![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
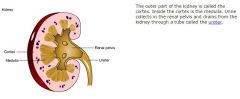
|
kidney anatomy |
|
|
nephron anatomy |
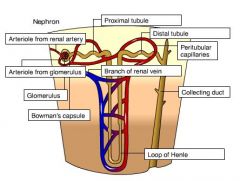
|
|
|
In the proximal tubule of the nephrons of the kidney |
In the proximal tubule, reabsorption of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) helps regulate the blood's pH. Sodium chloride (NaCl), glucose, and amino acids are actively transported out of the filtrate. This leaves the filtrate more dilute than the surroundinginterstitial fluid, so water follows by osmosis. These solutes and water reenter the blood. |
|
|
In the descending loop of Henle in the nephrons of the kidney, |
the concentration of solutes increases in theinterstitial fluid surrounding the nephrontubule. Since this portion of the tubule is permeable to water, water leaves by osmosisand is reabsorbed into the blood. This concentrates the filtrate. |
|
|
In the ascending loop of Henle |
In the ascending loop, the surrounding fluid becomes more dilute. This portion of the loop is impermeable to water, but not sodium chloride. Sodium chloride diffuses out, lowering the solute concentration of the filtrate and adding to the solute concentration of the surrounding fluid. Near the top of the loop, sodium chloride is actively transported out, further diluting the filtrate. |
|
|
In the distal tubule of the nephrons of the kidneys |
Sodium chloride is actively transported out of the filtrate. Bicarbonate ions may be reabsorbed too, helping to regulate body pH. Some drugs and poisons are secreted from the blood into the filtrate at this point. And this is another place wherehydrogen ions may also be secreted into the filtrate to further adjust pH. |
|
|
Which hormone would be triggered on a hot day when you are sweaty and thirsty to trigger more absorption of water from the collecting duct of a nephron? |
ADH, On a hot day, when you are sweaty and thirsty, blood solute concentration rises. In response, the brain signals the posterior pituitary to increase its output of the hormone ADH. ADH makes the walls of the collecting duct more permeable to water. |
|
|
Osmoregulatin |
the balance of water loss/gain and solutes |
|
|
Osmoconformers |
only marine animals, the are isosomatic with surroundings and do not regulate their osmolarity |
|
|
Osmoregulation |
is balancing the uptake and loss of water and solutes. |
|
|
Osmolarity ( osmotic pressure) |
Total solute concentration expressed as molarity The unit of measurement: milliosmoles per liter (mosm/L) Human blood 300 mosm/L Sea water 1000 mosm/L |
|
|
Osmoregulators expend energy to control ------ Ina --------- or ----------- environment |
contol water uptake/loss hypersmotic or hypoosmotic |
|
|
Most animals are said to be ------- when in reference to referring to changes in their external osmolarity |
Stenohaline (steno=“narrow”; haline = “salt”) cannot tolerate substantial changes in externalosmolarity |
|
|
Eurahaline and examples |
Euryhaline (eurys = “broad”) Cansurvive large fluctuations in external osmolarity Salmon§ Tilapia§ Salt concentration between fresh water and 2,000 mosm/L(twice that of sea water) |
|
|
Diabetes mellitus |
- lack of insulin in blood; glucose cannot beabsorbed by cells, therefore a high concentration of glucose in plasma andfiltrate; not all can be reabsorbed |
|
|
Ketonuria |
ketones in urine; ketones/acetone. Acetones are normal byproduct of digestedfatty acid. High amount in urineindicates abnormally high amount of fat digestion. Could be a result of dieting, starvation,etc. |

