![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
121 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1 |
Meth |
|
|
2 |
Eth |
|
|
3 |
Prop |
|
|
4 |
But |
|
|
5 |
Pent |
|
|
6 |
Hex |
|
|
7 |
Hept |
|
|
8 |
Oct |
|
|
9 |
Non |
|
|
10 |
Dec |
|
|
11 |
Undec |
|
|
12 |
Dodec |
|
|
13 |
Tridec |
|
|
14 |
Tetradec |
|
|
15 |
Pentadec |
|
|
Direction Position |
Prefix stands for? |
|
|
# of Carbons in Main Chain |
Root stands for? |
|
|
Type of Functional Group |
Suffix stands for? |
|
|
sp3 |
- Single Bonds, Tetrahedral/Pyramidal/Bent - Uses s & all 3 p orbitals |
|
|
sp2 |
- Double bonds, Trigonal Planar - Uses s & 2 p orbitals |
|
|
sp |
- Triple bonds, Linear - Uses s and 1 p orbital |
|
|
Saturated |
- As many hydrogens as possible - Single Bonds sp3 |
|
|
Unsaturated |
- Compound that contains at least on multiple bond (double or triple) sp2 or sp |
|
|
1 |
s orbital # |
|
|
3 |
p orbital # |
|
|
5 |
d orbital # |
|
|
Pi Bond |
- Approach from the side for more overlap |
|
|
Sigma Bond |
- Approach "head on" or directly - First bond made between carbon and another atom |
|
|
180 2 |
Linear Angle/ Bonds |
|
|
120 3 |
Trigonal Planar Angle/ Bonds |
|
|
<120 (~116) 2 Bonds, 1 Lone Pair |
Bent Trigonal Planar Angle and Bonds |
|
|
109.5 4 |
Tetrahedral Angle and Bond |
|
|
<109.5 (~107) 3 Bonds 1 Lone Pair |
Trigonal Pyramid Angle and Bond |
|
|
<109.5 (~104.5) 2 Bonds, 2 Lone Pairs |
Bent Tetrahedral Angle and Bond |
|
|
4 4 |
Normal Number of Bonds for Carbon, Valence Electrons |
|
|
3 Bonds, 1 Lone Pair 5 Electrons |
Normal Number of Bonds for Nitrogen, Valence Electrons |
|
|
2 Bonds, 2 Lone Pairs 6 Electrons |
Normal Number of Bonds for Oxygen, Valence Electrons |
|
|
Aufbau Principle Pauli Exclusion Principle |
- Lowest energy orbitals fill up first - 2 Electrons of opposite spin can occupy orbital |
|
|
Hund's Rule |
- If 2 or more empty orbitals of equal energy are available, one electron occupies each with spins parallel until all orbitals are half-full |
|
|
Oxygen |
Which element doesn't form triple bonds? |
|
|
[# Total Valence Electrons] - [# of Bonds] - # of Lone Pair Electrons] |
Equation for Formal Charge |
|
|
+1 |
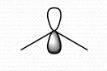
Formal Charge? |
|
|
Neutral |
Formal Charge? |
|
|
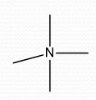
-1 |
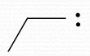
Formal Charge? |
|
|
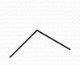
+1 |
Formal Charge? |
|
|
Neutral |
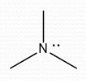
Formal Charge? |
|
|
-1 |
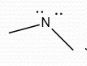
Formal Charge? |
|
|
+1 |
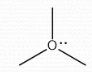
Formal Charge? |
|
|
Neutral |
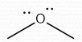
Formal Charge? |
|
|
-1 |
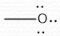
Formal Charge? |
|
|
Amide (Carbonyl + Amine) |
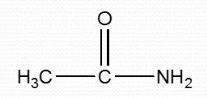
|
|
|
Alkyl Halides |
C-X |
|
|
Acid Halides |
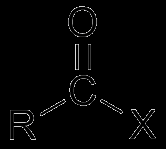
|
|
|
3sp3, 1 Lone Pair |
Hybridization of Nitrogen |
|
|
2sp3, 2 Lone pairs |
Hybridization of Oxygen |
|
|
3sp3, 1 sp2 (5 Covalent Bonds) |
Hybridization of Phosphorus |
|
|
2sp3, 2 Lone Pairs ( 4 Covalent Bonds) |
Hybridization of Sulfur |
|
|
DOWN INCREASES |
Electronegativity decreases going (up/down) and (increases/decreases) going across. |
|
|
Fluorine - 4 |
Which atom has the highest electronegativity and what charge? |
|
|
Inductive Effect |
Shifting of electrons in a bond in response to the electronegativity of nearby atoms |
|
|
-yl |
Suffix given for attachments on carbon chains? |
|
|
Iso- |
Prefix given for attachments on carbon chains that end in a 'V' shape |
|
|
Tert-Butyl |
T-Shape 4 Carbon Attachment called? |
|
|
Sec |
When there is another attachment on attachment? |
|
|
Fluoro |
Fluorine (F) attachment |
|
|
Chloro |
Chlorine (Cl) attachment |
|
|
Bromo |
Bromine (Br) attachment |
|
|
Iodo |
Iodine (i) attachment |
|
|
Cyclo |
Suffix for rings as attachments |
|
|
Cis |
Same Side |
|
|
Trans |
Opposite Side |
|
|
Alkane Alkene Alkyne |
- Contain single bond between adjacent carbon atoms - Double bond - Triple bond |
|
|
Aromatic Compounds |
- Contain benzene ring |
|
|
Hydroxyl (Alcohol) |
-OH |
|
|
Thiol |
-SH |
|
|
Ether |
-C-O-C- |
|
|
Carbonyl Aldehyde Ketone |
C=O H-C=O R1 - [C = O] - R2 |
|
|
Carboxylic Acid (Carbonyl + Hydroxyl) |
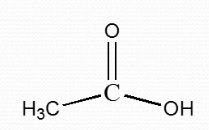
|
|
|
Ester |
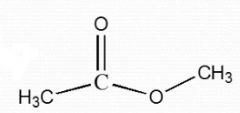
|
|
|
Amine |
-NH2 - R2-NH - R3-N |
|
|
1. Check for longest chain 2. Name & Number substituents 3. List attachments alphabetically (Except halogens go first) |
3 Steps of Naming |
|
|
1. Imaginary 2. pi 3. Non-bonding 4. Stable 5. sp3 (Single) 6. Equivalent |
Resonance Rules - Individual resonance forms are ___1___ - Forms differ only in the placement of their__2__ or ___3___ electrons - The more forms, the more __4__ than any individual resonance - Cannot jump a __5__ bond - Different forms do not have to be __6__ - Obey normal rules of valency |
|
|
Planar |
Amide bonds have a ___ form |
|
|
charge |
Typically you do not see a carbon with a double bond AND a _____ |
|
|
Inductive Effects |
- Groups donate or withdraw electrons through sigma bonds |
|
|
Resonance Effects |
Donate or withdraw electrons through pi bonds |
|
|
Electron Donating Group |
- When attachment has lone pair of electrons - "Activates the ring" |
|
|
Electron withdrawing group |
- When attachment has partial positive or even full positive charge - "Deactivates ring" |
|
|
An ionic bond is between ions (which fully support a charge). The polar covalent bond is shared between two atoms with a difference in electronegativity over 0.5 but less than 1.9 |
main difference between a polar covalent bond and an ionic bond? |
|
|
Cn H2n+2 |
How to calculate hydrogens and carbons for saturated hydrocarbons? |
|
|
Propyl Isopropyl |
2 Types of 3-Carbon Alkyl Groups |
|
|
Butyl Sec-Butyl Isobutyl Tert-butyl |
4 Types of 4 Carbon Alkyl Groups |
|
|
1. Primary 2. Secondary 3. Tertiary 4. Quaternary |
__1__ carbon is bonded to one other carbon __2__ carbon is bonded to two other carbons __3__ carbon is bonded to three other carbons __4__ carbon is bonded to four other carbons |
|
|
1. Iso 4. Substituent Di/Tri/Tetra 5. Halogens |
Select all those that order alphabetically 1. Iso 2. Sec/Tert "T" 3. Di/Tri/Tetra 4. Substituent Di/Tri/Tetera 5. Halogens |
|
|
Acid Base |
Bronsted Lowry Definition - Proton donor - Proton acceptor |
|
|
Acid Base |
Lewis Definition - Accepts e- pair - Donates e- pair |
|
|
- Conjugate base - Conjugate acid |
Product that results from acid losing proton Product that results from base accepting proton |
|
|
H-A [Acid]+ B:[Base] <=> A:[C. Base]- + H-B+[C. Acid] |
General Equation for Acid-Base Reaction |
|
|
Ka = 10^(-pKa) |
How to solve for the acidity constant, Ka given pKa |
|
|
1. Strong 2. Weaker 3. Weaker 4. Stronger |
The ___1___ the acid, the more its equilibrium shifts to the right, and has a ___2___ conjugate base. An acid shifting to the left of equilibrium is __3__ and has a ___4___ conjugate base. |
|
|
1. ortho 2. para 3. double |
Charges (+,-) are always on ___1___ and ___2__ carbons for resonance. There never is a carbon in the ring with both a charge and __3__ bond. |
|
|
greater 1. 25 2. 33 3. 50 |
the (weaker/greater) the percents character of the bond, the more acidic the compound is. sp3 is __1___ %, sp2 is __2__% and sp is __3__% |
|
|
pKA |
- pH at which hydrogen can be removed ( the lower it is, the more acidic) |
|
|
a. more stable A- c: loses hydrogen faster e: lower pKa |
Choose all statements in regards to more acidity a: More stable A- b: Less stable A- c: Loses hydrogen faster d: Loses hydrogen slower e: Lower pKa f: Higher pKa |
|
|
1. Size of anion 2. Electronegativity 3. Resonance 4. Inductive Effects (EDG vs. EWG) |
4 Things that help stabilize A- |
|
|
Iodine > Bromine > Chlorine > Fluorine Larger the anion, the more stable |
List the 4 halogens based on more stable to least stable. Explain why. |
|
|
1. EWG 2. EDG |
Inductive Effects: ___1___ make compound more acidic by lowering pKa by stabilizing the anion (spreading out charge). ___2____ makes compound less acidic by raising pKa because they destabilize the anion (concentrate charge in one area) |
|
|
1. Melting 2. Boiling 3. inert 4. parrafins 5. phobic |
Alkane properties: As molecular weight increases, so do __1__ and __2__ points. Typically ___3___; they have low affinity. Also called __4__. They are hydro__5__ and flammable. |
|
|
Gaseous Liquid Solid |
@ Room Temperature, what is its state? 1-4 Carbons 5-8 Carbons 10+ Carbons |
|
|
1. Resonance forms are imaginary. True form lies somewhere in between the structures called a "hybrid." 2. Involve change in placement of electrons in p-orbitals. Double bond changes places with lone pair, radical, or a positive charge. 3. Follows all valence rules & formal charge rules. 4. The more resonance a structure has, the more stable. 5. Resonance structures do not have to be equivalent. |
5 Main Rules of Resonance |
|
|
I > Br > Cl > F
|
Rank from best acid to worst acid. Iodine Chlorine Fluorine Bromine |
|
|
F > Cl > Br > I
|
Rank from most electronegative to least electronegative. Iodine Chlorine Fluorine Bromine |
|
|
Ethylene |
Common name for ethene |
|
|
Propylene
|
Common name for propylene |
|
|
Vinyl
|
Common name for Ethene attachment |
|
|
Allyl
|
Common name for Propene attachment |
|
|
1. Hydrophobic 2. Melting/Boiling Point a little higher than alkanes 3. Reactive because of extra electron between carbons of double bond (pi orbitals) |
3 Physical Properties of Alkenes |
|
|
n = # of Carbons
X = Halogens [(2n+2) - (#H -#N + #X)] /2 |
Degrees of Unsaturation Equation |
|
|
- Halogens, Oxygen, Nitrogen
- Metals |
List 3 Examples of Atoms with negative partial charge relative to Carbon. List 1 type of Atom with positive partial charge relative to carbon. |
|
|
1. MCPBA (Metachlorobenzoic acid)
2. Peracids |
Epoxides are formed by these 2 main reagents |
|
|
Carboxylic acids with extra oxygen |
What are peracids? |

