above the element on the table?
|
Atomic mass
|
|
|
What is the number below the element on the table?
|
Atomic number
(proton number = neutron number too) |
|
|
Which are the largest particles emitted in radioactive decay?
|
Alpha
|
|
|
Properties of an alpha particle?
|
Positive charge
Large mass Helium gas around it 2 protons, 2 neutrons |
|
|
What is an alpha particle?
|
A helium nucleus
|
|
|
Properties of a beta particle?
|
Negative charge
Very small mass Travels very fast |
|
|
What is a beta particle?
|
An electron
|
|
|
What happens to an alpha particle during decay?
|
Mass number decreases by 4
Nucleus has 2 less protons and 2 less neutrons Atomic number decrease by 2 |
|
|
What happens to a beta particle during decay?
|
Mass number is unchanged
Nucleus has one less proton Nucleus has one more proton Atomic number increases by 1 |
|
|
What is the atomic number?
|
Bottom number next to an element in the table. The number of protons in the nucleus and thus the number of neutrons.
|
|
|
Equation for decay of alpha?
|
238 234 4
92 U --> 90 Th + 2 He |
|
|
Equation for decay of beta?
|
14 14 0
6 C --> 7 N + -1 E |
|
|
What are some sources of background radiation?
|
Substances in rocks (especially granite)
Cosmic rays Radioactive waste from industry and hospitals |
|
|
Where does most background radiation come from?
|
Natural sources: all air contains radon and rocks/soil house uranium, thorium, and radium.
|
|
|
How are tracers used to find leak sites in pipes?
|
-A small amount of gamma emitter is put in
-Detector passed along the ground above pipe -Increase in activity followed by little or none shows where the leak is |
|
|
Why is gamma used in (pipe) tracers?
|
Radiation is able to penetrate to the surface of the ground through the pipe etc.
|
|
|
How do smoke detectors work?
|
An isotope emits alpha particles which ionise the air and thus create a tiny current that is detected. When smoke blocks particles, there's less ionisation and thus less current which the alarm notices and goes off.
|
|
|
How do we date rocks?
|
Over time, uranium in rocks decays and becomes lead. The proportion of lead will be higher the older the rock is.
|
|
|
How old is a rock if amounts of uranium and lead are equal?
|
4500 years old- a half life.
|
|
|
How does Radiocarbon dating work?
|
Carbon-14 is present in all living things and when something dies, no more is produced. As it decays, the activity decreases. By comparing activity of living matter to sample activity we can get a reasonably accurate death date.
|
|
|
Name a use for each alpha, beta and gamma radiation.
|
Alpha: smoke alarms
Beta: Monitor the thickness of paper Gamma: Treat cancer (radiotherapy) |
|
|
How can materials be made radioactive?
|
Nuclei absorb extra neutrons in a nuclear reactor.
|
|
|
How do X-rays work?
|
A hot cathode emits electrons that are attracted to a tungsten anode. On impact with the tungsten, some heat is produced and some Xray.
|
|
|
How do we use tracers in the human body?
|
Technetium-99m (or Iodine-123 for thyroid gland) is added to food or drink and we ingest it/injected into us. It emits gamma radiation which is traced around the body using a gamma camera.
|
|
|
What do we use to destroy a tumour in a body?
|
Radioisotope
|
|
|
How do we destroy a tumour in a body?
|
Circle three sources of radiation around the tumour so its receiving constant radiation but the healthy tissue is only receiving intermittent doses.
|
|
|
What does natural uranium consist of?
|
2 isotopes
Uranium-235 and Uranium-238 |
|
|
What does enriched uranium consist of?
|
Greater proportion of Uranium-235 isotope that occurs naturally
|
|
|
When does fission occur?
|
A large unstable nucleus splits up and energy is released as heat
|
|
|
How does nuclear energy work?
|
Fission occurs when an unstable nucleus splits up and energy is released as heat. This heat boils water and steam turns a turbine- this then turns the generator. BOOM.
|
|
|
In nuclear power stations, atoms of uranium-235 are bombarded with _____ to make them _____.
|
neutrons to make them split
|
|
|
How is the output of a nuclear reactor controlled?
|
Graphite moderator between the fuel rods slows down fast-moving neutrons so they are more likely to be captured by other uranium nuclei.
Boron control rods can be raised or lowered to absorb neutrons when the rate of reaction is too high. |
|
|
How does nuclear fusion happen?
|
Two light nuclei fuse together releasing large amounts of heat energy.
|
|
|
Why do we use fission not fusion to generate electricity?
|
Fusion needs high temperatures we can't achieve safely on earth and research in this area is very expensive. Cold fusion is not accepted since results have never been repeated.
|

