![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the bonds between aldehyde and ketone? |
Permanent dipole- permanent dipole bond |
|
|
Can aldehyde and ketone form hydrogen bond with water? |
Yes |
|
|
What happens to the solubility as the ketone or aldehyde increases in size? |
Solubility decreases as the non polar part gets bigger |
|
|
Can aldehyde and ketone form hydrogen bond between themselves? Why? |
No. Hydrogen is not directly attached to the oxygen |
|
|
Which is more reactive from aldehyde and ketone? |
Aldehyde |
|
|
Why is aldehyde more reactive? |
Has fewer R (alkyl groups). So magnitude of the carbocation still is greater. So more susceptible to be attacked by a nucleophile |
|
|
What do alkyl groups do to the magnitude of the carbocation? |
Decreases it |
|
|
What do we test aldehyde or ketones with? |
Brady's reagent/ 2, 4 dinitrophenylhydrazine/ 2, 4 DNPH |
|
|
What is the positive result? |
Colour changes from orange-red to a yellow solid if it is an aliphatic compound. Colour changes from Orange red to orage solid it is an aromatic compound |
|
|
What is the name of the reaction in this test? |
Condensation |
|
|
If propanal reacts with 2, 4 DNPH, what are the products? |
Water 2,4 dintriphenylhydrazone |
|
|
What should Brady's reagent be supplied wet ? |
Explosive when dry |
|
|
Why do we use Brady's reagent? |
It is less soluble It crystallizes easily |
|
|
What further proceedings are required after we get a derivative? |
Recrystallize it We get its purified form Has a melting point Match with Data Booklet |
|
|
Why do we match the M.P and not the B.P? |
B.P changes /cmvaries with atmosphere /altitude |
|
|
Why do we never use water bath and use oil bath or electric heater to recrystallize the derivative? |
The melting point of the derivative is above 100°C |
|
|
What 's the difference between aliphatic compound and aromatic compound? |
Aromatic compound has a benzene group attached to it |
|
|
How is the chiral carbon indicated? |
C* |
|
|
What is a mixture with equiimolar ratio of L and D called? |
Racemic mixture |
|
|
Does racemic mixture cause the plane of plane polarised light to rotate? |
No |
|
|
If the conc. of L or D in a mixture is higher, does it cause more rotation or less? |
More |
|
|
Features of the hydrolysis of 1° halogenoalkane : |
• less steric hindrance( nucleophile attcks without any hindrance) • CX bond breaks down heterolycally and nucleophile attacks at the same stage • step is slow, rate determining step • SN2 |
|
|
Does a transition state form in the hydrolysis of a 1° halogenoalkane? |
Yes |
|
|
What is the shape of the molecule at the transition state? |
Regional bipyramidal. 90°. 120°. |
|
|
Features of the hydrolysis of a 3° halogenoalkane : |
• more static hindrance ( nucleophile cannot attack immediately beacause there is hindrance ) • reaction occurs in step steps, first step is slow- the rate determining step, seco d step is slow • the CD bond breaks at the slow step • SN1 |
|
|
What is the shape of the intermediate formed when3° halogenoalkane is hydrolysed ? |
Planar, 120° |
|
|
In what ways could the nucleophile attack a 3° intermediate? |
In two ways. From below and from above |
|
|
What shape forms when nucleophile attacks the planar intermediate? |
Tetrahedral. 109. 5° |
|
|
The probability of L and D in the 3° alcohol that formed? |
50% |
|
|
Is the 3° alcohol formed from the hydrolysis of 3° halogenoalkane optically active? Why? |
No. Racemic mixture forms |
|
|
What is a carbonyl compound? |
C=0 bond containing compound |
|
|
What are the two types of carbonyl compound? |
Aldehyde and ketone |
|
|
How does an aldehyde look like? |
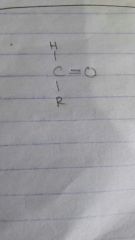
At least one H |

