![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lipase |
Breaks down oil and fat |
|
|
Protease |
Breaks down protein |
|
|
Amylase |
Breaks down sugar |
|
|
Active site |
Where a reaction takes place |
|
|
Tissue |
A group of similar cells |
|
|
Where is bile stored |
Gall bladder |
|
|
Benedicts solution checks for... |
Sugar |
|
|
Iodine checks for... |
Starch |
|
|
Sudan III stain checks for... |
Fat |
|
|
Biuret checks for... |
Protein |
|
|
What colour does Benedicts solution go if there is sugar? |
Green |
|
|
What colour does Iodine solution go if it has starch? |
Black |
|
|
What colour does Sudan III strain solution go if it contains fat? |
Red |
|
|
What colour does biuret solution go if it contains protein? |
Purple |
|

What is this? |
Active site |
|
|
Where are amylase produced? |
Salivary glands, pancreas and small intestine |
|
|
Where are lipase produced? |
Pancreas and small intestine |
|
|
Where are proteases produced? |
Stomach, pancreas and small intestine |
|
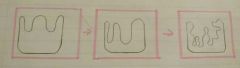
What is happening? |
Enzymes are denaturing |
|
|
At what temperature do enzymes start to denature? |
At 40*C |
|
|
Which side of the heart pumps to the lungs? |
Right |
|
|
Which side of the heart is bigger? |
Left |
|
|
Which side of the heart pumps to the body? |
The left |
|
|
What is a benign tumour? |
An abnormal growth in the membrane, contained in one place |
|
|
What is a malignant tumour? |
Cancerous cells that divide and spread round the body |
|
|
What does the xylem transport? |
Water |
|
|
What does the phloem transport? |
Sugars |

