![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Thermal Cracking
|
Occurs when high temperatures cause homolytic breaking of C-C and C-H bonds.
|
|
|
Homolytic Breaking
|
Each of the 2 product fragments leaves with 1 bonding electron from the 1 reactant.
Aka. symmetrical processes A type of radical reaction. |
|
|
Homolytic Bonding
|
When 1 electron from each of the 2 reactants are donated to a newly-formed product.
Aka. symmetrical processes A type of radical reaction. |
|
|
Heterolytic Breaking
|
1 of the 2 product fragments leaves with both bonding electrons from the reactant.
Aka. unsymmetrical processes A type of polar reaction. |
|
|
Heterolytic Bonding
|
Where both electrons from 1 of the 2 reactants are donated to a newly-formed product.
Aka. unsymmetrical processes A type of polar reaction. |
|
|
3 Steps of a simple Radical Substitution Reaction
|
1. Initiation - free radical is produced
2. Propagation - carries on chain reaction 3. Termination - 2 radicals react together to form a stable product |
|
|
Carbon is always _____________ly polarized, except when bonded to a metal.
|
positive
|
|
|
Nucleophile Examples
|
ammonia, water, hydroxide, chloride ion
|
|
|
Electrophile Examples
|
acids, alkyl halides, carbonyl compounds
|
|
|
Electrons move from a(n) _______philic source to a(n)_______philic source.
|
nucleo to electro
|
|
|
When ∆G° is negative, the reaction is _____________.
|
spontaneous
|
|
|
Formula for the relationship between K, e, ∆G°, and RT
|
K=e ^ -∆G°/RT
|
|
|
Bond Dissociation Energy (D)
|
Energy needed to break a bond homolytically to produce 2 radical fragments.
|
|
|
Solvation
|
Clustering of solvent molecules around a solute particle to stabilize it.
|
|
|
Solvent
|
Dissolves the solute. Is in greater quantity than the solute.
|
|
|
Exergonic Reaction
|
Product has lower energy level than reactant.
|
|
|
Endergonic Reaction
|
Product has higher energy level than reactant.
|
|
|
Formula for a Saturated Alkane
|
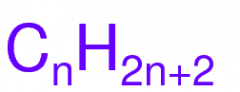
|
|
|
Common names for Ethene and Propene
|
Ethylene and Propylene
|
|
|
Bond lengths in alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes
|
154pm, 134pm, 120pm
|
|
|
Bond angles in alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes
|
109°, 120°, and 180°
|
|
|
Why isn't rotation possible about a carbon-carbon double bond?
|
π bond must break, then reform, costing 350kJ/mol
|
|
|
Cahn-Ingold Prelog rules (sequence rules)
|
Rules for assigning priorities to substituents or alkenes.
Aka. The E, Z designation |
|
|
Heat of Hydrogenation (∆H°hydrog)
|
Amount of heat released when a carbon-carbon double bond is hydrogenated.
|
|
|
Electrophilic Addition Reaction
|
Addition of an electrophile to a carbon-carbon double bond.
|
|
|
Markovnikov's Rule
|
In addition reactions, the H attaches to the C with fewer alkyl substituents.
|
|
|
Hyperconjugation
|
Stabilizing interaction between vacant p orbitals in a carbocation and C-H sigma bonds.
|
|
|
Inductive Effects
|
The electron-attracting or electron-withdrawing effect transmitted through sigma bonds. Occurs because of electronegativities of nearby atoms.
|
|
|
Hammond Postulate
|
The structure of a transition state resembles the structure of the nearest stable species.
|
|
|
Transition State
|
Highest energy point on a reaction curve.
|
|
|
Dehydration
|
Loss of water from an alcohol. Type of elimination reaction.
|
|
|
Dehydrogenation
|
Loss of HX from an alkyl halide. Type of elimination reaction.
|
|
|
Halogenation reactions.
They occur on a cycloalkane, form only the ___________stereoisomer. |
Halogens add rapidly to alkene to yield 1,2-dihalides.
trans |
|
|
Syn Addition Reaction
|
2 ends of double bond react from same side.
|
|
|
Syn Elimination Reaction
|
2 groups leave from the same side.
|
|
|
Anti Addition Reaction
|
2 ends of double bond react from different sides.
|
|
|
Anti Elimination Reaction
|
2 groups leave from opposite sides.
|
|
|
Halohydrin
|
A 1,2-disubstituted haloalcohol.
|
|
|
Bromohydrin
|
A 1,2-disubstituted bromoalcohol.
|
|
|
NBS
|
N-bromosuccinimide decomposes in water to form Br2.
|
|
|
Hydration
|
Addition of water to a molecule.
|
|
|
Oxymercuration
|
Method for double-bond hydration using mercuric acetate as the reagent.
|
|
|
Abbreviation for mercuric acetate.
|
Hg(OAc)2
|
|
|
THF
|
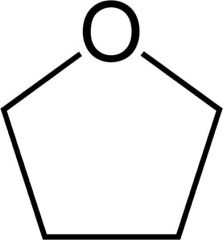
Tetrahydrofuran.
|
|
|
Hydrogen Peroxide
|
H202
|
|
|
Mercury (II) Acetate
|
Hg(OAc)2
|
|
|
Sodium Borohydride
|
NaBH4
|
|
|
Methylene, Vinyl, and Allyl groups.l
|
CH2, CH=CH2, and CH2-CH=CH2
|
|
|
Hydroboration-Oxidation Reaction
|
HYDROBORATION: Alkene + borane (BH3) to yield an organoborane intermediate (RBH2).
OXIDATION: Organoborane (RBH2) + hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to yield an alcohol. |
|
|
Deuterium (D)
|
Isotope of hydrogen consisting of 1 proton, 1 neutron, and 1 electron.
|
|
|
Oxymercuration Reaction
|
Alkene + mercury(II) acetate to yield an organomercury compound, then addition of sodium borohydride (NaBH4) to yield an alcohol.
|
|
|
Carbene
|
-R2C
-Neutral -Divalent C atom -6 electrons in outer shell |
|
|
Halohydrin Formation Reaction
|
Alkene + X2 to yield a halohydrin + HX.
|
|
|
Stereospecific
|
When only a single stereoisomer is produced in a given reaction rather than a mixture.
|
|
|
Simmons-Smith Reaction
|
Alkene + carbenoid + zinc-copper mixture yields a cyclopropane.
|
|
|
Adam's Catalyst
|
PtO2 catalyst used for hydrogenations.
|
|
|
Hydrogenation of Alkenes Reaction
|
aka. Reduction Reactions
Alkene + H2 + catalyst yields an alkane. Heterogenous reaction. |
|
|
Osmium Tetroxide
|
OsO4
|
|
|
Diol
|
Aka. Dialcohol , Glycol
Compound containing 2 -OH groups. |
|
|
Hydroxylation Reactions
|
Alkene yields a diol through one of 2 paths:
1. Alkene + osmium tetraoxide yields a cyclic osmate. Addition of aqueous sodium bisulfate (NaHSO3) yields a diol. 2. Alkene undergoes epoxidation to yield an epoxide. Epoxide undergoes hydrolysis to yield a diol. |
|
|
Epoxide
|
Aka. Oxirane
Cyclic ether with an O atom in a 3-membered ring. |
|
|
Peroxyacid
|
RCO3H
Ex. meta-chloroperoxy-benzoic acid |
|
|
Molozonide
|
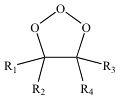
The initial addition product of ozone + an alkene.
|
|
|
Potassium permanganate
|
KMnO4
|
|
|
3 reagents that cause double-bond cleavage?
|
1. Ozone (O3)
2. Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4) 3. Periodic Acid (HIO4) |
|
|
Ozonide
|
The product formed by the addition of ozone (O3) to a C=C.
|
|
|
Monomer
|
The simple starting unit from which a polymer is made.
|
|
|
Polymer
|
A large molecule made up of repeating smaller units called monomers.
|
|
|
Vinyl Monomers
|
CH=CHX.
A substituted alkene monomer used to make chain-growth polymers. |

